Abstract
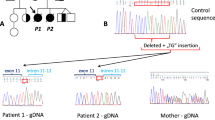
Donohue syndrome (DS) is a very rare autosomal recessive disease affecting less than one in a million life births. It represents the most severe form of insulin resistance due to mutations involving the insulin receptor (IR) gene “INSR”. DS is characterized by pre- and postnatal growth retardation with failure-to-thrive, lipoatrophy, acanthosis nigricans, hypertrichosis, and dysmorphic features. An exhaustive INSR gene sequencing was performed after PCR amplification of coding exons and introns boundaries. Bioinformatic tools, including ESEfinder, MFOLD and Proter software were also used to predict the impact of INSR mutation on INSR on gene expression as well as on the protein structure and function. The results have shown a novel unusual c.3003_3012delinsGGAAG (p.S1001_D1004delinsRE) insertion/deletion (indel) mutation within the exon 16 in the three patients, which represent the fourth indel mutation within the INSR gene. The mutation modifies the secondary structure of DNA and RNA, as well as the composition of exonic splicing enhancers of exon 16. Moreover, despite the conservation of the secondary structure of the IR, the p.S1001_D1004delinsRE in-frame mutation is accompanied by the loss of four amino acids replaced by two residues of different nature and hydrophobicity level in the juxtamembrane domain of the receptor. The results have confirmed the role of the juxtamembrane domain of IR involved in a crucial interaction of the IR with cellular effectors essentially the IR substrate 1 (IRS-1), the SHC and the Nck proteins that ensure the signal mediated by the insulin transduction pathway in target cells. Our findings have also proven the genotype/phenotype correlation between INSR mutation and DS phenotype severity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebina Y, Ellis L, Jarnagin K, Edery M, Graf L, Clauser E, Ou JH, Masiarz F, Kan YW, Goldfine ID et al (1985) The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell 40(4):747–758
Seino S, Bell GI (1989) Alternative splicing of human insulin receptor messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 159:312–316
Ullrich A, Bell JR, Chen EY, Herrera R, Petruzzelli LM, Dull TJ, Gray A, Coussens L, Liao YC, Tsubokawa M, Mason A, Seeburg PH, Grunfeld C, Rosen OM, Ramachandran J (1985) Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. Nature 313:756–761
Cheatham B, Kahn CR (1995) Insulin action and the insulin signaling network. Endocr Rev 16:117–142
Belfiore A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, Vigneri R (2009) Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev 30:586–623
Grasso V, Colombo C, Favalli V, Galderisi A, Rabbone I, Gombos S, Bonora E, Massa O, Meschi F, Cerutti F, Iafusco D, Bonfanti R, Monciotti C, Barbetti F (2013) Six cases with severe insulin resistance (SIR) associated with mutations of insulin receptor: is a Bartter-like syndrome a feature of congenital SIR? Acta Diabetol 50(6):951–957. doi:10.1007/s00592-013-0490-
Longo N, Langley SD, Griffin LD, Elsas LJ (1995) Two mutations in the insulin receptor gene of a patient with leprechaunism: application to prenatal diagnosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80(5):1496–1501
Semple RK, Soos MA, Luan J, Mitchell CS, Wilson JC, Gurnell M, Cochran EK, Gorden P, Chatterjee VK, Wareham NJ, O’Rahilly S (2006) Elevated plasma adiponectin in humans with genetically defective insulin receptors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3219–3223
Kawasaki E (1990) Sample preparation from blood, cells and other fluids. In: Innis M, Gelfand D, Snisky J, White T (eds) PCR protocols. A guide to methods and applications. Academic, San Diego, pp 146–152
Zuker M (2003) MFOLD web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3406–3415
Cartegni L, Wang J, Zhu Z, Zhang MQ, Krainer AR (2003) ESEfinder: a web resource to identify exonic splicing enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3568–3571
Hone J, Accili D, Psiachou H, Alghband-Zadeh J, Mitton S, Wertheimer E, Sinclair L, Taylor SI (1995) Homozygosity for a null allele of the insulin receptor gene in a patient with leprechaunism. Hum Mutat 6:17–22
Kazemi B, Seyed N, Moslemi E, Bandehpour M, Bikhof Torbati M, Saadat N, Eidi A, Ghayoor E, Azizi F (2009) Insulin receptor gene mutations in Iranian patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Iran Biomed J 13(3):161–168
Longo N, Singh R, Elsas LJ (2001) Decreased half-life of insulin-like growth factor I in Rabson–Mendenhall syndrome. J Inherit Metab Dis 24(5):546–550
Krawczak M, Cooper DN (1991) Gene deletions causing human genetic disease: mechanisms of mutagenesis and the role of the local DNA sequence environment. Hum Genet 86:425–541
Deeb KK, Smonskey MT, De Federicis H, Deeb G, Sait S, Eunice M, Wang S, Starostik P (2014) Deletion and deletion/insertion mutations in the juxtamembrane domain of the FLT3 gene in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res Rep 3:86–89
Qiaoli Li., C. Herbert Pratt., Louise A. Dionne, Heather Fairfield, Son Yong Karst, John P. Sundberg, Jouni Uitto (2014) Spontaneous asj-2 J Mutant Mouse as a Model for Generalized Arterial Calcification of Infancy: A Large Deletion/Insertion Mutation in the Enpp1 Gene. Plos One 9 (12) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113542
Presneau N, Laplace-Marieze V, Sylvain V, Lortholary A, Hardouin A, Bernard-Gallon D, Bignon YJ (1999) Mutation by deletion–insertion in BRCA1 gene in three unrelated French breast/ovarian cancer families: possible implication of a mobile element. Bull Cancer 86(4):385–390
Desbois-Mouthon C, Meier M, Vigouroux C, Stavrinadis C, Sinaniotis C, Caron M, Capeau Magré J, Karayanni C, Hadjiathanasiou CG (1997) Dominant transmission of insulin resistance in a type A family resulting from a heterozygous nonsense mutation in the insulin receptor gene and associated with decreased mRNA level and insulin binding sites. J Diabetes 46(11):1901–1903
McKern NM, Lawrence MC, Streltsov VA, Lou MZ, Adams TE, Lovrecz GO, Elleman TC, Richards KM, Bentley JD, Pilling PA, Hoyne PA, Cartledge KA, Pham TM, Lewis JL, Sankovich SE, Stoichevska V, Da Silva E, Robinson CP, Frenkel MJ, Sparrow LG, Fernley RT, Epa VC, Ward CW (2006) Structure of the insulin receptor ectodomain reveals a folded-over conformation. Nature 443(7108):218–221
Rahman OU, Khawar N, Khan MA, Ahmed J, Khattak K, Al-Aama JY et al (2013) Deletion mutation in BSCL2 gene underlies congenital generalized lipodystrophy in a Pakistani family. Diagn Pathol 8:78
Córdova-Palomera A, Fatjó-Vilas M, Kebir O, Gastó C, Krebs MO, Fañanás L (2015) Polymorphic variation in the epigenetic gene DNMT3B modulates the environmental impact on cognitive ability: a twin study. Eur Psychiatry 30(2):303–308
Burke JP, O’Connell RM, Lennon G, Doherty GA, Keegan D, O’Donoghue D, Mulcahy H, Hyland J, Winter DC, Sheahan K, O’Connell PR (2013) The influence of CTGF single-nucleotide polymorphisms on outcomes in Crohn’s disease. Ann Surg 258(5):767–773
Vicari P, Adegoke SA, Mazzotti DR, Cançado RD, Nogutti MA, Figueiredo MS (2014) Interleukin-1β and interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms are associated with manifestations of sicklecell anemia. Blood Cells Mol Dis 54(3):244–249. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2014.12.004
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and their families for their cooperation in the present study. We also express thanks to Mrs. Leila Mahfoudhi for having revised the English of this paper. This work was supported by funds from the Ministère de Recherche Scientifique (Tunisia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siala-Sahnoun, O., Dhieb, D., Ben Thabet, A. et al. First molecular diagnosis of Donohue syndrome in Africa: novel unusual insertion/deletion mutation in the INSR gene. Mol Biol Rep 43, 165–173 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-3951-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-016-3951-9