Abstract
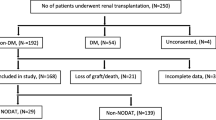
New-onset diabetes after transplantation (NODAT) is an important complication after solid organ transplantation. NODAT is a polygenic disease and KCNJ11 E23K polymorphism is considered as a diabetes-susceptibility gene. The present study aimed to assess the association between KCNJ11 (rs5219) variants and the risk of developing NODAT after liver transplantation. This study was conducted on 120 liver transplant recipients who had received tacrolimus-based immunosuppressive drugs. The liver transplant recipients were divided into an new onset diabetes mellitus (NODM) and a non-NODM group. The NODAT group consisted of 60 patients who developed diabetes in the first 6 months after transplantation, while the non-NODAT group included 60 patients who remained euglycemic. The patients were genotyped using polymerase chain reaction–restriction fragment length polymorphism and the incidence of NODAT was compared between the two groups. Nongenetic risk factors including donor gender and cold ischemia time, and recipient (MELD score, presence of viral hepatitis, acute rejection and steroid pulse therapy) were also considered. The KCNJ11 KK variant was associated with an increased risk for NODAT with respective odds ratio of 6.03 (95 % confidence interval 2.37–15.4; P < 0.001]. Donor age and male sex, recipient age as well as fasting plasma glucose before transplantation were significantly different between NODAT and non-NODAT groups (P < 0.05). The prednisolone daily dosage was significantly higher in the NODAT group (P = 0.01). These patients received pulse of methyl prednisolone for treatment of acute rejection. This study showed that polymorphisms in KCNJ11 might predispose the patients treated by tacrolimus to development of NODAT after liver transplantation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kesiraju S, Paritala P, Rao Ch UM, Sahariah S (2014) New onset of diabetes after transplantation. An overview of epidemiology, mechanism of development and diagnosis. Transpl Immunol 30(1):52–58
Samuelson AL, Lee M, Kamal A, Keeffe EB, Ahmed A (2010) Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of mortality following liver transplantation independent of MELD score. Dig Dis Sci 55:2089–2094
Van Laecke S, Desideri F, Geerts A, Van Vlierberghe H, Berrevoet F, Rogiers X, Troisi R, de Hemptinne B, Vanholder R, Colle I (2010) Hypomagnesemia and the risk of new-onset diabetes after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 16(11):1278–1287
Oufroukhi L, Kamar N, Muscari F, Lavayssière L, Guitard J, Ribes D, Esposito L, Alric L, Hanaire H, Rostaing L (2008) Predictive factors for posttransplant diabetes mellitus within one-year of liver transplantation. Transplantation 85(10):1436–1442
Gane EJ (2011) Diabetes mellitus following liver transplantation in patients with hepatitis C virus: risks and consequences. Am J Transplant 12:531–538
Saliba F, Lakehal M, Pageaux GP, Roche B, Vanlemmens C, Duvoux C, Dumortier J, Salamé E, Calmus Y, Maugendre D (2007) Risk factors for new-onset diabetes mellitus following liver transplantation and impact of hepatitis C infection: an observational multicenter study. Liver Transpl 13(1):136–144
Davidson J, Wilkinson A, Dantal J, Dotta F, Haller H, Hernández D, Kasiske BL, Kiberd B, Krentz A, Legendre C, Marchetti P, Markell M, van der Woude FJ, Wheeler DC (2003) New onset diabetes after transplantation: 2003 international consensus guidelines. In Proceedings of an international expert panel meeting. Barcelona, Spain, 19 February 2003. Transplantation 2003; 75(10 Suppl):SS3–SS24
Qin LJ, Lv Y, Huang QY (2013) Meta-analysis of association of common variants in the KCNJ11-ABCC8 region with type 2 diabetes. Genet Mol Res 12(3):2990–3002
Yang L, Zhou X, Luo Y, Sun X, Tang Y, Guo W, Han X, Ji L (2012) Association between KCNJ11 gene polymorphisms and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in East Asian populations: a meta-analysis in 42,573 individuals. Mol Biol Rep 39(1):645–659
Abdelhamid I, Lasram K, Meiloud G, Ben Halim N, Kefi R, Samb A, Abdelhak S, Houmeida A (2014) E23K variant in KCNJ11 gene is associated with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in the Mauritanian population. Prim Care Diabetes 8(2):171–175
Li YY (2013) The KCNJ11 E23K gene polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Chinese Han population: a meta-analysis of 6,109 subjects. Mol Biol Rep 40(1):141–146
Tavira B, Coto E, Torres A, Díaz-Corte C, Díaz-Molina B, Ortega F, Arias M, Díaz JM, Selgas R, López-Larrea C, Ruiz-Ortega M, Ortiz A, González E, Campistol JM, Alvarez V (2012) Pharmacogenetics of tacrolimus REDINREN study group. Association between a common KCNJ11 polymorphism (rs5219) and new-onset posttransplant diabetes in patients treated with tacrolimus. Mol Genet Metab 105(3):525–527
Kurzawski M, Dziewanowski K, Łapczuk J, Wajda A, Droździk M (2012) Analysis of common type 2 diabetes mellitus genetic risk factors in new-onset diabetes after transplantation in kidney transplant patients medicated with tacrolimus. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68(12):1587–1594
Davidson JA, Wilkinson A (2004) New-onset diabetes after transplantation 2003 international consensus guidelines: an endocrinologist’s view. Diabetes Care 27:805–812
Nikolac N, Simundic AM, Katalinic D, Topic E, Cipak A (2009) Zjacic Rotkvic V. Metabolic control in type 2 diabetes is associated with sulfonylurea receptor-1 (SUR-1) but not with KCNJ11 polymorphisms. Arch Med Res 40(5):387–392
Gloyn AL, Hashim Y, Ashcroft SJ, Ashfield R, Wiltshire S, Turner RC, UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 53) (2001) Association studies of variants in promoter and coding regions of beta-cell ATP sensitive K-channel genes SUR1 and Kir6.2 with type 2 diabetes mellitus (UKPDS 53). Diabet Med 18(3):206–212
Nielsen EM, Hansen L, Carstensen B, Echwald SM, Drivsholm T, Glümer C, Thorsteinsson B, Borch-Johnsen K, Hansen T, Pedersen O (2003) The E23K variant of Kir6.2 associates with impaired post-OGTT serum insulin response and increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52(2):573–577
Gloyn AL, Weedon MN, Owen KR, Turner MJ, Knight BA, Hitman G, Walker M, Levy JC, Sampson M, Halford S, McCarthy MI, Hattersley AT, Frayling TM (2003) Large-scale association studies of variants in genes encoding the pancreatic beta-cell KATP channel subunits Kir6.2 (KCNJ11) and SUR1 (ABCC8) confirm that the KCNJ11 E23K variant is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52(2):568–572
Schwanstecher C, Meyer U, Schwanstecher M (2002) K(IR) 6.2 polymorphism predisposes to type 2 diabetes by inducing overactivity of pancreatic beta-cell ATP-sensitive K channels. Diabetes 51(3):875–879
Schwanstecher C, Neugebauer B, Schulz M, Schwanstecher M (2002) The common single nucleotide polymorphism E23K in K(IR)6.2 sensitizes pancreatic beta-cell ATP-sensitive potassium channels toward activation through nucleoside diphosphates. Diabetes 51(Suppl 3):S363–S367
Barroso I, Luan J, Middelberg RP, Harding AH, Franks PW, Jakes RW, Clayton D, Schafer AJ, O’Rahilly S, Wareham NJ (2003) Candidate gene association study in type 2 diabetes indicates a role for genes involved in b-cell function as well as insulin action. PLoS Biol 1(1):E20
Ashcroft FM (2005) ATP-sensitive potassium channelopathies: focus on insulin secretion. J Clin Invest 115(8):2047–2058
Schwanstecher C, Schwanstecher M (2002) Nucleotide sensitivity of pancreatic ATP-sensitive potassium channels and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 51(Suppl 3):S358–S362
Yang J, Hutchinson II, Shah T, Min DI (2011) Genetic and clinical risk factors of new-onset diabetes after transplantation in Hispanic kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 91(10):1114–1119
Yang L, Zhou X, Luo Y, Sun X, Tang Y, Guo W, Han X, Ji L (2012) Association between KCNJ11 gene polymorphisms and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in East Asian populations: a meta-analysis in 42,573 individuals. Mol Biol Rep 39(1):645–659
Javorsky M, Klimcakova L, Schroner Z, Zidzik J, Babjakova E, Fabianova M, Kozarova M, Tkacova R, Salagovic J, Tkac I (2012) KCNJ11 gene E23K variant and therapeutic response to sulfonylureas. Eur J Intern Med 23(3):245–249
Balla A, Chobanian M (2009) New-onset diabetes after transplantation: a review of recent literature. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 14(4):375–379
Ling Q, Xie H, Lu D, Wei X, Gao F, Zhou L, Xu X, Zheng S (2013) Association between donor and recipient TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and the risk of new-onset diabetes mellitus after liver transplantation in a Han Chinese population. J Hepatol 58(2):271–277
Ollech JE, Kramer MR, Peled N, Ollech A, Amital A, Medalion B, Saute M, Shitrit D (2008) Post-transplant diabetes mellitus in lung transplant recipients: incidence and risk factors. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 33(5):844–848
Razeghi E, Heydarian P, Amerian M, Pourmand G (2010) The risk factors for diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 21(6):1038–1043
Kamar N, Mariat C, Delahousse M, Lefrançois N, Dantal J, Benhamou P (2006) New onset diabetes mellitus incidence and risk factors in kidney transplantation: results of the observational cross-sectional study diapason. Transplant Proc 38(7):2295–2297
Seifi S, Rahbar M, Lessan-Pezeshki M, Khatami MR, Abbasi MR, Mahdavi-Mazdeh M, Ahmadi F, Maziar S (2009) Posttransplant diabetes mellitus: incidence and risk factors. Transplant Proc 41(7):2811–2813
Ahn HY, Cho YM, Yi NJ, Suh KS, Lee KU, Park KS, Kim SY, Lee HK (2009) Predictive factors associated with the reversibility of post-transplantation diabetes mellitus following liver transplantation. J Korean Med Sci 24(4):567–570
Sarno G, Muscogiuri G, De Rosa P (2012) New-onset diabetes after kidney transplantation: prevalence, risk factors, and management. Transplantation 93(12):1189–1195
Kurzawski M, Dziewanowski K, Kędzierska K, Wajda A, Lapczuk J, Droździk M (2011) Association of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphism with posttransplant diabetes mellitus in kidney transplant patients medicated with tacrolimus. Pharmacol Rep 63(3):826–833
Madziarska K, Weyde W, Krajewska M, Patrzalek D, Janczak D, Kusztal M, Augustyniak-Bartosik H, Szyber P, Kozyra C, Klinger M (2011) The increased risk of post-transplant diabetes mellitus in peritoneal dialysis-treated kidney allograft recipients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(4):1396–1401
Sakamoto Y, Inoue H, Keshavarz P, Miyawaki K, Yamaguchi Y, Moritani M, Kunika K, Nakamura N, Yoshikawa T, Yasui N, Shiota H, Tanahashi T, Itakura M (2007) SNPs in the KCNJ11-ABCC8 gene locus are associated with type 2 diabetes and blood pressure levels in the Japanese population. J Hum Genet 52(10):781–793
Acknowledgments
The present article was extracted from Zahra Parvizi’s M. Sc. thesis in cellular developmental biology. Hereby, the authors would like to thank Organ Transplant Research Center of Nemazee Hospital for their assistance in performance of this project. They are also grateful for Ms. A. Keivanshekouh at the Research Improvement Center of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences for improving the use of English in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parvizi, Z., Azarpira, N., Kohan, L. et al. Association between E23K variant in KCNJ11 gene and new-onset diabetes after liver transplantation. Mol Biol Rep 41, 6063–6069 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3483-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3483-0