Abstract
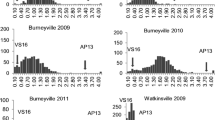
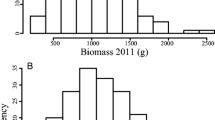
Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) is an important perennial C4 species due to its large potential for cellulosic bioenergy feedstock production. Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTL) controlling important developmental traits is valuable to understanding the genetic basis and using marker-assisted selection (MAS) in switchgrass breeding. One F1 hybrid population derived from NL94 (♀) × SL93 (♂) and one S1 (first-generation selfed) population from NL94 were used in this study. Both the populations showed significant variations for genotype and genotype by environment interactions for three traits studied: plant vigor, spring green-up, and plant biomass. Plant vigor had strong and positive correlations with plant biomass in both populations. Broad-sense heritability estimates for plant vigor ranged from 0.46 to 0.74 and 0.45 to 0.74 in the hybrid and selfed population, respectively. Spring green-up had similar heritability estimates, 0.42–0.78 in the hybrid population, and 0.47–0.82 in the selfed population. Heritability of plant biomass was 0.54–0.64 in the hybrid population and 0.64–0.74 in the selfed population. Fifteen QTLs for spring green-up, 6 QTLs for plant vigor, and 3 QTLs for biomass yield were detected in the hybrid population, whereas 4 QTLs for spring green-up, 4 QTLs for plant vigor, and 1 QTL for biomass yield were detected in the selfed population. Markers associated with these QTLs can be used in MAS to accelerate switchgrass breeding program. This study provided new information in understanding the genetic control of biomass components and demonstrated substantial heterotic vigor that could be explored for breeding hybrid cultivars in switchgrass.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Yes.
Code availability
Yes.
References
Ali S, Serba DD, Jenkins J et al (2019) High-density linkage map reveals QTL under-lying growth traits in AP13×VS16 biparental population of switchgrass. GCB Bi-Oenergy 11:672–690. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12592
Bates D, Mächler M, Bolker B, Walker SC (2015) Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J Stat Softw 67:1–48
Bhandari HS, Saha MC, Mascia PN et al (2010) Variation among half-sib families and heritability for biomass yield and other traits in lowland switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Crop Sci 50:2355–2363. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2010.02.0109
Bhandari HS, Saha MC, Fasoula VA et al (2011) Estimation of genetic parameters f-or biomass yield in lowland switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). Crop Sci 51:1525–1533. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2010.10.0588
Bouton JH (2007) Molecular breeding of switchgrass for use as a biofuel crop. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17(6):553–558
Casler MD (2010) Changes in mean and genetic variance during two cycles of within-family selection in switchgrass. Bioenergy Res 3:47–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-009-9071-9
Chang D, Wu Y, Liu L et al (2016) Quantitative trait loci mapping for tillering-related traits in two switchgrass populations. Plant Genom 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2016.01.0010
Chen G, Wang Q, Liu YY et al (2012) Modelling analysis for enhancing seed vigour of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) using an ultrasonic technique. Biomass Bioenergy 47:426–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.09.015
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait m-apping. Genetics. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.080101
Clifton-Brown J, Harfouche A, Casler MD et al (2019) Breeding progress and prepar-edness for mass-scale deployment of perennial lignocellulosic biomass crops sw-itchgrass, miscanthus, willow and poplar. GCB Bioenergy 11:118–151. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12566
Curran WS, Ryan MR, Myers MW et al (2011) Effectiveness of sulfosulfuron and qu-inclorac for weed control during switchgrass establishment. Weed Technol 25:598–603. https://doi.org/10.1614/wt-d-11-00010.1
Dong H, Thames S, Liu L et al (2015) QTL mapping for reproductive maturity in low-land switchgrass populations. Bioenergy Res 8:1925–1937. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-015-9651-9
Dong H, Liu S, Clark LV et al (2018) Genetic mapping of biomass yield in three inte-rconnected Miscanthus populations. GCB Bioenergy 10:165–185. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12472
Dong H, Clark LV, Lipka AE et al (2019a) Winter hardiness of Miscanthus (III): Ge-nome-wide association and genomic prediction for overwintering ability in Misc-anthus sinensis. GCB Bioenergy 11:930–955. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12615
Dong H, Liu S, Clark LV et al (2019b) Winter hardiness of Miscanthus (II): genetic mapping for overwintering ability and adaptation traits in three interconnected Miscanthus populations. GCB Bioenergy 11:706–726. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12587
East EM (1936) Heterosis. Genetics 21(4):375–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF0298-2541
Feltus FA, Hart GE, Schertz KF et al (2006) Alignment of genetic maps and QTLs be-tween inter- and intra-specific sorghum populations. Theor Appl Genet 112:1295–1305
Gallais A (1988) Heterosis: its genetic basis and its utilization in plant breeding. Euphytica 39(2):95–104. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039859
Griffing B (1990) Use of a controlled-nutrient experiment to test heterosis hypotheses. Genetics 126(3):753
Huang X, Yang S, Gong J et al (2016) Genomic architecture of heterosis for yield traits in rice. Nature 537:629–633. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19760
Lippman ZB, Zamir D (2007) Heterosis: revisiting the magic. Trends Genet 23:60–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2006.12.006
Liu L, Wu Y (2012) Identification of a selfing compatible genotype and mode of inheritance in switchgrass. Bioenergy Res 5:662–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-011-9173-z
Liu L, Wu Y, Wang Y et al (2012) A high-density simple sequence repeat-based gene-tic linkage map of switchgrass. G3 Genes Genom Genet 2:357–370. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.111.001503
Lovell JT, MacQueen AH, Mamidi S et al (2021) Genomic mechanisms of climate a-daptation in polyploid bioenergy switchgrass. Nature 590:438–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03127-1
Lowry DB, Taylor SH, Bonnette J et al (2015) QTLs for biomass and developmental traits in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum). Bioenergy Res 8:1856–1867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-015-9629-7
Lowry DB, Lovell JT, Zhang L et al (2019) QTL × environment interactions underlie adaptive divergence in switchgrass across a large latitudinal gradient. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116:12933–12941. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1821543116
Lynd LR, Cushman JH, Nichols RJ et al (1991) Fuel etanol from cellulosic biomass. Science 251:1318–1323. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.251.4999.1318
Makaju SO, Wu Y, Anderson MP et al (2018) Yield-height correlation and QTL local-ization for plant height in two lowland switchgrass populations. Front Agric Sci Eng 5:118–128. https://doi.org/10.15302/J-FASE-2018201
Munshaw GC, Ervin EH, Shang C et al (2006) Influence of late-season iron, nitrogen, and seaweed extract on fall color retention and cold tolerance of four bermudagrass cultivars. Crop Sci 46:272–283. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2005.0078
Okada M, Lanzatella C, Saha MC et al (2010) Complete switchgrass genetic maps reveal subgenome collinearity, preferential pairing and multilocus interactions. Genetics 185(3):745–760. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.110.113910
Parrish DJ, Fike JH (2005) The biology and agronomy of switchgrass for biofuels. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 24:423–459. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352680500316433
Pauli D, Andrade-Sanchez P, Carmo-Silva AE et al (2016) Field-based high-through-put plant phenotyping reveals the temporal patterns of quantitative trait loci associated with stress-responsive traits in cotton. G3 6(4):865–879. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.115.023515
Redfearn DD, Moore KJ, Vogel KP et al (1997) Canopy architecture and morphology of switchgrass populations differing in forage yield. Agron J 89:262–269. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1997.00021962008900020018x
Rimi F, Macolino S, Leinauer B et al (2011) Green-up of seeded bermudagrass cultivars as influenced by spring scalping. Horttechnology 21:230–235. https://doi.org/10.21273/horttech.21.2.230
Rose LW IV, Das MK, Taliaferro CM (2008) Estimation of genetic variability and he-ritability for biofuel feedstock yield in several populations of switchgrass. Ann Appl Biol 152:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.2007.00186.x
Sadeghpour A, Hashemi M, DaCosta M et al (2014a) Switchgrass establishment infl-uenced by cover crop, tillage systems, and weed control. Bioenergy Res 7:1402–1410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-014-9485-x
Sadeghpour A, Hashemi M, Herbert SJ (2014b) A simple vigor test for adjusting swit-chgrass seeding rate in marginal and fertile soils. Grassl Sci 60:252–255. https://doi.org/10.1111/grs.12066
Sanderson MA, Reed RL, McLaughlin SB et al (1996) Switchgrass as a sustainable b-ioenergy crop. Biores Technol 56:83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(95)00176-X
Sarath G, Baird LM, Mitchell RB (2014) Senescence, dormancy and tillering in pere-nnial C4 grasses. Plant Sci 217–218(1):140–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.12.012
Schnell FW, Cockerham CC (1992) Multiplicative vs. arbitrary gene action in heteros-is. Genetics 131:461–469. https://doi.org/10.1016/1050-3862(92)90005-P
Serba D, Daverdin G, Bouton JH, Devos KM et al (2015) Quantitative trait loci(QTL) underlying biomass yield and plant height in switchgrass. BioEnerg Res 8:307–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-014-9523-8
Sladden SE, Bransby DI, Aiken GE (1991) Biomass yield, composition and production costs for eight switchgrass varieties in Alabama. Biomass Bioenergy 1:119–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/0961-9534(91)90034-A
Taylor M, Tornqvist CE, Zhao X et al (2018) Genome-wide association study in pseu-do-F2 populations of switchgrass identifies genetic loci affecting heading and an-thesis dates. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01250
Taylor M, Tornqvist CE, Zhao X et al (2019) Identification of quantitative trait loci f-or plant height, crown diameter, and plant biomass in a pseudo-F2 population of switchgrass. Bioenergy Res 12:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-019-09978-5
Team CR (2019) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R for St-atistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.R-Project.org
Tobias CM, Sarath G, Twigg P et al (2008) Comparative genomics in switchgrass using 61,585 high-quality expressed sequence tags. Plant Genom 1(2). https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2008.08.0003
Tornqvist CE, Taylor M, Jiang Y et al (2018) Quantitative trait locus mapping for flo-wering time in a lowland × upland switchgrass pseudo-F2 population. Plant Genom 11:1–9. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2017.10.0093
Van Ooijen JW (2009) MapQTL®6. Software for the mapping of quantitative trait lo-ci in experimental populations of diploid species. Kyazma B V
Walsh ME, de la Torre Ugarte DG, Shapouri H et al (2003) Bioenergy crop producti-on in the United States: potential quantities, land use changes, and economic impacts on the agricultural sector. Environ Resource Econ 24:313–333. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023625519092
Wang D, Lebauer DS, Dietze MC (2010) A quantitative review comparing the yield of switchgrass in monocultures and mixtures in relation to climate and manageme-nt factors. GCB Bioenergy 2:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1757-1707.2010.01035.x
Wang YW, Samuels TD, Wu YQ (2011) Development of 1,030 genomic SSR markers in switchgrass. Theor Appl Genet 122:677–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1477-4
Williams W (1959) Heterosis and the genetics of complex characters. Nature 184:527–530. https://doi.org/10.1038/184527a0
Wullschleger SD, Davis EB, Borsuk ME et al (2010) Biomass production in switchg-rass across the United States: database description and determinants of yield. Ag-Ron J 102:1158–1168. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2010.0087
Würschum T, Liu W, Busemeyer L et al (2014) Mapping dynamic QTL for plant heig-ht in triticale. BMC Genom Data 15:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2156-15-59
Xu Y, Li Y, Qiu Y (2021) Growth dynamics and heritability for plant high-throughput phenotyping studies using hierarchical functional data analysis. Biometr J. https://doi.org/10.1002/bimj.202000315
Yu J, Holland JB, McMullen MD, Buckler ES et al (2008) Genetic design and statisti-cal power of nested association mapping in maize. Genetics 178:539–551. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.107.074245
Zhang L, Weng X, Behrman K, et al (2020) QTL x environment interactions for panic-le traits in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum). https://doi.org/10.22541/au.160460109.97406017/v1
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Gary Williams for field wok assistance. Special thanks go to Dr. Carla Goad for her guidance and support in this study. The project was in part sponsored by NSF-EPSCoR, Sun Grant Initiative, Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station, and USDA Hatch to Y.Q. Wu.
Funding
The project was in part sponsored by NSF-EPSCoR, Sun Grant Initiative, Oklahoma Agricultural Experiment Station, and USDA Hatch to Y.Q. Wu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D. Chang carried out the experiment, data analysis, and writing of the manuscript, H.X. Dong conducted data analysis and writing of the manuscript, S.Q. Bai designed and supervised the experiment, and Y.Q. Wu conceived and supervised the experiment, wrote, and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors approved the submission.
Consent to participate
N/A
Consent for publication
Yes.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, D., Dong, H., Bai, S. et al. Mapping QTLs for spring green-up, plant vigor, and plant biomass in two lowland switchgrass populations. Mol Breeding 42, 27 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01296-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-022-01296-7