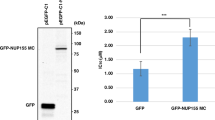
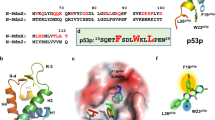
Abstract
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-interacting kinases (MNKs) can regulate cellular mRNA translation by controlling the phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E (eIF4E), which plays an important role in tumor initiation, development, and metastasis. Although small-molecule MNK inhibitors have made significant breakthroughs in the treatment of various malignancies, their clinical application can be limited by drug resistance, target selectivity and other factors. The strategy of MNK-PROTACs which selectively degrades MNK kinases provides a new approach for developing small-molecule drugs for related diseases. In this study, DS33059, a small-molecule compound modified based on the ongoing clinical trials drug ETC-206, was chosen as the target protein ligand. A series of novel MNK-PROTACs were designed, synthesized and evaluated biological activity. Several compounds showed good inhibitory activities against MNK1/2. Besides, compounds exhibited moderate to excellent anti-proliferative activity in A549 and TMD-8 cells in vitro. In particular, compound II-5 significantly inhibited A549 (IC50 = 1.79 μM) and TMD-8 (IC50 = 1.07 μM) cells. The protein degradation assay showed that compound II-5 had good capability to degrade MNK1. The MNK-PROTACs strategy represents a new direction in treating tumors and deserves further exploration.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pinto-Diez C, Ferreras-Martin R, Carrion-Marchante R, Gonzalez VM, Elena MM (2020) Deeping in the role of the MAP-kinases interacting kinases (MNKs) in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21(8):2967. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21082967
Buxade M, Parra-Palau JL, Proud CG (2008) The Mnks: MAP kinase-interacting kinases (MAP kinase signal-integrating kinases). FBL 13(14):5359–5373. https://doi.org/10.2741/3086
Jauch R, Jakel S, Netter C, Schreiter K, Aicher B, Jackle H et al (2005) Crystal structures of the Mnk2 kinase domain reveal an inhibitory conformation and a zinc binding site. Structure 13(10):1559–1568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2005.07.013
Roux PP, Blenis J (2004) ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68(2):320–344. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.68.2.320-344.2004
Scheper GC, Proud CG (2002) Does phosphorylation of the cap-binding protein eIF4E play a role in translation initiation? Eur J Biochem 269(22):5350–5359. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03291.x
Yang X, Zhong W, Cao R (2020) Phosphorylation of the mRNA cap-binding protein eIF4E and cancer. Cell Signal 73:109689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109689
Fernandez A, Monsen PJ, Platanias LC, Schiltz GE (2023) Medicinal chemistry approaches to target the MNK-eIF4E axis in cancer. RSC Med Chem 14(6):1060–1087. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3md00121k
Batool A, Aashaq S, Andrabi KI (2019) Eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E): a recap of the cap-binding protein. J Cell Biochem 120(9):14201–14212. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28851
Hay N (2010) Mnk earmarks eIF4E for cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(32):13975–13976. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008908107
Yang J, Li G, Huang Y, Liu Y (2023) Decreasing expression of Prohibitin-2 lowers the oncogenicity of renal cell carcinoma cells by suppressing eIF4E-mediated oncogene translation via MNK inhibition. Toxicol Appl Pharmacolo 466:116458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2023.116458
Ueda T, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Fukuyama H, Nagata S, Fukunaga R (2004) Mnk2 and Mnk1 are essential for constitutive and inducible phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E but not for cell growth or development. Mol Cell Biol 24(15):6539–6549. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.24.15.6539-6549.2004
Xu W, Kannan S, Verma CS, Nacro K (2022) Update on the development of MNK inhibitors as therapeutic agents. J Med Chem 65(2):983–1007. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00368
Santag S, Siegel F, Wengner AM, Lange C, Boemer U, Eis K et al (2017) BAY 1143269, a novel MNK1 inhibitor, targets oncogenic protein expression and shows potent anti-tumor activity. Cancer Lett 390:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.12.029
Santag S, Siegel F, Wegner AM, Schneider C, Boemer U, Eis K et al (2015) Preclinical anti-tumor efficacy and mode of action of a novel, orally available, selective MKNK1 inhibitor BAY 1143269. Can Res 75:2604. https://doi.org/10.1158/1538-7445.Am2015-2604
Reich SH, Sprengeler PA, Chiang GG, Appleman JR, Chen J, Clarine J et al (2018) Structure-based design of pyridone-aminal eFT508 targeting dysregulated translation by selective mitogen-activated protein kinase interacting kinases 1 and 2 (MNK1/2) Inhibition. J Med Chem 61(8):3516–3540. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01795
Teneggi V, Novotny-Diermayr V, Lee LH, Yasin M, Yeo P, Ethirajulu K et al (2020) First-in-human, healthy volunteers integrated protocol of ETC-206, an oral Mnk 1/2 kinase inhibitor oncology drug. Clin Transl Sci 13(1):57–66. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.12678
Yang H, Chennamaneni LR, Ho MWT, Ang SH, Tan ESW, Jeyaraj DA et al (2018) Optimization of selective mitogen-activated protein kinase interacting kinases 1 and 2 inhibitors for the treatment of blast crisis leukemia. J Med Chem 61(10):4348–4369. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b01714
Bu H, Yuan X, Wu H, Zhou J, Zhang H (2021) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of imidazopyridazine derivatives containing isoquinoline group as potent MNK1/2 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 40:116186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116186
Zhang X, Meng T, Cui S, Feng L, Liu D, Pang Q et al (2021) Ubiquitination of nonhistone proteins in cancer development and treatment. Front Oncol 10:621294. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.621294
Neklesa TK, Winkler JD, Crews CM (2017) Targeted protein degradation by PROTACs. Pharmacol Ther 174:138–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.027
Sun Y, Zhao X, Ding N, Gao H, Wu Y, Yang Y et al (2018) PROTAC-induced BTK degradation as a novel therapy for mutated BTK C481S induced ibrutinib-resistant B-cell malignancies. Cell Res 28(7):779–781. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0055-1
Gu S, Cui D, Chen X, Xiong X, Zhao Y (2018) PROTACs: an emerging targeting technique for protein degradation in drug discovery. BioEssays 40(4):e1700247. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201700247
Lai AC, Crews CM (2017) Induced protein degradation: an emerging drug discovery paradigm. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 16(2):101–114. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.211
Toure M, Crews CM (2016) Small-molecule PROTACS: new approaches to protein degradation. Angew Chem Int Ed 55(6):1966–1973. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201507978
Yamanaka S, Furihata H, Yanagihara Y, Taya A, Nagasaka T, Usui M et al (2023) Lenalidomide derivatives and proteolysis-targeting chimeras for controlling neosubstrate degradation. Nat Commun 14(1):4683. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40385-9
Ito T, Ando H, Suzuki T, Ogura T, Hotta K, Imamura Y et al (2010) Identification of a primary target of thalidomide teratogenicity. Science 327(5971):1345–1350. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1177319
Webster KR, Goel VK, Hung INJ, Parker GS, Staunton J, Neal M et al (2015) eFT508, a potent and selective mitogen-activated protein kinase interacting kinase (MNK) 1 and 2 inhibitor, is efficacious in preclinical models of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood 126(23):1554. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V126.23.1554.1554
Funding
This study was supported by the Lingang Laboratory (Grant No. LG202103-02-08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SX and WQY wrote the manuscript, designed the study, performed experiments and analyzed the data. BH designed the study, performed experiments and analyzed the data. PYF carried out the research on molecular docking and analyzed the data. GDZ and GS provided materials and important suggestions. ZJP and ZHB designed the study, supervised the study and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Wu, Q., Bu, H. et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of MNK-PROTACs. Mol Divers (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10776-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-023-10776-7