Abstract
This study investigates the factors affecting maize farmers’ decisions to adopt climate-smart agricultural (CSA) technologies and estimates the impacts of CSA technology adoption on maize yields and net farm income. Unlike most previous studies that analyze a single technology, we consider different combinations of three CSA technologies (zero tillage, row planting, and drought-resistant seed). A multinomial endogenous switching regression model addresses selection bias issues arising from observed and unobserved factors and analyses data collected from 3197 smallholder farmers in three Ghana regions (Brong-Ahafo, Northern, and Ashanti). The findings show that smallholder farmers’ decisions to adopt multiple CSA technologies are influenced by farmer-based organization membership, education, resource constraints such as lack of land, access to markets, and production shocks such as perceived pest and disease stress and drought. We also find that adopting all three CSA technologies together has the largest impact on maize yields, while adopting row planting and zero tillage as a combination has the largest impact on net farm income. Governments should collaborate with farmer-based groups and extension officers to improve farmers’ awareness and understanding of the benefits associated with CSA technologies and help them adopt multiple technologies that generate higher benefits.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Smallholder farmers in Africa are the largest private sector group, accounting for roughly 70% of the population in the continent (Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa, AGRA 2017). These farmers cultivate fewer than 2 hectares of land, relying heavily on traditional farming practices. However, traditional farming practices are usually not sustainable. They are associated with poor soil fertility and lower productivity, leading to food insecurity and poverty (Kassie et al. 2015; Grabowski et al. 2016; Quarshie et al. 2023; Tabe-Ojong et al. 2023; Wakweya 2023). In addition, African smallholder farmers are typically the most vulnerable to climate risks, resulting in weak farming system resilience.
Development partners and climate action stakeholders have made great efforts to promote farmers’ adoption of climate-smart agricultural (CSA) technologies to mitigate the negative impacts of climate change on agriculture and improve farm performance. For example, there is a widespread promotion of drought-tolerant maize and stress-tolerant maize seeds among smallholder farmers to reduce their potential risk of meagre yields or total crop failure caused by erratic and low rainfall patterns in various maize-producing ecologies (Fisher et al. 2015; Setimela et al. 2017; Simtowe et al. 2019; Gebre et al. 2021). Other key CSA technologies, such as row planting and zero tillage, have also been promoted to help increase crop yields and income, as well as build climate resilience (Teklewold and Mekonnen 2017; Fentie and Beyene 2019; Martey et al. 2021). Sova et al. (2018) emphasized that the CSA technologies are especially suited to households that rely on rain-fed agriculture, such as those in dryland areas of Africa and other parts of the world.
Like other SSA countries, smallholder farmers in Ghana are subject to climatic shocks. Therefore, the National Climate Change Policy has adopted CSA practices and technologies as a component of sustainable agricultural development policy (Atta-Aidoo et al. 2022). Despite the implementation of various initiatives aimed at promoting the adoption of CSA practices, the adoption rate among smallholder farmers in several regions of Ghana is still low (Martey et al. 2021; Atta-Aidoo et al. 2022; Tetteh Quarshie et al. 2023). As a result, evidence is required to comprehensively understand the drivers and barriers in CSA technology adoption to develop policies and programs that effectively address this issue.
Some studies in Africa have examined the impact of adopting CSA technologies on farm performance, focusing on the adoption of a single agricultural technology (Manda et al. 2016, 2018; Ng’ombe et al 2017; Teklewold and Mekonnen 2017; Martey et al. 2021). For example, Fentie and Beyene (2019) concluded that row planting positively impacts per-hectare crop income in Ethiopia. In practice, some farmers adopt a combination of technologies rather than one technology to address production challenges such as climate change and unexpected shocks. In this case, studies focusing on the effects of a single technology may overlook the importance of other complementary technologies that farmers may adopt to address such challenges.
This paper investigates the association between CSA technology adoption and farm performance, captured by maize yields and net farm income. We analyze data collected from 3197 smallholder farmers in Ghana’s three regions (Brong-Ahafo, Northern, and Ashanti). These three regions are selected based on their status as the leading maize producers in Ghana. We focus on three CSA technologies in this study: row planting, zero tillage, and drought-tolerant maize seeds. We concentrated on these three technologies because they were the only ones disseminated to the maize farmers in our sample. Row planting is critical for improved soil fertility, temperature regulation, and moisture management. Drought-tolerant maize seeds are critical for stress (drought, heat, disease, and pest) management, whereas zero tillage is important for reducing soil erosion and increasing soil biological activity.
We attempt to make three contributions to the literature on climate-smart agriculture. First, we explore the factors affecting maize farmers’ decisions to adopt different combinations of CSA technologies. To achieve this, we categorize the three CSA technologies (row planting, zero tillage, and drought-tolerant maize seeds) into eight groups by considering non-adoption, adopting only one type of technology, combining one technology with another, and adopting all three technologies. Second, we examine the impact of CSA adoption on maize yields and net farm income. As an exception, Martey et al. (2020) explored the impacts of adopting row planting and drought-tolerant maize varieties on the yields and intensity of maize commercialization. Still, they did not consider the adoption of zero tillage. Third, we employ the multinomial endogenous switching regression (MESR) model to address the selection bias issues arising from both observed factors (e.g., age, gender, farm size, and household size) and unobserved factors (e.g., farmers’ innate ability and motivations). The MESR model acknowledges that farmers choose one of those eight technology options to maximize the expected benefit. The policy implications are significant. Identifying determinants that influence smallholder farmers’ adoption of single or multiple CSA technologies could provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of various information channels, such as radio, extension services, and FBOs, in facilitating CSA technology adoption.
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows. The review of the literature is presented in Sect. 2. The econometric framework is introduced in Sect. 3, and the survey sites, data, and descriptive statistics are presented in Sect. 4. Section 5 presents and discusses the empirical results. The final section summarizes the findings, suggests policy implications, and discusses the limitations.
2 Literature review
Many studies have been conducted globally to investigate the factors influencing the adoption of CSA technologies in smallholder farming systems in Africa. There exist two strands of literature. The first strand of literature considers the single CSA technology, such as improved crop varieties and row planting (Teklewold et al. 2013; Keil et al. 2017; Amadu et al. 2020; Manda et al. 2020a; Martey et al. 2020; Ehiakpor et al. 2021; Guo et al. 2022; Mossie 2022). For example, Manda et al. (2018) found that socioeconomic, farm-level, and institutional factors influence farmers’ decisions to adopt improved maize varieties in Zambia. Ayal et al. (2018) investigated the factors influencing row planting adoption in Ethiopia. They found that household heads’ educational levels, family labor, farm size, membership in training and associations, and livestock ownership positively and significantly impact row planting adoption. According to Martey et al. (2020), the main factors influencing farmers’ adoption of drought-tolerant maize varieties in Ghana are access to seeds and extension, gender, labor availability, and location. Kimathi et al. (2021) found that access to information, quality seeds, training, group membership, and variations in agroecological zones are the most important factors influencing farmers’ decisions to adopt climate-resilient potato varieties.
The second strand of literature has investigated the factors that influence smallholder farmers’ decisions to adopt multiple agricultural innovations/technologies (Makate et al. 2019; Ehiakpor et al. 2021; Bese et al. 2021; Antwi-Agyei and Amanor 2023; Jones et al. 2023). For example, Makate et al. (2019) found that access to extension, fertilizer, credit, marital status, experience, and residential status are the main factors affecting farmers’ adoption of multiple CSA innovations (conservation agriculture, improved legume, and drought-tolerant maize) in Malawi and Zimbabwe. Amadu et al. (2020) found that program participation has a positive and statistically significant effect on the adoption of CSA practices (residue addition, non-woody plant cultivation, assisted regeneration, woody plant cultivation, physical infrastructure, and mixed measures) in general, with the strongest effects on resource-intensive CSA categories in southern Malawi. Ehiakpor et al. (2021) found that off-farm income, perceived low soil fertility, pest and disease incidence, experience, field demonstration and group membership, land ownership, distance to market, and credit access all influence the adoption of multiple sustainable practices (e.g., adoption of improved maize seeds, maize-legume rotation, animal manure, legume intercropping, and crop residue retention). By estimating data from southern Ghana, Jones et al. (2023) reported a positive relationship between mobile phone agriculture extension delivery and the adoption of CSA practices.
In addition to the factors influencing CSA technology adoption, the existing studies have also assessed the effects of CSA technology adoption. Most of those studies have focused on the impact of adopting a single CSA technology on various outcome variables such as farm income, agrochemical use, labor demand, crop yields, and poverty (Manda et al. 2016; Ng’ombe et al. 2017; Teklewold and Mekonnen 2017; Martey et al. 2020). Only a few studies have assessed the effects of adopting multiple CSA technologies (Gebremariam and Wünscher 2016; Manda et al. 2016; Khonje et al. 2018; Makate et al. 2019). For example, Makate et al. (2019) found that adopting CSA technologies (conservation agriculture, improved legumes, and drought-tolerant maize) increases farm productivity and income in southern Africa than using them separately. Khonje et al. (2018) demonstrated that in Zambia, the simultaneous adoption of innovative technologies (improved maize varieties and conservation agriculture practices) has a greater impact on farm output, income, and poverty than individual innovation package adoption.
Although the studies above have provided rich insights into the factors influencing CSA technology adoption and its impacts, significant research gaps remain. Specifically, most previous research on the adoption of multiple CSA technologies has focused on Eastern and Southern African countries (Teklewold et al. 2013; Makate et al. 2019; Bese et al. 2021), with little focus on West African countries such as Ghana (Ehiakpor et al. 2021; Lu et al. 2021; Faye et al. 2021; Setsoafia et al. 2022). The maize production environment in West Africa differs from that in Southern and Eastern Africa due to different varieties and production practices. In their meta-analysis, Xie and Huang (2021) emphasized that technology adoption is heterogeneous, so policymakers and other stakeholders must consider geographical differences and farming systems, the technology needs of different farmers, and costs when designing policies to encourage the adoption of agricultural technologies. Given that no predefined combinations of CSA technologies work in every environment, it has been claimed that adopting CSA technologies is context-specific (Amadu et al. 2020; Xie and Huang 2021). As a result, empirical studies demonstrating the impact of CSA technologies in various environmental settings are critical for designing policies and technologies. This study adds to the literature by examining how adopting CSA technologies, specifically row planting, zero tillage, and drought-tolerant maize seeds, affects maize yields and net farm income in Ghana.
3 Econometric framework
3.1 Selection bias issue and model selection
Agriculture is risky, especially in much of the developing world, where farmers rely heavily on rainfall, plant in degraded soils, face pest and disease outbreaks, and frequently lack access to high-quality inputs or markets (Sova et al. 2018). These external shocks may prompt smallholder farmers to adopt CSA technologies to mitigate crop production shocks. Farmers’ decisions to adopt one of the CSA technologies can be influenced by socioeconomic factors that can be observed (e.g., age, gender, size of the farm, and years of education) as well as factors that cannot be observed (e.g., motivations and managerial skills) (Kassie et al. 2013; Teklewold et al. 2013; Manda et al. 2016; Ehiakpor et al. 2021). Due to self-selection issues, farmers who adopt CSA technologies may systematically differ from those who do not adopt the technologies regarding observed and unobserved characteristics. It should be emphasized that any selection bias issues that arise should be addressed to estimate the impacts of CSA technology adoption on farm performance consistently.
When technology adoption is a binary decision (i.e., adoption or non-adoption), approaches such as the propensity score matching (PSM) model (Ma et al., 2022) or endogenous switching regression (ESR) model (Liu et al. 2021; Zheng et al. 2021) can be used to estimate its impact. However, when technology adoption involves multiple choices, PSM and ESR models become inefficient in addressing selection bias issues. In this case, previous studies have suggested using the multinomial endogenous switching regression (MESR) model (Kassie et al. 2015; Lu et al. 2021; Oparinde 2021; Ahmed 2022; Asante et al. 2023) and multivalued treatment effects (MVTE) model (Cattaneo 2010; Lu et al. 2021; Ma and Zheng 2021; Czyżewski et al. 2022; Asante et al. 2023). The MESR model enables one to account for both observed and unobserved factors when addressing the selection bias issues, while the MVTE model only mitigates the observed selection bias issues. Because the MVTE model has limitations in addressing unobserved selection bias, we use the MESR model in this study to estimate the treatment effects of CSA technology adoption on farm performance.
3.2 Multinomial endogenous switching regression
The MESR model consists of three steps. The first stage is to investigate the factors influencing farmers’ decisions to adopt the three CSA technologies: drought-resistant seeds (D), row planting (R), and zero tillage (Z). These three CSA technologies can present eight options for an individual farmer. If a farmer chooses not to adopt the three CSA technologies, it can be recorded as (1) non-adoption (D0R0Z0). That is, farmers did not adopt any of those three CSA technologies. Adopters have seven options which are (2) drought-resistant seeds only (D1R0Z0); (3) row planting only (D0R1Z0); (4) zero tillage only (D0R0Z1); (5) drought-resistant seeds and row planting (D1R1Z0); (6) drought-resistant seeds and zero tillage (D1R0Z1); (7) row planting and zero tillage (D0R1Z1); and (8) combination of drought-resistant seed, row planting and zero tillage (D1R1Z1). These eight combinations are all mutually exclusive. An individual farmer, therefore, chooses one of those eight possible options in farm production to maximize their expected benefits.
We assume that the random terms are identical and independently distributed based on the Gumbel distribution, with the likelihood that an ith farmer with \({H}_{i}\) attributes would select jth CSA technology from those eight possible options. This is captured by a multinomial logit (MNL) model within the MESR model framework (Ma et al. 2022; Teklewold et al. 2013; Zhou et al. 2020), which is specified as follows:
where \({L}_{ij}\) refers to the likelihood that ith farmer selects to adopt jth CSA technology; \({H}_{i}\) is a vector of observed explanatory factors captured by household, farm level, institutional and location variables; \({\alpha }_{j}\) is a vector of parameters to be estimated.
In the second step of the MESR model, an ordinary least squares (OLS) approach was employed to examine the relationship between a set of explanatory variables (represented as \({X}_{i}\)) and outcome variables (i.e., maize yields and net farm income). The non-adoption (D0R0Z0) of the CSA technology is represented by \(j=1\), while other combinations are represented by \(j=2, 3, 4, \dots , 8.\) Thus, we express each regime of equations as follows:
where \({W}_{iJ}\) refers to the outcome variable for the ith farmer when adopting CSA technology J; \({X}_{i}\) indicates a vector of explanatory variables; \({\beta }_{1}\) and \({\beta }_{J}\) are parameters to be estimated; \({\mu }_{i1}\) and \({\mu }_{iJ}\) refer to disturbance terms.
In Eq. (2), \({X}_{i}\) could help address the observed selection bias issues. However, when the same unobserved factors (e.g., farmers’ innate abilities and aspirations) influence farmers’ decisions to adopt CSA technologies and outcome variables simultaneously, the disturbance terms in Eqs. (1) and (2) will be correlated. If the correlation coefficients of the disturbance terms do not equal zero, selection bias issues occur (Setsoafia et al. 2022). Failure to account for such an issue may result in biased and inconsistent estimates. Therefore, the MESR model includes the selectivity-correction terms computed after estimating Eq. (1) and automatically fit into Eq. (2) to eliminate the unobserved selection bias. By including the selectivity-correction terms, Eq. (2) can be rewritten as follows:
where \({\lambda }_{1}\) and \({\lambda }_{J}\) refer to selectivity-correction terms; \({\sigma }_{1} {\text{and}} {\sigma }_{J}\) are covariances between disturbance errors in Eqs. (1) and (2). The rest of the parameters are already defined from the above equations. Further, the multinomial selection framework allows for \(J-1\) selectivity-correction terms where one represents each option of CSA technology combination.
According to Di Falco et al. (2011) and Asante et al. (2023), estimations of the MESR model must include at least one instrumental variable (IV) for model identification. The employed IV is included in the \({H}_{i}\) of the MNL model in Eq. (1), but not in the \({X}_{i}\) of the outcome Eq. (2). In this paper, we use four information variables (i.e., membership of a farmer-based group, information from radio, colleague farmer, and extension contacts) as IVs for the identification purpose of the model. The selected IVs are not expected to influence maize yields and net farm income directly. The validity of these IVs was evaluated using the falsification test (Di Falco et al. 2011; Ma and Zheng 2021; Asante et al. 2023) and Pearson correlation analysis (Asante et al. 2023; Ma and Zheng 2021; Ma et al. 2022). Tables 5 and 6 in the Appendix present the validation results for the instruments.
In the third stage, the average treatment effect on the treated (ATT) is computed by comparing the expected outcome variables of CSA technology adopters and non-adopters. In practice, estimating the impacts on experimental data is easier, whereas it is quite challenging to establish the impacts using cross-sectional data. The MESR model helps calculate the counterfactual outcome (i.e., the outcome of CSA technology adopters if they had not adopted the CSA technology), making the calculation of ATT possible. Following previous studies (see Ahmed 2022; Asante et al. 2023; Kassie et al. 2015; Oparinde 2021), the ATT estimates for the actual and counterfactual scenarios are derived using the following equations.
CSA technology adopters with adoption (actual adoption observed):
The CSA technology adopters had they decided not to adopt (counterfactual):
Finally, subtracting Eq. (5) from Eq. (4) gives the ATT. It is specified as
4 Survey sites, data, and descriptive statistics
4.1 Survey sites
The data used in the present study were collected from Ghana’s Brong-Ahafo, Northern, and Ashanti regions (Fig. 1) from August to September 2022. These three regions are considered in our analysis because they account for most maize production in Ghana (Kankam-Boadu et al. 2018; Food and Agriculture Organization 2019). The Brong-Ahafo region is in the southern half of the country between longitude 0° 15′ E-3° W and 8° 45′ N-7° 30′ S. The region is bordered on the north by the Northern region, the south by the Ashanti and Western regions, the east by the Volta region, and the west by the Eastern region. Its population is 2,282,128, and 69.1% is engaged in agriculture (Ghana Statistical Services 2021). The region has fertile soils, favorable climatic conditions, and a diverse vegetation cover. It is also considered an agricultural-based economic activity in Ghana, contributing about 30% of its food supply (GSS 2021).
The Northern region, located in northern Ghana, covers a total area of 70,384 km2. The region lies approximately within N 9° 32′ 38.1372″, W 0° 54′ 20.3832 and is bordered on the west by the Savannah region, on the east by the international border with Togo, on the south by the Oti region, and in the north by the North East region. The Northern region has a population of approximately 1,948,913 people (GSS 2021), with agriculture being the primary source of income for approximately 75% of the population, primarily cultivating sorghum, cowpea, millet, and maize. The region lies within the Guinea Savannah agroecological zone, characterized by aridity, densely clustered grassland, and drought-resistant trees. Temperatures in the region range from 14 °C at night to 40 °C during the day.
The Ashanti region, located in the center of Ghana, has a total land area of 24,389 km2 and is located between longitudes 0.15° E and 2.25° W and latitudes 5.50° N and 7.46° S. The region shares its southern, northern, western, and eastern borders with the Central, Bono East, Western, and Eastern regions. With a population of 5,924,498 in 2020, the Ashanti region was Ghana’s most populous (GSS 2021). Agriculture is the primary source of income for the majority of the population in the region. The region has a bimodal rainfall pattern, with annual precipitation ranging from 1300 to 1500 mm (GSS 2021), and relatively rich soils supporting major crops such as maize, rice, roots and tubers, and sorghum.
4.2 Data
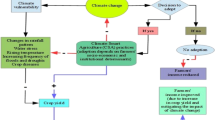
A total of 3197 maize farmers were sampled from six districts (Nkoranza North, Kintampo South, Ejura-Sekyeredumasi, Zabzugu, Ejisu municipal and Northeast Gonja), two districts for each of the three regions (Brong-Ahafo, Northern and Ashanti). A multistage sampling technique was used to select a district purposively, in which three communities were purposively sampled in each district, and 180 farmers were also randomly selected to obtain a total of 540 from each district. Each region had a sample size of 1080 maize farmers. The final analysis included a sample of 3197 farmers (see Fig. 2 for the methodological flow chart). The data have various socioeconomic characteristics, agricultural land holdings, maize outputs and sales, livestock production, farmers’ access to CSA technology information, institutional factors, and income.
Following previous studies that estimate the impact of adopting CSA technologies and other agricultural innovations (e.g., Bopp et al. 2019; Kassie et al. 2013; Ma and Wang 2020; Ma and Zheng 2021; Manda et al. 2016; Setsoafia et al. 2022; Teklewold et al. 2013) we consider two outcome variables: maize yields and net farm income. The maize yields are measured by the maize output per unit of land during the 2021/2022 production season, i.e., kg/acre. The net farm income refers to the difference between the gross revenue of maize production and the maize production costs of all variable inputs (such as labor, seed, agrochemicals, and fertilizers), which is measured at GHS/acre.
4.3 Descriptive statistics
Table 1 shows the definitions and summary attributes of farmers. The average maize yields are 2490 kg/acre, and the net farm income is 3716 GHS/acre. Of the sampled farmers, 86.6% are males, and their mean age is 47.49 years. Most of the farmers (86.5%) were married, with a mean family size of 6.7. A typical farmer has 8.91 years of formal education and 21.32 years of farming experience. Fifty-five percent of farmers were members of farmer-based organizations. Approximately 58.7% of farmers received CSA technology information from extension agents, while 83.9% and 41.3% received it from colleague farmers and radio, respectively.
Table 1 also shows that males make up the majority of CSA adopters who use at least two types of CSA technologies. Farmers who adopted at least two types of CSA technologies were more educated, implying that they may be better able to understand the benefits of CSA technologies than farmers who adopted a single technology or were non-adopters. Relatively large family sizes used at least two types of CSA technologies. The majority (54%) of farmers who adopted all three CSA technologies had market information, and 74.7% owned their farmland. Furthermore, farmers who experienced shocks, such as pest and disease stress (52.4%) and drought stress (50.1%), are more likely to adopt a combination of all CSA technologies.
Table 2 shows the distributions of various categories of CSA technologies maize farmers adopt. Out of the eight possible CSA groups, around 15.98% of farmers did not adopt any type of CSA technology (D0R0Z0). Among the adopters, the largest proportion of farmers (26.62%) adopted drought-resistant seeds and zero-tillage (D1R0Z1). This is followed by the proportion of farmers (20.21%) who adopted all three CSA technologies (D1R1Z1). Only 4.22% of farmers combined drought-resistant seeds and row planting (D1R1Z0) as CSA technologies.
5 Empirical results and discussions
5.1 Determinants of choosing different combinations of CSA technologies
Table 3 presents the results of the MNL model estimates, revealing the factors influencing farmers’ decisions to select and adopt CSA technologies. We used non-adopters (D0R0Z0) as the reference group in MNL estimations. Because the interpretation of the coefficients is not straightforward and it gives only the direction of the variables, the marginal effects of the MNL model are presented in Table 3 to provide a better understanding of factors influencing maize farmers’ decisions to adopt CSA technologies (Nguyen-Van et al. 2017). Our results show that the marginal effects differ greatly among the different CSA technology combinations.
The results reveal that the farmer’s age has a positive and significant marginal effect (see columns 5, 6, 7, and 8 of Table 3). The findings imply that older farmers are more likely to integrate drought-resistant seeds and row planting (D1R1Z0), drought-resistant seeds and zero tillage (D1R0Z1), row planting and zero tillage (D0R1Z1), and combinations of all the CSA technologies (D1R1Z1). For example, the positive and significant marginal effect in column 5 of Table 3 suggests that older farmers are 16% more likely to integrate drought-resistant seeds and row planting (D1R1Z0) than younger ones. The findings on age resonate with the results of previous studies (Vatsa et al. 2023; Zhou et al. 2023), opining that older farmers have more knowledge and experience, motivating them to adopt productivity-enhancing technologies. Also, the age square variable, which captures the long-term effect of age on CSA technology adoption, has a significant and negative coefficient. This implies that as farmers grow older beyond a certain age, their likelihood of adopting CSAs decreases. Older farmers are 1.2% less likely to adopt CSAs. This finding suggests that diminishing physical strength over time may contribute to the reduced adoption of CSA technologies among older farmers. This is consistent with the findings of Mossie (2022) and Tanti et al. (2022), who found an inverse relationship between the age square of farmers and the adoption of CSA technology.
Education positively and significantly affects all the combinations in the last column. The finding suggests that one 1-year increase in education would increase the probability of adopting drought-resistant seed, row planting, and zero tillage (D1R1Z1) by 23.2%. Better education improves farmers’ awareness and understanding of the benefits associated with CSA technologies, increasing their adoption motivation. This finding resonates with the findings of Gebremariam and Wünscher (2016) and Li et al. (2024).
Married farmers are 68.9% more likely to incorporate row planting and zero tillage (D0R1Z1) as CSA technologies. Married households have more members due to increased household size; hence, there is a desire to produce more food using CSA technologies. Makate et al. (2019) reported similar findings. They indicated that married farmers are more likely to adopt CSA technologies, specifically to improve legume seeds, because marriage is an institution in Southern Africa. The results also show that an additional year spent on farming by a typical farmer would reduce the likelihood of adopting row planting alone (D0R1Z0) by 57% and reduce the likelihood of incorporating drought-resistant seeds and zero tillage (D1R1Z0) by 62.6%. Most experienced farmers are more conservative in their adoption of modern productivity-enhancing technologies. However, the experience variable positively affects adopting CSA technology, specifically zero tillage alone (D0R0Z1). Experience is linked to training and information obtained on CSA technologies, as well as less drudgery and no/low cost of zero tillage, which could encourage farmers to adopt zero tillage technology easily.
The positive and significant effect of household size on all CSA technologies adoption (D1R1Z1) suggests that a one-member increase in family size would increase the probability of adopting the three CSA technologies (D1R1Z1) together by 38.7%. Bigger families generally signal greater resource endowment, such as labor, assisting farmers in crop cultivation and adopting CSA technologies, than smaller families. Previous studies have also found that household units positively influence the adoption of sustainable agricultural practices in Ghana (Setsoafia et al. 2022). An additional acre increase in farm size would increase the likelihood of adopting all three CSA technologies (D1R1Z1) by 47%. Farmland is commonly described as a source of wealth, which motivates farm families, particularly those with large farms, to adopt CSA technologies. Anang and Amikuzuno (2015) discovered similar results in northern Ghana. In addition, land ownership has a positive and significant effect on the adoption of drought-resistant seeds and zero tillage (D1R0Z1), as well as all three CSA technologies (D1R1Z1), which increases the adoption probability by 59.4% and 46.2%, respectively.
The distance from the farmer’s homestead to the nearest market positively influences the adoption of all three CSA technologies (D1R1Z1). This finding indicates that the greater the distance farmers travel to the nearest agricultural market, the less probability of adopting CSA technologies. This is consistent with the findings of Anang and Amikuzuno (2015), who asserted that longer market distances are associated with higher transportation and transaction costs, thus reducing the likelihood of adopting CSA practices. The variable representing the perceived pest and disease stress positively and significantly influences the adoption of all CSA technologies. Specifically, farmers who encountered an infestation of pests and diseases are more likely to adopt a blend of drought-resistant seeds and zero tillage (D1R0Z1) and all three (D1R1Z1). This is consistent with Teklewold et al. (2013), who found that increased pest and disease stress increases the adoption of improved seeds in Ethiopia. In Ghana, Danso-Abbeam and Baiyegunhi (2018) indicated that high-incidence pests and diseases encourage adopting pesticide management practices. However, this may not be the case everywhere, as our findings indicate that pest and disease stress negatively affect the adoption of zero tillage (D0R0Z1), giving rise to the diverse influences of CSA technologies among Ghanaian smallholder farmers.
Farmers who receive CSA technology information via extension have a higher likelihood of adopting CSA technologies such as drought-resistant seeds (D1R0Z0) alone and drought-resistant seeds and row planting (D1R1Z0), which increases their adoption probability by 15.2% and 13.1%, respectively. Better extension services for farmers, such as training and education on climate-sustainable agricultural practices, tend to boost crop productivity, which may drive most farmers’ adoption of CSA technologies. Membership in farmer-based organizations has a positive and significant effect on the adoption of multiple CSA technologies, specifically incorporating drought-resistant seeds and zero tillage (D1R0Z1), combining row planting and zero tillage (D0R1Z1) and all three CSA technologies (D1R1Z1). The findings confirm the extensive discussions about the advantages of farmer-based groups (see Manda et al. 2020a, b; Yu et al. 2021; Zhang et al. 2020). For example, being a FBO member increases the desire to adopt improved seeds in Zambia (Manda et al. 2020a, b) and soil and water conservation practices in Ghana (Amadu et al. 2020). Also, farmers who obtain information from a colleague are more likely to adopt multiple CSA technologies. Specifically, the likelihood of adopting a combination of drought-resistant seeds and zero tillage (D1R0Z1), row planting and zero tillage (D0R1Z1), and all three CSA technologies (D1R1Z1) would increase by 67.9%, 16.3%, and 17.5%, respectively, if they received CSA technology information from colleagues.
The location dummies in columns 2, 4, and 5 are statistically significant. Our findings suggest that farmers in Ashanti and Brong-Ahafo are more likely to adopt only drought-resistant seeds (D1R0Z0) than farmers in the Northern region (reference group). The findings highlight the importance of including location control variables in model estimations by demonstrating how other socioeconomic conditions, resource endowments, climatic conditions, and institutional arrangements may influence smallholder farmers’ decisions to adopt CSA technologies.
5.2 Treatment effects of CSA technology adoption
Table 4 shows the treatment effects of CSA technology adoption on maize yields and net farm income. The results estimated from the second stage of the MESR model are not presented in the study for simplicity but are available upon request. The results show that relative to non-adoption (D0R0Z0), adopting either row planting only (D0R1Z0) or zero tillage only (D0R0Z1) significantly reduces maize yields by 80 kg/acre and 94 kg/acre, respectively. One possible explanation for this phenomenon is that smallholder maize farmers in Ghana fail to adopt row planting and zero tillage appropriately, resulting in yield losses. Furthermore, the common practice of slash-and-burn agriculture among Ghana’s rural farmers can have a negative impact on soil performance, resulting in lower yields.
In comparison, adopting any two combinations of CSA technologies significantly increases maize yields. For example, relative to non-adoption (D0R0Z0), adopting drought-resistant seeds and row planting (D1R1Z0) together significantly increases maize yields by 208 kg/acre, and adopting drought-resistant seeds and zero tillage (D1R0Z1) significantly increases maize yields by 153 kg/acre. The yield effect is the largest when adopting all three technologies together. Specifically, relative to non-adoption (D0R0Z0), the adoption of all three technologies (D1R1Z1) significantly increases maize yields by 548 kg/acre.
The results that estimate the treatment effects of CSA technology adoption on net farm income are presented in the last column of Table 4. The results provide some interesting insights. When a single CSA technology is adopted, row planting has the largest impact on net farm income (D0R1Z0). Relative to non-adoption (D0R0Z0), adopting row planting (D0R1Z0) significantly increases net farm income by 643 GHS/acre. When farmers combine two of the three CSA technologies, row planting and zero tillage (D0R1Z1) adoption have the largest impact of any CSA technology adoption option, increasing net farm income by 2078 GHS/acre. Relative to non-adoption (D0R0Z0), adoption of all three CSA technologies (D1R1Z1) significantly increases net farm income by 815 GHS/acre, and the impact is the second largest among all CSA technology options. Our findings corroborate with the recent findings (Amadu et al. 2020; Oduniyi and Chagwiza 2021; Setsoafia et al. 2022), highlighting that the adoption of multiple agricultural innovations has greater impacts on farm performance than the adoption of a single innovation.
5.3 Additional estimations
To ensure the robustness of our findings, we conducted an additional analysis using ordinary least squares (OLS) to estimate the impact of CSA technology adoption on maize yields and net farm income. The results are presented in Table 7 in the Appendix. The estimates reveal that the intensity of CSA adoption is associated with a 2.1% increase in maize yields and an 11.9% increase in net farm income. These findings provide valuable insights into the relationship between the intensity of CSA technology adoption and smallholder maize farmers’ maize yields and net farm income. Nevertheless, we emphasize here the OLS regression cannot account for the endogeneity related to the CSA technology adoption variable, and it tends to generate biased estimates regarding the impacts of CSA adoption intensity. Therefore, the results obtained from the MESR model should be considered more reliable and comprehensive in understanding the association between CSA technology adoption, maize yields, and the net farm income of smallholder maize farmers.
6 Conclusions, implications, and limitations
The research and development community and governments are increasingly promoting the adoption of CSA technology to enhance food security and alleviate poverty among smallholder farmers in developing nations. We used random sampling to gather data from a sample of 3197 farmers to evaluate the concurrent adoption and effects of CSA technology in Ghana. The MESR model and OLS regressions were used to assess the impact of CSA adoption on maize yields and net farm income. While the OLS model estimates provide insight into the impact of CSA adoption on maize yields and net farm income, the model does not adequately address the endogeneity problem associated with the CSA technology adoption variable. Therefore, the MESR was utilized to account for potential selection bias arising from both observed and unobserved factors, and hence, the results from this model are used for our analysis.
According to the treatment effects estimates, integrating any CSA technology or adopting all three CSA technologies will greatly enhance maize yields and net farm income. Furthermore, our results showed that the adoption of all three CSA technologies has the largest impact on maize yields, while row planting and zero tillage have the greatest impact on net farm income. Most importantly, our findings suggest that smallholder farmers in Ghana and other developing areas in Sub-Saharan Africa should combine CSA technologies rather than use them separately to reap the greatest benefits from the essential synergistic effects of CSA technologies.
The MESR model has identified several factors influencing smallholder farmers’ decisions to adopt multiple CSA technologies. These factors include farmer-based organization (FBO) membership, education, access to land, market access, and production shocks such as perceived pest and disease stress and drought. The findings suggest that enhanced institutional and policy measures are necessary to remove barriers that prevent smallholder farmers from adopting multiple CSA technologies. For instance, the implications of FBO membership, education, and extension services highlight the importance of governments working with farmer-based groups to improve extension services and educate farmers about the benefits of CSA technologies through radio programs and extension services. Through these channels, the likelihood of smallholder farmers adopting multiple CSA technologies will likely increase, which will provide greater benefits.
The study has three limitations that need to be addressed in future research. Firstly, the analysis was unable to capture the adoption and impacts of CSA technology adoption over time because only cross-sectional data was available. When panel data is available, future studies should explore the dynamic relationship between CSA technology adoption, farm performance, and household welfare. Secondly, this study only considered three CSA technologies (row planting, zero tillage, and drought-resistant seeds) because farmers in Ghana are heavily encouraged to use these three technologies to combat the effects of climate change and variability. However, CSA technology adoption is context-specific to the local environment, and some farmers may adopt more than three CSA technologies. Therefore, more studies focusing on other CSA technologies and other countries could be carried out to improve our understanding of this field. Lastly, further studies should examine the intensity of CSAs on household welfare to understand better the impact of CSA technology adoption on household welfare.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from Bright Asante upon request.
References
AGRA (2017) Africa agriculture status report: the business of smallholder agriculture in Sub-Saharan Africa. Nairobi, Kenya: Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA). Issue No. 5. Retrieved from: https://agra.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/Final-AASR-2017-Aug-28.pdf. Accessed Aug 2023
Ahmed MH (2022) Impact of improved seed and inorganic fertilizer on maize yield and welfare: evidence from Eastern Ethiopia. J Agric Food Res 7:100266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafr.2021.100266
Amadu FO, Mcnamara PE, Miller DC (2020) Understanding the adoption of climate-smart agriculture: a farm-level typology with empirical evidence from southern Malawi. World Dev 126:104692. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2019.104692
Anang BT, Amikuzuno J (2015) Factors influencing pesticide use in smallholder rice production in Northern Ghana. Agric For Fish 4:77. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.aff.20150402.19
Antwi-Agyei P, Amanor K (2023) Typologies and drivers of the adoption of climate smart agricultural practices by smallholder farmers in rural Ghana. Curr Res Environ Sustain 5:100223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crsust.2023.100223
Asante BO, Addai KN, Prah S, et al (2023) Hand pollination, mass spraying, and hybrid seedlings: do these technologies affect the welfare of smallholder cocoa farmers in Ghana? Rev Dev Econ 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/rode.13014
Atta-Aidoo J, Antwi-Agyei P, Dougill AJ et al (2022) Adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices by smallholder farmers in rural Ghana: an application of the theory of planned behavior. PLOS Clim 1:e0000082. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pclm.0000082
Ayal M, Negash R, Abebe A (2018) Determinants of adoption of Teff row planting practice: the case of Baso Liben Woreda, East Gojjam Zone, Amhara Region, Ethopia. 6: 16–22. https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcrar.2018.610.003
Bese D, Zwane E, Cheteni P (2021) The use of sustainable agricultural methods amongst smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape province, South Africa. African J Sci Technol Innov Dev 13:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1080/20421338.2020.1724388
Bopp C, Engler A, Poortvliet PM, Jara-Rojas R (2019) The role of farmers’ intrinsic motivation in the effectiveness of policy incentives to promote sustainable agricultural practices. J Environ Manage 244:320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.04.107
Cattaneo MD (2010) Efficient semiparametric estimation of multi-valued treatment effects under ignorability. J Econom 155:138–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeconom.2009.09.023
Czyżewski B, Polcyn J, Brelik A (2022) Political orientations, economic policies, and environmental quality: multi-valued treatment effects analysis with spatial spillovers in country districts of Poland. Environ Sci Policy 128:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2021.11.001
Danso-Abbeam G, Baiyegunhi LJS (2018) Welfare impact of pesticides management practices among smallholder cocoa farmers in Ghana. Technol Soc 54:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2018.01.011
Di Falco S, Veronesi M, Yesuf M (2011) Does adaptation to climate change provide food security? A micro-perspective from Ethiopia. Am J Agric Econ 93:825–842. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajae/aar006
Ehiakpor DS, Danso-Abbeam G, Mubashiru Y (2021) Adoption of interrelated sustainable agricultural practices among smallholder farmers in Ghana. Land Use Policy 101:105142
Faye JB, Hopple AM, Bridgham SD (2021) Indigenous farming practices increase millet yields in Senegal, West Africa. Agroecol Sustain Food Syst 45:159–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/21683565.2020.1815927
Fentie A, Beyene AD (2019) Climate-smart agricultural practices and welfare of rural smallholders in Ethiopia: does planting method matter? Land Use Policy 85:387–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.04.020
Fisher M, Abate T, Lunduka RW et al (2015) Drought tolerant maize for farmer adaptation to drought in sub-Saharan Africa: determinants of adoption in eastern and southern Africa. Clim Change 133:283–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-015-1459-2
Food and Agriculture Organization (2019) The state of food and agriculture 2019. Moving forward on food loss and waste reduction. Rome. Retrieved from: https://www.fao.org/3/ca6030en/ca6030en.pdf. Accessed June 2023
Gebre GG, Mawia H, Makumbi D, Rahut DB (2021) The impact of adopting stress-tolerant maize on maize yield, maize income, and food security in Tanzania. Food Energy Secur 10:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.313
Gebremariam G, Wünscher T (2016) Combining sustainable agricultural practices pays off: evidence on welfare effects from Northern Ghana. African Association of Agricultural Economists (AAAE). http://dx.doi.org/10.22004/ag.econ.246452
Ghana Statistical Services (2021) Ghana 2021 population and housing census: population regions and districts. General report, vol 3A. Retrieved from: https://statsghana.gov.gh/gssmain/fileUpload/pressrelease/2021%20PHC%20General%20Report%20Vol%203A_Population%20of%20Regions%20and%20Districts_181121.pdf. Accessed Aug 2023
Grabowski PP, Kerr JM, Haggblade S, Kabwe S (2016) Determinants of adoption and disadoption of minimum tillage by cotton farmers in eastern Zambia. Agric Ecosyst Environ 231:54–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.06.027
Guo S, Guo E, Zhang Z et al (2022) Impacts of mean climate and extreme climate indices on soybean yield and yield components in Northeast China. Sci Total Environ 838:156284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156284
Jones EO, Tham-Agyekum EK, Ankuyi F et al (2023) Mobile agricultural extension delivery and climate-smart agricultural practices in a time of a pandemic: evidence from southern Ghana. Environ Sustain Indic 19:100274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indic.2023.100274
Kankam-Boadu I, Sarkodie-Addo J, Amagloh FK (2018) Profitability of maize production in the Northern Region of Ghana. Artic Int J Dev Res 8:22861–22869
Kassie M, Jaleta M, Shiferaw B et al (2013) Adoption of interrelated sustainable agricultural practices in smallholder systems: evidence from rural Tanzania. Technol Forecast Soc Change 80:525–540
Kassie M, Teklewold H, Jaleta M et al (2015) Understanding the adoption of a portfolio of sustainable intensification practices in eastern and southern Africa. Land Use Policy 42:400–411
Keil A, D’souza A, McDonald A (2017) Zero-tillage is a proven technology for sustainable wheat intensification in the Eastern Indo-Gangetic Plains: what determines farmer awareness and adoption? Food Secur 9:723–743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-017-0707-x
Khonje MG, Manda J, Mkandawire P et al (2018) Adoption and welfare impacts of multiple agricultural technologies: evidence from eastern Zambia. Agric Econ (united Kingdom) 49:599–609. https://doi.org/10.1111/agec.12445
Kimathi SM, Ayuya OI, Mutai B (2021) Adoption of climate-resilient potato varieties under partial population exposure and its determinants: case of smallholder farmers in Meru County, Kenya. Cogent Food Agric 7. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311932.2020.1860185
Li J, Ma W, Zhu H (2024) A systematic literature review of factors influencing the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices. Springer, Netherlands
Liu M, Min S, Ma W, Liu T (2021) The adoption and impact of E-commerce in rural China: application of an endogenous switching regression model. J Rural Stud 83:106–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2021.02.021
Lu W, Addai KN, Ng’ombe JN (2021) Does the use of multiple agricultural technologies affect household welfare? Evidence from Northern Ghana. Agrekon 60:370–387. https://doi.org/10.1080/03031853.2021.1992290
Ma W, Wang X (2020) Internet use, sustainable agricultural practices and rural incomes: evidence from China. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 64:1087–1112. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12390
Ma W, Zheng H (2021) Heterogeneous impacts of information technology adoption on pesticide and fertiliser expenditures: evidence from wheat farmers in China*. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 66:72–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12446
Ma W, Vatsa P, Zheng H, Guo Y (2022) Learning to eat from others: does nutritional information acquired from peers affect nutrition intake? Journal of Rural Studies. 95:449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrurstud.2022.09.023
Makate C, Makate M, Mango N, Siziba S (2019) Increasing resilience of smallholder farmers to climate change through multiple adoption of proven climate-smart agriculture innovations. Lessons from Southern Africa. J Environ Manage 231:858–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.069
Manda J, Alene AD, Gardebroek C et al (2016) Adoption and impacts of sustainable agricultural practices on maize yields and incomes: evidence from rural Zambia. J Agric Econ 67:130–153. https://doi.org/10.1111/1477-9552.12127
Manda J, Gardebroek C, Kuntashula E, Alene AD (2018) Impact of improved maize varieties on food security in Eastern Zambia: a doubly robust analysis. Rev Dev Econ 22:1709–1728. https://doi.org/10.1111/rode.12516
Manda J, Alene AD, Tufa AH et al (2020a) Market participation, household food security, and income: the case of cowpea producers in northern Nigeria. Food Energy Secur 9:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.211
Manda J, Khonje MG, Alene AD et al (2020b) Does cooperative membership increase and accelerate agricultural technology adoption? Empirical evidence from Zambia. Technol Forecast Soc Change 158:120160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120160
Martey E, Etwire PM, Kuwornu JKM (2020) Economic impacts of smallholder farmers’ adoption of drought-tolerant maize varieties. Land Use Policy 94:104524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104524
Martey E, Etwire PM, Mockshell J (2021) Climate-smart cowpea adoption and welfare effects of comprehensive agricultural training programs. Technol Soc 64:101468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101468
Mossie WA (2022) The impact of climate-smart agriculture technology on productivity: does row planting matter? Evidence from Southern Ethiopia. Sci World J 2022:. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3218287
Ng’ombe JN, Kalinda TH, Tembo G (2017) Does adoption of conservation farming practices result in increased crop revenue? Evidence from Zambia. Agrekon 56:205–221
Nguyen-Van P, Poiraud C, To-The N (2017) Modeling farmers’ decisions on tea varieties in Vietnam: a multinomial logit analysis. Agric Econ (united Kingdom) 48:291–299. https://doi.org/10.1111/agec.12334
Oparinde LO (2021) Fish farmers’ welfare and climate change adaptation strategies in southwest, Nigeria: application of multinomial endogenous switching regression model. Aquac Econ Manag 25:450–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/13657305.2021.1893863
Quarshie PT, Abdulai S, Fraser EDG (2023) (Re)assessing Climate-Smart Agriculture practices for sustainable food systems outcomes in sub-Saharan Africa: the case of Bono East Region, Ghana. Geogr Sustain 4:112–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geosus.2023.02.002
Setimela PS, Magorokosho C, Lunduka R et al (2017) On-farm yield gains with stress-tolerant maize in eastern and Southern Africa. Agron J 109:406–417. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2015.0540
Setsoafia ED, Ma W, Renwick A (2022) Effects of sustainable agricultural practices on farm income and food security in northern Ghana. Agric Food Econ 10:. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40100-022-00216-9
Simtowe F, Marenya P, Amondo E, et al (2019) Heterogeneous seed access and information exposure: implications for the adoption of drought-tolerant maize varieties in Uganda. Agric Food Econ 7:. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40100-019-0135-7
Sova CA, Grosjean G, Baedeker T, Nguyen T. N, Wallner M, Jarvis, A, Nowak A, Corner-Dolloff C, Girvetz, E, Laderach P, Lizarazo M (2018) Bringing the concept of climate-smart agriculture to life: Insights from CSA country profiles across Africa, Asia, and latin America.” World bank, and the international centre for tropical agriculture, Washington, DC. Retrieved from: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/agriculture/publication/bringing-the-concept-ofclimate-smart-agriculture-to-life. Accessed Aug 2023
Tabe-Ojong MP, Aihounton GBD, Lokossou JC (2023) Climate-smart agriculture and food security: cross-country evidence from West Africa. Glob Environ Chang 81:102697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2023.102697
Tanti PC, Jena PR, Aryal JP, Rahut DB (2022) Role of institutional factors in climate-smart technology adoption in agriculture: evidence from an Eastern Indian state. Environ Challenges 7:100498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2022.100498
Teklewold H, Mekonnen A (2017) The tilling of land in a changing climate: empirical evidence from the Nile Basin of Ethiopia. Land Use Policy 67:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.06.010
Teklewold H, Kassie M, Shiferaw B, Köhlin G (2013) Cropping system diversification, conservation tillage and modern seed adoption in Ethiopia: impacts on household income, agrochemical use and demand for labor. Ecol Econ 93:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2013.05.002
Tetteh Quarshie P, Abdulai AR, Duncan E et al (2023) Myth or reality? The Digitalization of Climate-Smart Agriculture (DCSA) practices in smallholding agriculture in the Bono East Region of Ghana. Clim Risk Manag 42:100553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crm.2023.100553
Vatsa P, Ma W, Zheng H, Li J (2023) Climate-smart agricultural practices for promoting sustainable agrifood production: yield impacts and implications for food security. Food Policy 121:102551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodpol.2023.102551
Wakweya RB (2023) Challenges and prospects of adopting climate-smart agricultural practices and technologies: implications for food security. J Agric Food Res 14:100698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafr.2023.100698
Xie H, Huang Y (2021) Influencing factors of farmers’ adoption of pro-environmental agricultural technologies in China: meta-analysis. Land Use Policy 109:105622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105622
Yu L, Chen C, Niu Z et al (2021) Risk aversion, cooperative membership and the adoption of green control techniques: evidence from China. J Clean Prod 279:123288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123288
Zhang S, Sun Z, Ma W, Valentinov V (2020) The effect of cooperative membership on agricultural technology adoption in Sichuan. China China Econ Rev 62:101334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2019.101334
Zheng H, Ma W, Li G (2021) Adoption of organic soil amendments and its impact on farm performance: evidence from wheat farmers in China*. Aust J Agric Resour Econ 65:367–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8489.12406
Zhou X, Ma W, Renwick A, Li G (2020) Off-farm work decisions of farm couples and land transfer choices in rural China. Appl Econ 52:6229–6247. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2020.1788709
Zhou X, Ma W, Zheng H, et al (2023) Promoting banana farmers’ adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices: the role of agricultural cooperatives. Clim Dev 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2023.2218333
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the extension staff of the Ministry of Food and Agriculture in the study districts for their delightful support during the data collection.
Funding
Open Access funding enabled and organized by CAUL and its Member Institutions
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Asante, B.O., Ma, W., Prah, S. et al. Farmers’ adoption of multiple climate-smart agricultural technologies in Ghana: determinants and impacts on maize yields and net farm income. Mitig Adapt Strateg Glob Change 29, 16 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-024-10114-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11027-024-10114-8