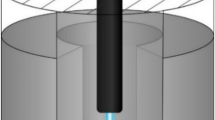
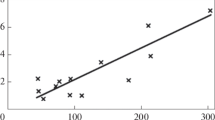
This article examines aspects of the propagation of heat flows in an arc furnace operated with different types of graphite electrodes: standard (solid) electrodes and electrodes with an axial opening. There are certain distinctive features to the formation of the electric arc at the end of the electrode when it contains such an opening. A model is constructed to calculate the heat flows in the system comprised of the arc, the bath, and the furnace’s working space. The data obtained from modeling show that charging pellets into the furnace through electrodes with axial openings makes it possible to intensify the steelmaking operation, increase the efficiency of the arcs, reduce oxidation-related losses of metal under the electrodes, and improve the energy-engineering indices of the production process.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. I. Trakhimovich and A. G. Shalimov, The Use of Direct-Reduced Iron in Steel Production, Metallurgiya, Moscow (1982).
E. E. Merker, “Energy-saving conditions for refining metallized pellets in the bath of an arc furnace,” Chern. Metall.: Byull. NTiEI, No. 1(1297), 35–39 (2008).
A. V. Sazonov, E. E. Merker, and A. I. Kochetov, “Study of the oxidation and heating of metal during the refining of pellets in an arc furnace,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Chern. Metall., No. 9, 67–68 (2008).
S. G. Bratchikov, B. Sh. Statnikov, V. V. Volkov, et al., “Calculation and analysis of heat transfer during the refining of pellets in an EAF. Report No. 1,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Chern. Metall., No. 12, 92–95 (1981).
E. E. Merker, E. A. Chermenev, and A. V. Sazonov, “Study of the efficiency of the electrical refining of metallized pellets charged continuously into the bath of an arc furnace,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Chern. Metall., No. 5, 14–17 (2012).
A. V. Sazonov, E. E. Merker, and E. A. Chermenev, “Intensification of the refining of pellets by charging them into the zone of the slag-metal melt affected directly by the electric arc of an EAF,” Chern. Metall.: Byull. NTiEI, No. 8, 62–64 (2011).
E. E. Merker, V. V. Fedina, A. I. Kochetov, et al., “Energy-saving regime for refining metallized pellets in a 150-ton EAF,” Elektrometallurgiya, No. 9, 43–44 (2003).
E. E. Merker, A. V. Sazonov, and A. A. Grishin, “Features of a technology for the electrical refining of metallized pellets in the bath of an arc furnace,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Chern. Metall., No. 2, 31–33 (2008).
V. A. Arutyunov, V. V. Bukhmirov, and S. A. Krupennikov, Mathematical Modeling of the Thermal Performance of Industrial Furnaces: Textbook, Metallurgiya, Moscow (1990).
E. E. Merker and G. A. Karpenko, Patent No. 2476603 RF, C21C5/52, “Method of making steel in an arc furnace,” subm. 06.14.2011, publ. 02.27.2013, Byull., No. 6.
E. E. Merker, G. A. Karpenko, and E. A. Chermenev, Patent No. 2487172 RF, C21C5/52, “Method of charging metallized pellets into an arc furnace,” subm. 11.02.2011, publ. 07.10.2013, Byull., No. 9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Metallurg, No. 10, pp. 32–36, October, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merker, E.E., Chermenev, E.A. Mathematical Model of Heat-Flow Distribution in an Electric-Arc Furnace When the Arc is Formed at the End of a Tubular Flux-Cored Electrode. Metallurgist 58, 859–865 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-015-0008-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11015-015-0008-6