Abstract
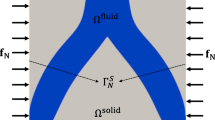
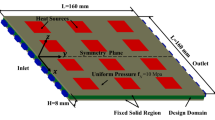
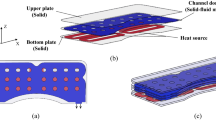
This paper designs a water-cooled pseudo 3D heat sink structure using two-layer heat sink model applying the topology optimization method (TOM) based on rational approximation of material properties (RAMP) functions. The governing equations consist of the continuity, Navier–Stokes, and energy balance equations with forced convection and the optimization design problem is formulated as the minimization of power dissipation and thermal resistance. Compared with the one-layer heat sink model in terms of optimized design, temperature distribution and velocity distribution, the two-layer heat sink model was proved to have better heat transfer capability because it does not ignore the resistance in fluid channel regions. The optimized heat sink structure is manufactured, and measured about temperature distributions on the upper surface of the heat sink and pressure drop between inlet and outlet. Through the comparison of temperature distribution and pressure drop between numerical results and experimental tests under different spacial position and Reynolds numbers, the physical validity of the developed model is verified.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuckerman DB, Pease RFW (1981) High-performance heat sinking for VLSI. IEEE Electron Device Lett 2(5):126–129
Liu S, Zhang Y, Liu P (2006) Heat transfer and pressure drop in fractal microchannel heat sink for cooling of electronic chips. Int J Heat Mass Transf 44(2):221–227
Bendsøe MP, Kikuch N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech 71(2):197–224
Gersborg-Hansen A, Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2006) Topology optimization of heat conduction problems using the finite volume method. Struct Multidisc Optim 31(2):251–259
Bruns TE (2007) Topology optimization of convection-dominated, steady-state heat transfer problems. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50(15–16):2859–2873
Borrval T, Petersson J (2003) Topology optimization of fluids in Stokes flow. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 41(2):77–107
Aage N, Poulsen TH, Gersborg-Hansen A (2008) Topology optimization of large scale Stokes flow problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 35(2):175–180
Gersborg-Hansen A, Sigmund O, Haber R (2005) Topology optimization of channel flow problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 30(2):181–192
Olesen LH, Okkels F, Bruus H (2006) A high-level programming-language implementation of topology optimization applied to steady-state Navier–Stokes flow. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65:975–1001
Pingen G, Egrafov A, Maute K (2007) Topology optimization of flow domains using the lattice Boltzmann method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 34(6):507–524
Sigmund O (2001) Design of multiphysics actuators using topology optimization—part I: one-material structures. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(49):6577–6604
Adham AM, Mohd-Ghazalia N, Ahmad R (2013) Thermal and hydrodynamic analysis of microchannel heat sinks. A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 21(C):614–622
Dede EM (2009) Multiphysics topology optimization of heat transfer and fluid flow systems. COMSOL Conference
Yoon GH (2010) Topological design of heat dissipating structure with forced convective heat transfer. Int J Mech Sci 24(6):1225–1233
Marck G, Nemer M, Harion JL (2013) Topology optimization of heat and mass transfer problems: laminar flow. Numer Heat Transf Part B 63(6):508–539
Alexandersen J, Sigmund O, Aage N (2016) Large scale three-dimensional topology optimisation of heat sinks cooled by natural convection. Int J Heat Mass Transf 100:876–891
Dilgen SB, Dilgen CB, Fuhrman DR, Sigmund O (2018) Density based topology optimization of turbulent flow heat transfer systems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 57(5):1905–1918
Koga AA, Lopes ECC, Villa Nova HF, De Lima CRD, Silva ECN (2013) Development of heat sink device by using topology optimization. Int J Heat Mass Transf 64:759–772
Li H, Ding X, Fz M, Dl J, Xiong M (2019) Optimal design and thermal modelling for liquid-cooled heat sink based on multi-objective topology optimization: an experimental and numerical study. Int J Heat Mass Transf 144:1–18
Li H, Pan S, Ding X, Dl J, Xiong M (2019) Experimental and numerical investigation of liquid-cooled heat sinks designed by topology optimization. Int J Therm Sci 146:1–8
McConnell C, Georg P (2012) Multi-layer, pseudo 3D thermal topology optimization of heat sinks. ASME Int Mech Eng Congr Expo Proc (IMECE) 7(D):2381–2392
Haertel JHK, Engelbrecht K, Lazarov BS, Sigmund O (2018) Topology optimization of a pseudo 3D thermofluid heat sink model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 121:1073–1088
Suna Y, Fengwen W, Jun H (2019) Topology optimization of microchannel heat sinks using a two-layer model. Int J Heat Mass Transf 143:1–16
Kays W, Crawford M (1993) Convective heat and mass transfer, 3rd edn. Tata McGraw-Hill Education, New York
Zeng S, Kanargi B, Lee PS (2018) Experimental and numerical investigation of a mini channel forced air heat sink designed by topology optimization. Int J Heat Mass Transf 121:663–679
Alexandersen J, Niels A, Andreasen CS, Sigmund O (2014) Topology optimisation for natural convection problems. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 76(10):699–721
Lazarov BS, Sigmund O (2010) Filters in topology optimization based on Helmholtz-type differential equations. Int J Numer Methods Eng 86(6):765–781
Wang FW, Lazarov BS, Sigmund O (2011) On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(6):767–784
COMSOL Multiphysics 5.4 Reference Manual
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
Zhao J, Zhang M, Zhu Y, Cheng R, Wang L (2021) Topology optimization of planar cooling channels using a three-layer thermos-fluid model in fully developed laminar flow problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 63:2789–2809
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Commission under Grant Number 19-163-00-KX-002-016-02; Science and Technology Commission of Sichuan Province under Grant Number 2019YFG0335.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no known conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Fu, Y., Yang, X. et al. A pseudo 3D cooling heat sink model designed by multi-objective topology optimization method. Meccanica 57, 2101–2116 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-022-01554-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-022-01554-0