Abstract
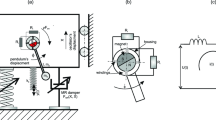
This paper demonstrates that vibration mitigation and energy harvesting can be achieved simultaneously by using of an electricity-generating from autoparametric vibration absorber system (AVAS) and non-ideal system (NIS). The NIS consists of a simple portal frame excited by a small dc motor with eccentric mass, with limited power supply and located on the top. The AVAS consists of a cantilever beam with tip mass parallel coupled to NIS. A piezoelectric material is considered for energy harvesting installed in the base of the AVAS and an electric circuit is connected to the piezoelectric material in order to produce voltage output. Several numerical simulations were carried out focusing on the passage through the resonance of NIS, when the motor rotational frequency is near the portal frame natural frequency and when the non-ideal subsystem frequency is approximately twice the absorber beam frequency (two-to-one internal resonance). The results showed the existence of Sommerfeld effect in NIS and saturation phenomenon in the NIS–AVAS.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nayfeh AH (2000) Nonlinear interactions: analytical, computational, and experimental methods. Wiley, New York
Haxton RS, Barr ADS (1972) The autoparametric vibration absorber. J Eng Ind 94(1):119–125. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3428100
Rocha RT (2016) On saturation phenomenon in energy harvesting based on nonlinear piezoelectric materials coupled to a portal frame foundation with ideal and non-ideal excitations. Ph.D. Dissertation, 2016
Preumont A (2006) Mechatronics: dynamics of electromechanical and piezoelectric systems, vol 136. Springer, Berlin
Priya S, Inman DJ (2009) Energy harvesting technologies, vol 21. Springer, New York
Erturk A, Hoffmann J, Inman DJ (2009) A piezomagnetoelastic structure for broadband vibration energy harvesting. Appl Phys Lett 94(25):254102. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3159815
Erturk A, Inman DJ (2011) Piezoelectric energy harvesting. Wiley, Hoboken
Litak G, Friswell MI, Kwuimy CAK, Adhikari S, Borowiec M (2012) Energy harvesting by two magnetopiezoelastic oscillators with mistuning. Theor Appl Mech Lett 2(4):043009. https://doi.org/10.1063/2.1204309
Stephen NG (2006) On energy harvesting from ambient vibration. J Sound Vib 293(1):409–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physd.2010.01.019
Kononenko VO (1969) Vibrating systems with limited power supply. Illife Books, London
Balthazar JM, Mook DT, Weber HI, Brasil RMLRF, Fenili A, Belato D, Felix JLP (2003) An overview on non-ideal vibrations. Meccanica 38(6):613–621. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025877308510
Felix JLP, Balthazar JM, Brasil RMLRF (2009) Comments on nonlinear dynamics of a non-ideal Duffing–Rayleigh oscillator: numerical and analytical approaches. J Sound Vib 319(3):1136–1149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2008.06.036
Warminski J, Balthazar JM, Brasil RMLRF (2001) Vibrations of a non-ideal parametrically and self-excited model. J Sound Vib 245(2):363–374. https://doi.org/10.1006/jsvi.2000.3515
Samantaray AK, Dasgupta SS, Bhattacharyya R (2010) Sommerfeld effect in rotationally symmetric planar dynamical systems. Int J Eng Sci 48(1):21–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijengsci.2009.06.005
Nayfeh AH, Mook DT (2008) Nonlinear oscillations. Wiley, Hoboken
Bisoi A, Samantaray AK, Bhattacharyya R (2017) Control strategies for DC motors driving rotor dynamic systems through resonance. J Sound Vib 411:304–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2017.09.014
Bisoi A, Samantaray AK, Bhattacharyya R (2018) Sommerfeld effect in a two-disk rotor dynamic system at various unbalance conditions. Meccanica 53(4–5):681701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-017-0757-3
Bisoi A, Samantaray AK, Bhattacharyya R (2017) Sommerfeld effect in a gyroscopic overhung rotor-disk system. Nonlinear Dyn 88(3):1565–1585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3329-0
Balthazar JM, Tusset AM, Brasil RMLRF, Felix JLP, Rocha RT, Janzen FC, Nabarrete A, Oliveira C (2018) An overview on the appearance of the Sommerfeld effect and saturation phenomenon in non-ideal vibrating systems (NIS) in macro and MEMS scales. Nonlinear Dyn 93:19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4126-0
Palacios JLP, Balthazar JM, Brasil RMLRF (2002) On non-ideal and non-linear portal frame dynamics analysis using bogoliubov averaging method. J Braz Soc Mech Sci 24(4):257–265. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-73862002000400002
Brasil RMLRF, Garzeri FJ, Balthazar JM (2001) An experimental study of the nonlinear dynamics of a portal frame foundation for a non-ideal motor. In: Proceedings of DETC01 ASME 2001 design engineering technical conference and computers and information in engineering conference, pp 9–12
Rocha RT, Balthazar JM, Quinn DD, Tusset AM, Felix JLP (2016, August). Non-ideal system with quadratic nonlinearities containing a two-to-one internal resonance. In: ASME 2016 international design engineering technical conferences and computers and information in engineering conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, pp V008T10A015–V008T10A015. https://doi.org/10.1115/DETC2016-59372
Felix JLP, Balthazar JM, Brasil RMLRF (2005) On saturation control of a non-ideal vibrating portal frame foundation type shear-building. J Vib Control 11(1):121–136. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546305047656
Oueini SS, Nayfeh AH, Golnaraghi MF (1997) A theoretical and experimental implementation of a control method based on saturation. Nonlinear Dyn 13(2):189–202. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008207124935
Oueini SS (1999) Techniques for controlling structural vibrations. Ph.D. Thesis
Pai PF, Schulz MJ (2000) A refined nonlinear vibration absorber. Int J Mech Sci 42(3):537–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7403(98)00135-0
Pai PF, Wen B, Naser AS, Schulz MJ (1998) Structural vibration control using PZT patches and non-linear phenomena. J Sound Vib 215(2):273–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7403(98)00135-0
Haddow AG, Barr ADS, Mook DT (1984) Theoretical and experimental study of modal interaction in a two-degree-of-freedom structure. J Sound Vib 97(3):451–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-460X(84)90272-4
Bux SL, Roberts JW (1986) Non-linear vibratory interactions in systems of coupled beams. J Sound Vib 104(3):497–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-460X(86)90304-4
Hamed YS, Amer YA (2014) Nonlinear saturation controller for vibration supersession of a nonlinear composite beam. J Mech Sci Technol 28(8):2987–3002. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0706-1
Xu J, Chen Y, Chung KW (2015) An improved time-delay saturation controller for suppression of nonlinear beam vibration. Nonlinear Dyn 82(4):1691–1707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2270-3
Balthazar JM, Rocha RT, Brasil RMFL, Tusset AM, de Pontes BR, Silveira M (2014) Mode saturation, mode coupling and energy harvesting from ambient vibration in a portal frame structure. In: ASME 2014 international design engineering technical conferences and computers and information in engineering conference. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, pp V008T11A044–V008T11A044. https://doi.org/10.1115/DETC2014-34268
Rocha RT, Balthazar JM, Tusset AM, Piccirillo V, Felix JLP (2016) Comments on energy harvesting on a 2:1 internal resonance portal frame support structure, using a nonlinear-energy sink as a passive controller. Int Rev Mech Eng (IREME) 10(3):147–156. https://doi.org/10.15866/ireme.v10i3.8795
Iliuk I, Balthazar JM, Tusset AM, Piqueira JRC, de Pontes BR, Felix JLP, Bueno AM (2013) A non-ideal portal frame energy harvester controlled using a pendulum. Eur Phys J Spec Top 222(7):1575–1586. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01946-4
Iliuk I, Balthazar JM, Tusset AM, Piqueira JR, de Pontes BR, Felix JLP, Bueno AM (2014) Application of passive control to energy harvester efficiency using a nonideal portal frame structural support system. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 25(4):417–429. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X13500570
Lee WK, Cho DS (2000) Damping effect of a randomly excited autoparametric system. J Sound Vib 236(1):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1006/jsvi.2000.2965
Sado D, Kot M (2007) Chaotic vibration of an autoparametrical system with a non-ideal source of power. J Theor Appl Mech 45(1):119–131
Mitura A, Kecik K (2016) Influences of system parameters on energy harvesting from autoparametric absorber. Numerical research. Vib Phys Syst 27:281–286
Kecik K, Borowiec M (2013) An autoparametric energy harvester. Eur Phys J Spec Top 222(7):1597–1605. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2013-01948-2
Erturk A, Renno JM, Inman DJ (2009) Modeling of piezoelectric energy harvesting from an L-shaped beam-mass structure with an application to UAVs. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 20(5):529–544. https://doi.org/10.1177/1045389X08098096
Harne RL, Sun A, Wang KW (2016) Leveraging nonlinear saturation-based phenomena in an L-shaped vibration energy harvesting system. J Sound Vib 363:517531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2015.11.017
Cao DX, Leadenham S, Erturk A (2015) Internal resonance for nonlinear vibration energy harvesting. Eur Phys J Spec Top 224:28672880. https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2015-02594-4
Jia Y, Seshia AA (2014) An auto-parametrically excited vibration energy harvester. Sens Actuators A 220:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2014.09.012
Sodano HA, Park G, Inman DJ (2004) Estimation of electric charge output for piezoelectric energy harvesting. Strain 40(2):49–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-1305.2004.00120.x
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support by FAPERGS, CNPq, CAPES and FAPESP, all Brazilian research funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felix, J.L.P., Balthazar, J.M., Rocha, R.T. et al. On vibration mitigation and energy harvesting of a non-ideal system with autoparametric vibration absorber system. Meccanica 53, 3177–3188 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-018-0881-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-018-0881-8