Abstract
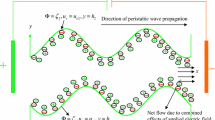
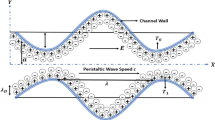
A theoretical study is presented of peristaltic hydrodynamics of an aqueous electrolytic non-Newtonian Jeffrey bio-rheological fluid through an asymmetric microchannel under an applied axial electric field. An analytical approach is adopted to obtain the closed form solution for velocity, volumetric flow, pressure difference and stream function. The analysis is also restricted under the low Reynolds number assumption (Stokes flow) and lubrication theory approximations (large wavelength). Small ionic Peclét number and Debye–Hückel linearization (i.e. wall zeta potential ≤ 25 mV) are also considered to simplify the Nernst–Planck and Poisson–Boltzmann equations. Streamline plots are also presented for the different electro-osmotic parameter, varying magnitudes of the electric field (both aiding and opposing cases) and for different values of the ratio of relaxation to retardation time parameter. Comparisons are also included between the Newtonian and general non-Newtonian Jeffrey fluid cases. The results presented here may be of fundamental interest towards designing lab-on-a-chip devices for flow mixing, cell manipulation, micro-scale pumps etc. Trapping is shown to be more sensitive to an electric field (aiding, opposing and neutral) rather than the electro-osmotic parameter and viscoelastic relaxation to retardation ratio parameter. The results may also help towards the design of organ-on-a-chip like devices for better drug design.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brasseur JG, Corrsin S, Lu NQ (1987) The influence of a peripheral layer of different viscosity on peristaltic pumping with Newtonian fluids. J Fluid Mech 174:495–519
Rao AR, Usha S (1995) Peristaltic transport of two immiscible viscous fluids in a circular tube. J Fluid Mech 298:271–285
Misra J, Pandey S (1999) Peristaltic transport of a non-Newtonian fluid with a peripheral layer. Int J Eng Sci 37:1841–1858
Takagi D, Balmforth N (2011) Peristaltic pumping of viscous fluid in an elastic tube. J Fluid Mech 672:196–218
Aboelkassem Y, Staples AE (2013) Selective pumping in a network: insect-style microscale flow transport. Bioinspir Biomim 8:026004
Herzburn PA, Irvine RL, Malinowski KC (1985) Biological treatment of hazardous waste in sequencing batch reactors. J Water Pollut Control Fed 57:1163–1167
DeFlaun MF, Condee CW (1997) Electrokinetic transport of bacteria. J Hazard Mater 55:263–277
Jaffrin M, Shapiro A (1971) Peristaltic pumping. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 3:13–37
Pozrikidis C (1987) A study of peristaltic flow. J Fluid Mech 180:515–527
Hayat T, Ali N, Asghar S (2007) Hall effects on peristaltic flow of a Maxwell fluid in a porous medium. Phys Lett A 363:397–403
Wang Y, Hayat T, Ali N, Oberlack M (2008) Magnetohydrodynamic peristaltic motion of a Sisko fluid in a symmetric or asymmetric channel. Phys A Stat Mech Appl 387:347–362
Hina S, Hayat T, Alsaedi A (2012) Heat and mass transfer effects on the peristaltic flow of Johnson-Segalman fluid in a curved channel with compliant walls. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55:3511–3521
Mekheimer KS (2011) Non-linear peristaltic transport of a second-order fluid through a porous medium. Appl Math Model 35:2695–2710
Sutradhar A, Mondal JK, Murthy P, Gorla RSR (2016) Influence of starling’s hypothesis and joule heating on peristaltic flow of an electrically conducting Casson fluid in a permeable microvessel. J Fluids Eng 138:111106
Tripathi D, Bég OA (2014) Peristaltic propulsion of generalized Burgers’ fluids through a non-uniform porous medium: a study of chyme dynamics through the diseased intestine. Math Biosci 248:67–77
Abd-Alla A, Abo-Dahab S (2015) Magnetic field and rotation effects on peristaltic transport of a Jeffrey fluid in an asymmetric channel. J Magn Magn Mater 374:680–689
Tripathi D, Bég OA (2014) Mathematical modelling of peristaltic propulsion of viscoplastic bio-fluids. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part H J Eng Med 228:67–88
Mekheimer KS (2002) Peristaltic transport of a couple stress fluid in a uniform and non-uniform channels. Biorheology 39:755–765
Chakraborty S (2006) Augmentation of peristaltic microflows through electro-osmotic mechanisms. J Phys D Appl Phys 39:5356
Bandopadhyay A, Tripathi D, Chakraborty S (2016) Electroosmosis-modulated peristaltic transport in microfluidic channels. Phys Fluids 28:052002
Tripathi D, Bushan S, Beg O (2016) Analytical study of electroosmosis modulated capillary peristaltic hemodynamics. J Mech Med Biol (JMMB)
Goswami P, Chakraborty J, Bandopadhyay A, Chakraborty S (2016) Electrokinetically modulated peristaltic transport of power-law fluids. Microvasc Res 103:41–54
Shit GC, Ranjit NK, Sinha A (2016) Electro-magnetohydrodynamic flow of biofluid induced by peristaltic wave: a non-newtonian model. J Bionic Eng 13:436–448
Tripathi D, Bhushan S, Bég OA (2016) Transverse magnetic field driven modification in unsteady peristaltic transport with electrical double layer effects. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 506:32–39
Tripathi D, Yadav A, Bég OA (2017) Electro-kinetically driven peristaltic transport of viscoelastic physiological fluids through a finite length capillary: mathematical modeling. Math Biosci 283:155–168
Afonso A, Alves M, Pinho F (2009) Analytical solution of mixed electro-osmotic/pressure driven flows of viscoelastic fluids in microchannels. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 159:50–63
Das S, Chakraborty S (2006) Analytical solutions for velocity, temperature and concentration distribution in electroosmotic microchannel flows of a non-Newtonian bio-fluid. Anal Chim Acta 559:15–24
Zhao C, Yang C (2011) An exact solution for electroosmosis of non-Newtonian fluids in microchannels. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 166:1076–1079
Zhao C, Yang C (2013) Electroosmotic flows of non-Newtonian power-law fluids in a cylindrical microchannel. Electrophoresis 34:662–667
Zhao C, Yang C (2013) Electrokinetics of non-Newtonian fluids: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 201:94–108
Zhao M, Wang S, Wei S (2013) Transient electro-osmotic flow of Oldroyd-B fluids in a straight pipe of circular cross section. J Nonnewton Fluid Mech 201:135–139
Carpi F, Menon C, De Rossi D (2010) Electroactive elastomeric actuator for all-polymer linear peristaltic pumps. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 15:460–470
Wang C, Gao Y, Nguyen N-T, Wong TN, Yang C, Ooi KT (2005) Interface control of pressure-driven two-fluid flow in microchannels using electroosmosis. J Micromech Microeng 15:2289
Polson NA, Hayes MA (2000) Electroosmotic flow control of fluids on a capillary electrophoresis microdevice using an applied external voltage. Anal Chem 72:1088–1092
Ericson C, Holm J, Ericson T, Hjertén S (2000) Electroosmosis-and pressure-driven chromatography in chips using continuous beds. Anal Chem 72:81–87
Dutta P, Beskok A, Warburton TC (2002) Numerical simulation of mixed electroosmotic/pressure driven microflows. Numer Heat Transf Part A Appl 41:131–148
Gillespie D, Pennathur S (2013) Separation of ions in nanofluidic channels with combined pressure-driven and electro-osmotic flow. Anal Chem 85:2991–2998
Kothandapani M, Srinivas S (2008) Peristaltic transport of a Jeffrey fluid under the effect of magnetic field in an asymmetric channel. Int J Nonlinear Mech 43:915–924
Tripathi D, Pandey S, Anwar Bég O (2013) Mathematical modelling of heat transfer effects on swallowing dynamics of viscoelastic food bolus through the human oesophagus. Int J Therm Sci 70:41–53
Ellahi R, Bhatti MM, Pop I (2016) Effects of hall and ion slip on MHD peristaltic flow of Jeffrey fluid in a non-uniform rectangular duct. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow 26:1802–1820
Bhatti M, Ellahi R, Zeeshan A (2016) Study of variable magnetic field on the peristaltic flow of Jeffrey fluid in a non-uniform rectangular duct having compliant walls. J Mol Liq 222:101–108
Afonso AM, Alves MA, Pinho FT (2013) Analytical solution of two-fluid electro-osmotic flows of viscoelastic fluids. J Colloid Interface Sci 395:277–286
Afonso AM, Ferrás LL, Nóbrega JM, Alves MA, Pinho FT (2014) Pressure-driven electrokinetic slip flows of viscoelastic fluids in hydrophobic microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluidics 16(6):1131–1142
Ferrás LL, Afonso AM, Alves MA, Nóbrega JM, Pinho FT (2014) Analytical and numerical study of the electro-osmotic annular flow of viscoelastic fluids. J Colloid Interface Sci 420:152–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict interest among the authors listed in manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, D., Jhorar, R., Anwar Bég, O. et al. Electroosmosis modulated peristaltic biorheological flow through an asymmetric microchannel: mathematical model. Meccanica 53, 2079–2090 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-017-0795-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-017-0795-x