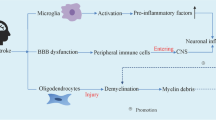
Abstract
Ischemic stroke is one of the most common and undertreated cerebral diseases with high mortality and disability rate. Various intrinsic and extrinsic factors regulate the onset, severity, and progression of ischemic stroke. As an integral part of the neuronal glia system, astrocytes provide many housekeeping functions in nervous system, and perform multiple functions both beneficial and detrimental for neuronal survival after ischemic stroke. In addition, the small GTPase Rho and its downstream Rho kinase (ROCK) are associated with various neuronal functions such as dendrite development, migration and axonal extension, and numerous central nervous system (CNS) diseases. The aim of this review is to summarize the role of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway and astrocytes on neurological function after ischemic stroke. We also discuss the interaction of RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway and astrocytes on the tissue repair after brain injury.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Akaneya Y, Tsumoto T, Kinoshita S, Hatanaka H (1997) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances long-term potentiation in rat visual cortex. J Neurosci 17:6707–6716
Alvarez-Buylla A, Ihrie RA (2014) Sonic hedgehog signaling in the postnatal brain. Semin Cell Dev Biol 33:105–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.05.008
Arvidsson A, Collin T, Kirik D, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2002) Neuronal replacement from endogenous precursors in the adult brain after stroke. Nat Med 8:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm747
Becerra-Calixto A, Cardona-Gomez GP (2017) The Role of Astrocytes in Neuroprotection after Brain Stroke: Potential in Cell Therapy. Front Mol Neurosci 10:88. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00088
Ben Haim L, Rowitch DH (2017) Functional diversity of astrocytes in neural circuit regulation. Nat Rev Neurosci 18:31–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.159
Bergami M, Santi S, Formaggio E, Cagnoli C, Verderio C, Blum R, Berninger B, Matteoli M, Canossa M (2008) Uptake and recycling of pro-BDNF for transmitter-induced secretion by cortical astrocytes. J Cell Biol 183:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200806137
Bidmon HJ, Jancsik V, Schleicher A, Hagemann G, Witte OW, Woodhams P, Zilles K (1998) Structural alterations and changes in cytoskeletal proteins and proteoglycans after focal cortical ischemia. Neuroscience 82:397–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00289-3
Bradbury EJ, Moon LD, Popat RJ, King VR, Bennett GS, Patel PN, Fawcett JW, McMahon SB (2002) Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature 416:636–640. https://doi.10.1038/416636a
Brea D, Sobrino T, Ramos-Cabrer P, Castillo J (2009) Reorganisation of the cerebral vasculature following ischaemia. Rev Neurol 49:645–654
Bryan BA, Dennstedt E, Mitchell DC, Walshe TE, Noma K, Loureiro R, Saint-Geniez M, Campaigniac JP, Liao JK, D’Amore PA (2010) RhoA/ROCK signaling is essential for multiple aspects of VEGF-mediated angiogenesis. FASEB J 24:3186–3195. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.09-145102
Burda JE, Bernstein AM, Sofroniew MV (2016) Astrocyte roles in traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 275(Pt 3):305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.03.020
Chen X, Hou XM, Fan YF, Jin YT, Wang YL (2016) Sonic hedgehog protein regulates fibroblast growth factor 8 expression in metanephric explant culture from BALB/c mice: Possible mechanisms associated with renal morphogenesis. Mol Med Rep 14:2929–2936. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5614
Chinchilla P, Xiao L, Kazanietz MG, Riobo NA (2010) Hedgehog proteins activate pro-angiogenic responses in endothelial cells through non-canonical signaling pathways. Cell Cycle 9:570–579. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.9.3.10591
Christie KJ, Turbic A, Turnley AM (2013) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis, Rho kinase inhibition and enhancement of neuronal survival. Neuroscience 247:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.019
Codega P, Silva-Vargas V, Paul A, Maldonado-Soto AR, Deleo AM, Pastrana E, Doetsch F (2014) Prospective identification and purification of quiescent adult neural stem cells from their in vivo niche. Neuron 82:545–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.02.039
Croft DR, Sahai E, Mavria G, Li S, Tsai J, Lee WM, Marshall CJ, Olson MF (2004) Conditional ROCK activation in vivo induces tumor cell dissemination and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64:8994–9001. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2052
Dai RL, Zhu SY, Xia YP, Mao L, Mei YW, Yao YF, Xue YM, Hu B (2011) Sonic hedgehog protects cortical neurons against oxidative stress. Neurochem Res 36:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0264-6
Dashti M, Peppelenbosch MP, Rezaee F (2012) Hedgehog signalling as an antagonist of ageing and its associated diseases. BioEssays 34:849–856. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201200049
Didangelos A, Iberl M, Vinsland E, Bartus K, Bradbury EJ (2014) Regulation of IL-10 by chondroitinase ABC promotes a distinct immune response following spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 34:16424–16432. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2927-14.2014
Ding J, Yu JZ, Li QY, Wang X, Lu CZ, Xiao BG (2009) Rho kinase inhibitor Fasudil induces neuroprotection and neurogenesis partially through astrocyte-derived G-CSF. Brain Behav Immun 23:1083–1088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2009.05.002
Du K, Zhao C, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhang KZ, Shen XY, Sun HX, Gao W, Lu X (2019) MiR-191 inhibit angiogenesis after acute ischemic stroke targeting VEZF1. Aging 11:2762–2786. https://doi.10.18632/aging.101948
Farhy-Tselnicker I, Allen NJ (2018) Astrocytes, neurons, synapses: a tripartite view on cortical circuit development. Neural Dev 13:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13064-018-0104-y
Feng GD, He BR, Lu F, Liu LH, Zhang L, Chen B, He ZP, Hao DJ, Yang H (2014) Fibroblast growth factor 4 is required but not sufficient for the astrocyte dedifferentiation. Mol Neurobiol 50:997–1012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8649-1
Gao L, Guan W, Wang M, Wang H, Yu J, Liu Q, Qiu B, Yu Y, Ping Y, Bian X, Shen L, Pei G (2017) Direct Generation of Human Neuronal Cells from Adult Astrocytes by Small Molecules. Stem Cell Rep 8:538–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.01.014
Haber M, Zhou L, Murai KK (2006) Cooperative astrocyte and dendritic spine dynamics at hippocampal excitatory synapses. J Neurosci 26:8881–8891. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1302-06.2006
Han YG, Spassky N, Romaguera-Ros M, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Aguilar A, Schneider-Maunoury S, Alvarez-Buylla A (2008) Hedgehog signaling and primary cilia are required for the formation of adult neural stem cells. Nat Neurosci 11:277–284. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn2059
He QW, Xia YP, Chen SC, Wang Y, Huang M, Huang Y, Li JY, Li YN, Gao Y, Mao L, Mei YW, Hu B (2013) Astrocyte-derived sonic hedgehog contributes to angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells via RhoA/ROCK pathway after oxygen-glucose deprivation. Mol Neurobiol 47:976–987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8396-8
He H, Huang M, Sun S, Wu Y, Lin X (2017) Epithelial heparan sulfate regulates Sonic Hedgehog signaling in lung development. PLoS Genet 13:e1006992. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006992
Hirota S, Liu Q, Lee HS, Hossain MG, Lacy-Hulbert A, McCarty JH (2011) The astrocyte-expressed integrin alphavbeta8 governs blood vessel sprouting in the developing retina. Development 138:5157–5166. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.069153
Jin K, Sun Y, Xie L, Peel A, Mao XO, Batteur S, Greenberg DA (2003) Directed migration of neuronal precursors into the ischemic cerebral cortex and striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:171–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1044-7431(03)00159-3
Kajihara H, Tsutsumi E, Kinoshita A, Nakano J, Takagi K, Takeo S (2001) Activated astrocytes with glycogen accumulation in ischemic penumbra during the early stage of brain infarction: immunohistochemical and electron microscopic studies. Brain Res 909:92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(01)02640-3
Kasai K, Takahashi M, Osumi N, Sinnarajah S, Takeo T, Ikeda H, Kehrl JH, Itoh G, Arnheiter H (2004) The G12 family of heterotrimeric G proteins and Rho GTPase mediate Sonic hedgehog signalling. Genes Cells 9:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1356-9597.2004.00701.x
Kawagishi H, Xiong J, Rovira II, Pan H, Yan Y, Fleischmann BK, Yamada M, Finkel T (2018) Sonic hedgehog signaling regulates the mammalian cardiac regenerative response. J Mol Cell Cardiol 123:180–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.09.005
Koyanagi M, Takahashi J, Arakawa Y, Doi D, Fukuda H, Hayashi H, Narumiya S, Hashimoto N (2008) Inhibition of the Rho/ROCK pathway reduces apoptosis during transplantation of embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors. J Neurosci Res 86:270–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21502
Lai K, Kaspar BK, Gage FH, Schaffer DV (2003) Sonic hedgehog regulates adult neural progenitor proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Nat Neurosci 6:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn983
Liepert J, Bauder H, Wolfgang HR, Miltner WH, Taub E, Weiller C (2000) Treatment-induced cortical reorganization after stroke in humans. Stroke 31:1210–1216. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.31.6.1210
Liu Z, Chopp M (2016) Astrocytes, therapeutic targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 144:103–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2015.09.008
Liu J, Wada Y, Katsura M, Tozawa H, Erwin N, Kapron CM, Bao G, Liu J (2018) Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase (ROCK) in molecular regulation of angiogenesis. Theranostics 8:6053–6069. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.30305
Maldonado H, Calderon C, Burgos-Bravo F, Kobler O, Zuschratter W, Ramirez O, Hartel S, Schneider P, Quest AF, Herrera-Molina R, Leyton L (2017) Astrocyte-to-neuron communication through integrin-engaged Thy-1/CBP/Csk/Src complex triggers neurite retraction via the RhoA/ROCK pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1864:243–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.11.006
Malone K, Amu S, Moore AC, Waeber C (2019) The immune system and stroke: from current targets to future therapy. Immunol Cell Biol 97:5–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/imcb.12191
Monnier PP, Sierra A, Schwab JM, Henke-Fahle S, Mueller BK (2003) The Rho/ROCK pathway mediates neurite growth-inhibitory activity associated with the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans of the CNS glial scar. Mol Cell Neurosci 22:319–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1044-7431(02)00035-0
Mukherjee N, Nandi S, Garg S, Ghosh S, Ghosh S, Samat R, Ghosh S (2020) Targeting chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans: an emerging therapeutic strategy to treat CNS injury. ACS Chem Neurosci 11:231–232. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.0c00004
Murakoshi H, Wang H, Yasuda R (2011) Local, persistent activation of Rho GTPases during plasticity of single dendritic spines. Nature 472:100–104. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09823
Nakabayashi H, Shimizu K (2011) HA1077, a Rho kinase inhibitor, suppresses glioma-induced angiogenesis by targeting the Rho-ROCK and the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK/ERK) signal pathways. Cancer Sci 102:393–399. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01794.x
Niu W, Zang T, Smith DK, Vue TY, Zou Y, Bachoo R, Johnson JE, Zhang CL (2015) SOX2 reprograms resident astrocytes into neural progenitors in the adult brain. Stem Cell Rep 4:780–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2015.03.006
Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E (1980) Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature 287:795–801. https://doi.org/10.1038/287795a0
Osborn LM, Kamphuis W, Wadman WJ, Hol EM (2016) Astrogliosis: An integral player in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 144:121–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.01.001
Peng T, Frank DB, Kadzik RS, Morley MP, Rathi KS, Wang T, Zhou S, Cheng L, Lu MM, Morrisey EE (2015) Hedgehog actively maintains adult lung quiescence and regulates repair and regeneration. Nature 526:578–582. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14984
Pola R, Ling LE, Silver M, Corbley MJ, Kearney M, Blake Pepinsky R, Shapiro R, Taylor FR, Baker DP, Asahara T, Isner JM (2001) The morphogen Sonic hedgehog is an indirect angiogenic agent upregulating two families of angiogenic growth factors. Nat Med 7:706–711. https://doi.org/10.1038/89083
Polizio AH, Chinchilla P, Chen X, Kim S, Manning DR, Riobo NA (2011) Heterotrimeric Gi proteins link Hedgehog signaling to activation of Rho small GTPases to promote fibroblast migration. J Biol Chem 286:19589–19596. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.197111
Rattner A, Williams J, Nathans J (2019) Roles of HIFs and VEGF in angiogenesis in the retina and brain. J Clin Invest 129:3807–3820. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI126655
Renault MA, Roncalli J, Tongers J, Thorne T, Klyachko E, Misener S, Volpert OV, Mehta S, Burg A, Luedemann C, Qin G, Kishore R, Losordo DW (2010) Sonic hedgehog induces angiogenesis via Rho kinase-dependent signaling in endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 49:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.05.003
Rossini PM, Calautti C, Pauri F, Baron JC (2003) Post-stroke plastic reorganisation in the adult brain. Lancet Neurol 2:493–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(03)00485-x
Sa-Pereira I, Brites D, Brito MA (2012) Neurovascular unit: a focus on pericytes. Mol Neurobiol 45:327–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8244-2
Scemes E, Suadicani SO, Spray DC (2000) Intercellular communication in spinal cord astrocytes: fine tuning between gap junctions and P2 nucleotide receptors in calcium wave propagation. The Journal of neuroscience: the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 20:1435–1445
Scott A, Powner MB, Gandhi P, Clarkin C, Gutmann DH, Johnson RS, Ferrara N, Fruttiger M (2010) Astrocyte-derived vascular endothelial growth factor stabilizes vessels in the developing retinal vasculature. PloS One 5:e11863. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011863
Shibuya M (2009) Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes: therapeutic aspects of vascular endothelial growth factor. FEBS J 276:4636–4643. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07175.x
Shin YJ, Kim HL, Park JM, Cho JM, Kim SY, Lee MY (2013) Characterization of nestin expression and vessel association in the ischemic core following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Cell Tissue Res 351:383–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-012-1538-x
Silver J, Miller JH (2004) Regeneration beyond the glial scar. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:146–156. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1326
Sofroniew MV (2009) Molecular dissection of reactive astrogliosis and glial scar formation. Trends Neurosci 32:638–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2009.08.002
Soleman S, Filippov MA, Dityatev A, Fawcett JW (2013) Targeting the neural extracellular matrix in neurological disorders. Neuroscience 253:194–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.08.050
Spadafora R, Gonzalez FF, Derugin N, Wendland M, Ferriero D, McQuillen P (2010) Altered fate of subventricular zone progenitor cells and reduced neurogenesis following neonatal stroke. Dev Neurosci 32:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1159/000279654
Stellwagen D, Malenka RC (2006) Synaptic scaling mediated by glial TNF-alpha. Nature 440:1054–1059. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04671
Stenzel D, Lundkvist A, Sauvaget D, Busse M, Graupera M, van der Flier A, Wijelath ES, Murray J, Sobel M, Costell M, Takahashi S, Fassler R, Yamaguchi Y, Gutmann DH, Hynes RO, Gerhardt H (2011) Integrin-dependent and -independent functions of astrocytic fibronectin in retinal angiogenesis. Development 138:4451–4463. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.071381
Tang X, Davies JE, Davies SJ (2003) Changes in distribution, cell associations, and protein expression levels of NG2, neurocan, phosphacan, brevican, versican V2, and tenascin-C during acute to chronic maturation of spinal cord scar tissue. J Neurosci Res 71:427–444. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.10523
Thier MC, Hommerding O, Panten J, Pinna R, Garcia-Gonzalez D, Berger T, Worsdorfer P, Assenov Y, Scognamiglio R, Przybylla A, Kaschutnig P, Becker L, Milsom MD, Jauch A, Utikal J, Herrmann C, Monyer H, Edenhofer F, Trumpp A (2019) Identification of Embryonic Neural Plate Border Stem Cells and Their Generation by Direct Reprogramming from Adult Human Blood Cells. Cell Stem Cell 24:166–182 e113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2018.11.015
Tonges L, Koch JC, Bahr M, Lingor P (2011) ROCKing regeneration: rho kinase inhibition as molecular target for neurorestoration. Front Mol Neurosci 4:39. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2011.00039
van der Meel R, Symons MH, Kudernatsch R, Kok RJ, Schiffelers RM, Storm G, Gallagher WM, Byrne AT (2011) The VEGF/Rho GTPase signalling pathway: a promising target for anti-angiogenic/anti-invasion therapy. Drug Discov Today 16:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2011.01.005
Wang C, Fong H, Huang Y (2015) Direct reprogramming of RESTing astrocytes. Cell Stem Cell 17:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2015.06.011
Washida N, Wakino S, Tonozuka Y, Homma K, Tokuyama H, Hara Y, Hasegawa K, Minakuchi H, Fujimura K, Hosoya K, Hayashi K, Itoh H (2011) Rho-kinase inhibition ameliorates peritoneal fibrosis and angiogenesis in a rat model of peritoneal sclerosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:2770–2779. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr012
Wen JY, Gao SS, Chen FL, Chen S, Wang M, Chen ZW (2019) Role of CSE-Produced H2S on cerebrovascular relaxation via RhoA-ROCK inhibition and cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:1565–1574. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00533
Xia YP, Dai RL, Li YN, Mao L, Xue YM, He QW, Huang M, Huang Y, Mei YW, Hu B (2012) The protective effect of sonic hedgehog is mediated by the phosphoinositide [corrected] 3-kinase/AKT/Bcl-2 pathway in cultured rat astrocytes under oxidative stress. Neuroscience 209:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.02.019
Xing C, Hayakawa K, Lok J, Arai K, Lo EH (2012) Injury and repair in the neurovascular unit. Neurol Res 34:325–330. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743132812Y.0000000019
Yang H, Liu C, Fan H, Chen B, Huang D, Zhang L, Zhang Q, An J, Zhao J, Wang Y, Hao D (2019) Sonic hedgehog effectively improves oct4-mediated reprogramming of astrocytes into neural stem cells. Mol Ther 27:1467–1482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.05.006
Yao PJ, Petralia RS, Mattson MP (2016) Sonic hedgehog signaling and hippocampal neuroplasticity. Trends Neurosci 39:840–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2016.10.001
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Cui L, Chen R, Zhang C, Li Y, He T, Zhu X, Shen Z, Dong L, Zhao J, Wen Y, Zheng X, Li P (2017) Salvianolic Acids for Injection (SAFI) promotes functional recovery and neurogenesis via sonic hedgehog pathway after stroke in mice. Neurochem Int 110:38–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.09.001
Funding
This study was funded by grants for teaching and research project of Hefei Technology College (No. 2019JYXM022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lu WZ and Wen JY: Participated in writing of the manuscript; Chen ZW: Participated in review design.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, W., Chen, Z. & Wen, J. RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway and astrocytes in ischemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis 36, 1101–1108 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00709-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00709-4