Abstract
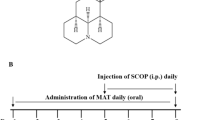
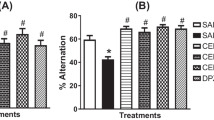
The present study evaluated the anti-amnesic activity of 1-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)-5-methyl-N-phenyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide (QTCA-1) against scopolamine (SCO)-induced amnesia in mice. It was evaluated cholinergic dysfunction, oxidative stress and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex and hippocampus of mice. Male Swiss mice were treated with QTCA-1 (10 mg/kg, intragastrically (i.g.), daily) for nine days. Thirty minutes after the treatment with compound, the animals received a injection of SCO (0.4 mg/kg, intraperitoneally (i.p.)). Mice were submitted to the behavioral tasks 30 min after injection of SCO (Barnes maze, open-field, object recognition and location, and step-down inhibitory avoidance tasks) during nine days. In day 9, cerebral cortex and hippocampus of mice were removed to determine the thiobarbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) levels, and catalase (CAT), Na+/K+-ATPase and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activities. SCO caused amnesia in mice for changing in step-down inhibitory avoidance, Barnes maze, and object recognition and object location tasks. QTCA-1 treatment attenuated the behavioral changes caused by SCO. Moreover, SCO increased AChE and CAT activities, decreased Na+/K+-ATPase activity and increased TBARS levels in the cerebral structures of mice. QTCA-1 protected against these brain changes. In conclusion, QTCA-1 had anti-amnesic action in the experimental model used in the present study, through the anticholinesterase effect, modulation of Na+/K+-ATPase activity and antioxidant action.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Ali EHA, Arafa NMS (2011) Comparative protective action of curcumin, memantine and diclofenac against scopolamine-induced memory dysfunction. Fitoterapia 82:601–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2011.01.016
Azman KF, Zakaria R, Abdul-Aziz C, Othman Z, Al-Rahbi B (2015) Tualang honey improves memory performance and decreases depressive-like behavior in rats exposed to loud noise stress. Noise Health 17:83–89. https://doi.org/10.4103/1463-1741.153388
Balaban H, Nazıroglu M, Demirci K, Övey IS (2016) The protective role of selenium on scopolamine-induced memory impairment, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in aged rats: the involvement of TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels. Mol Neurobiol 54:2852–2868. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9835-0
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chen W, Cheng X, Chen J, Yi X, Nie D, Sun X (2014) Lycium barbarum polysaccharides prevent memory and neurogenesis impairments in scopolamine-treated rats. PLoS One 9(2):e88076. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0088076
Cruz R, Almaguer MW, Bergado RJ (2002) Glutathione in cognitive function and neurodegeneration. Rev Neurol 36:877–886. https://doi.org/10.33588/rn.3609.2002395
da Silva FD, Pinz MP, de Oliveira RL, Rodrigues KC, Ianiski FR, Bassaco MM, Silveira CC, Jesse CR, Roman SS, Wilhelm EA, Luchese C (2017) Organosulfur compound protects against memory decline induced by scopolamine through modulation of oxidative stress and Na+/K+ ATPase activity in mice. Metab Brain Dis 6:1819–1828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0067-4
Dix SL, Aggleton JP (1999) Extending the spontaneous preference test of recognition:evidence of object location and object-context recognition. Behav Brain Res 99:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-4328(98)00079-5
Eduviere AT, Umukoro S, Aderibigbe AO, Ajayi AM, Adewole FA (2015) Methyl jasmonate enhances memory performance through inhibition of oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase activity in mice. Life Sci 132:20–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2015.04.007
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres JV, Featherstone MR (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Ferreira-Vieira HT, Guimaraes IM, Silva FR, Ribeiro FM (2016) Alzheimer's disease: targeting the cholinergic system. Curr Neuropharmacol 14:101–115. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X13666150716165726
Fiske CH, Subbarow YJ (1925) The calorimetic determination of phosphorus. Biol Chem 66:375–381
Freeman SE, Dawson RM (1991) Tacrine: a pharmacological review. Prog Neurobiol 36:255–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-0082(91)90002-I
Fukuda T, Ayabe T, Ohya R, Ano Y (2019) Matured hop bitter acids improve spatial working and object recognition memory via nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Psychopharmacology 236(9):2847–2854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05263-7
Guo C, Shen J, Meng Z, Yang X, Li F (2016) Neuroprotective effects of polygalacic acid on scopolamine-induced memory deficits in mice. Phytomedicine 23:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2015.12.009
Gutierres JM, Carvalho FB, Schetinger MRC, Agostinho P, MariscoPC VJM, Spanevello R (2014) Neuroprotective effect of anthocyanins on acetylcholinesterase activity and attenuation of scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 33:88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.12.006
Habiba R, Aamra M, Touqeer A (2017) Title: role of cholinergic receptors in memory retrieval. Depends on Gender and Age of Memory Behav Brain Res 331:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.05.017
Jiang HL, Wang X, Huang L, Luo Z, Su T, Ding K, Li X (2011) Benzenediol-berberine hybrids: multifunctional agents for Alzheimer's disease. Bioorg Med Chem 19:7228–7235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2011.09.040
Kim MS, Lee DY, Lee J, Kim HW, Sung SH, Han JS, Jeon WK (2018) Terminalia chebula extract prevents scopolamine-induced amnesia via cholinergic modulation and anti-oxidative effects in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med 18:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-018-2212-y
Kumar A, Singh A, Ekavali (2015) A review on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology and its management: an update. Pharmacol Rep 67:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2014.09.004
Libro RGS, Rajan ST, Bramanti P, Mazzon E (2016) Natural phytochemicals in the treatment and prevention of dementia: an overview. Molecules 21:1–38. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040518
Lin J, Ling H, Jie Y, Siying X, Jialing W, Jinrong Z, Xiaojun Y, Wei C, Shan H, Qinwen W (2016) Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid, reverses scopolamine-induced cognitive impairments in mice and inhibits acetylcholinesterase in vitro. Mar Drugs 14:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14040067
Lobo A, Launer LJ, Fratiglioni L, Andersen K, Di Carlo A, Breteler MMB, Soininen H (2000) Prevalence of dementia and major subtypes in Europe: a collaborative study of population-based cohorts. Neurology 54:4–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-9-55
Mancino AM, Hindo SS, Kochi A, Lim MH (2009) Effects of clioquinol on metal- triggered amyloid-b aggregation revisited. Inorg Chem 48:9596–9598. https://doi.org/10.1021/ic9014256
Martini F, Pesarico AP, Brüning CA, Zeni G, Nogueira CW (2018) Ebselen inhibits the activity of acetylcholinesterase globular isoform G4 in vitro and attenuates scopolamine-induced amnesia in mice. J Cell Biochem 119:5598–5608. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26731
Mattson MP, Pedersen WA, Duan W, Culmsee C, Camandola S (1999) Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying perturbed energy metabolism and neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci 893:154–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07824.x
Mazumder MK, Choudhury S, Borah A (2019) An in silico investigation on the inhibitory potential of the constituents of pomegranate juice on antioxidant defense mechanism: relevance to neurodegenerative diseases. IBRO Rep 6:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibror.2019.05.003
Mignani S, El Kazzouli S, Bousmina M, Majoral JP (2013) Expand classical drug administration ways by emerging routes using dendrimer drug delivery systems: a concise overview. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 10:1316–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2013.01.001
Nath C, Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Saxena G (2009) Cholinergic influence on memory stages: a study on scopolamine amnesic mice. Indian J Pharmacol 41:192–196. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7613.56072
Nelson PT, Head E, Schmitt FA, Davis PR, Neltner JH, Jicha GA, Abner EL, Smith CD, Van Eldik LJ, Kryscio RJ, Scheff SW (2011) Alzheimer’s disease is not “brain aging”: neuropathological, genetic, and epidemiological human studies. Acta Neuropathol 121:571–587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-011-0826-y
Ngoupaye GT, Pahaye DB, Ngondi J, Moto FCO, Bum EN (2017) Gladiolus dalenii lyophilisate reverses scopolamineinduced amnesia and reduces oxidative stress in rat brain. Biomed Pharmacother 91:350–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.061
Niedzielska E, Smaga I, Gawlik M, Moniczewski A, Stankowicz P, Pera J, Filip M (2016) Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol 53:4094–4125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9337-5
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Oz M, Lorke DE, Petroianu GA (2009) Methylene blue and Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Pharmacol 78:927–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2009
Pahaye DB, Bum EN, Taïwé GS, Ngoupaye GT, Sidiki S, Moto FCO, Kouemou N, Njapdounke NSJK, Nkantchoua G, Kandeda O, Mairaira V, Ojong JL (2017) Neuroprotective and antiamnesic effects of mitragyna inermis willd (Rubiaceae) on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Behav Neurol 2017:5952897. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/595289
Parent MB, Baxter MG (2004) Septohippocampal acetylcholine: involved in but not necessary for learning and memory? Learn Mem 11:9–20. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.69104
Pinz MP, Reis AS, Vogt AG, Krüger R, Alves D, Jesse CR, Roman SS, Soares MP, Wilhelm EA, Luchese C (2018) Current advances of pharmacological properties of 7-chloro-4-(phenylselanyl) quinoline: prevention of cognitive deficit and anxiety in Alzheimer’s disease model. Biomed Pharmacother 105:1006–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.049
Pompl PN, Mullan MJ, Bjugstad K, Arendash GW (1999) Adaptation of the circular platform spatial memory task for mice: use in detecting cognitive impairment in the APP(SW) transgenic mouse model for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Methods 87:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0270(98)00169-1
Puri A, Srivastava P, Pandey P, Yadav RS, Bhatt PC (2014) Scopolamine induced behavioral and biochemical modifications and protective effect of Celastrus paniculatous and Angelica glauca in rats. Int J Nutr Pharmacol Neurol Dis 4:158–169. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-0738.132675
Ritchie CW, Terrera GM, Quinn TJ (2015) Dementia trials and dementia tribulations: methodological and analytical challenges in dementia research. Alzheimers Res Ther 7:31–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-015-0113-6
Russell WMS, Burch RL (1959) The principles of humane experimental technique. Methuen, London
Sakaguchi M, Koseki M, Wakamatsu M, Matsumura E (2006) Effects of systemic administration of beta-casomorphin-5 on learning and memory in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 530:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.11.014
Sambon M, Napp A, Demelenne A, Vignisse J, Wins P, Fillet M, Bettendorff L (2019) Thiamine and benfotiamine protect neuroblastoma cells against paraquat and β-amyloid toxicity by a coenzyme-independent mechanism. Heliyon. 5:e01710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01710
Souza MA, Magni DV, Guerra GP, Oliveira MS, Furian AF, Pereira L, Marquez SV, Ferreira J, Fighera MR, Roves LFF (2012) Involvement of hippocampal CAMKII/CREB signaling in the spatial memory retention induced by creatine. Amino Acids 43:2491–2503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1329-4
Souza ACG, Brüning CA, Leite MR, Zeni G, Nogueira CW (2010) Diphenyl diselenide improves scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Behav Pharmacol 21:556–562. https://doi.org/10.1097/FBP.0b013e32833befcf
Stangherlin EC, Rocha JBT, Nogueira CW (2009) Diphenyl ditelluride impairs short term memory and alters neurochemical parameters in young rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:430–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2008.08.020
Tao S, Liu L, Shi L, Li X, Shen P, Xun Q, Guo X, Yu Z, Wang J (2015) Spatial learning and memory deficits in young adult mice exposed to a brief intense noise at postnatal age. J Otol 10:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joto.2015.07.001
Van de Vorst IE, Vaartjes I, Sinnecker LF, Beks LJM, Bots ML, Koel HL (2015) The validity of national hospital discharge register data on dementia: a comparative analysis using clinical data from a university medical Centre. Neth J Med 73:69–75
Walsh RN, Cummins RA (1976) Open-field test: critical review. Psychol Bull 83:482–504
Weon JB, Jung YS, Ma CJ (2016) Cognitive-enhancing effect of Dianthus superbus Var. Longicalycinus on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Biomol Ther 24:298–304. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2015.083
Wilhelm EA, Machado NC, Pedroso AB, Goldani BS, Seus N, Moura S, Savegnago L, Jacob RG, Alves D (2014) Organocatalytic synthesis and evaluation of 7-chloroquinoline-1,2,3-triazoylcarboxamides as potential antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory and anticonvulsant agent. RSC Adv 04:41437–41445. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20150239
World Health Organization (WHO) (2017). Global action plan on the public health response to dementia 2017–2025. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
Zemek F, Drtinova L, Nepovimova E, Sepsova V, Korabecny J, Klimes J, Kuca K (2014) Outcomes of Alzheimer’s disease therapy with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and memantine. Expert Opin Drug Saf 13:759–774. https://doi.org/10.1517/14740338.2014.914168
Zhang LN, Sun YJ, Pan S, Li JX, Qu YE, Li Y, Wang YL, Gao ZB (2013) Na+-K+-ATPase, a potent neuroprotective modulator against Alzheimer disease. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 27:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12000
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support and scholarships from the Brazilian agencies CNPq (UNIVERSAL 408874/2016-3), FAPERGS (PRONEM 16/2551-0000240-1, PRONUPEQ 16/2551-0000526-5 and PqG 17/2551-0001013-2). CNPq is also acknowledged for the fellowship to C.L., D.A. and E.A.W. This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível superior – Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luchese, C., Vogt, A.G., Pinz, M.P. et al. Amnesia-ameliorative effect of a quinoline derivative through regulation of oxidative/cholinergic systems and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in mice. Metab Brain Dis 35, 589–600 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00535-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00535-0