Abstract
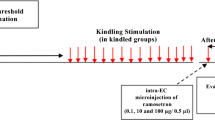
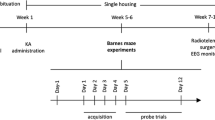
Numerous studies indicate that one of the bad effects of epilepsy is cognitive impairment. In this study we focused on the effect of LFS as a potential anticonvulsant agent, during epileptogenesis on cognitive impairments induced by amygdala kindling in rat. Twenty-one adult rats were divided into 3 groups including control (n = 7), kindled (n = 7), and Kindled+LFS (KLFS) (n = 7). Animals in the kindled group received kindling stimulation in a rapid kindling manner (a 3 s train of 50 Hz monophasic pulses of 1 ms duration, 12 times a day) in amygdala whereas control animals had no stimulation. Four packages of LFS (each package consisting of 200 monophasic square pulses, 0.1 ms pulse duration at 1 Hz) were applied daily after termination of kindling stimulation in KLFS group. Spatial memory of all animals was tested using radial arm maze after termination of stimulation on acquisition trial days and 14 days after the final acquisition trial test. Epileptogenesis process significantly increased working and reference memory error compared to control groups whereas application of LFS immediately after kindling stimulation prevented this impairment in 8 arm radial maze and there was no significant difference between KLS and control groups. Our results indicated that application of LFS during kindling acquisition suppresses memory impairment in epileptogenesis by kindling stimulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beldhuis HJ, Everts HG, Van der Zee EA, Luiten PG, Bohus B (1992) Amygdala kindling-induced seizures selectively impair spatial memory. 2. Effects on hippocampal neuronal and glial muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Hippocampus 2(4):411–419
Boison D (2006) Adenosine kinase, epilepsy and stroke: mechanisms and therapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27(12):652–658
Cain DP, Hargreaves EL, Boon F, Dennison Z (1993) An examination of the relations between hippocampal long-term potentiation, kindling, afterdischarge, and place learning in the water maze. Hippocampus 3(2):153–163
Da Silva FL, Gorter J, Wadman W (1986) Kindling of the hippocampus induces spatial memory deficits in the rat. Neurosci Lett 63(2):115–120
da Silva FL, Kamphuis W, Titulaer M, Vreugdenhil M, Wadman WJ (1995) An experimental model of progressive epilepsy: the development of kindling of the hippocampus of the rat. Ital J Neurol Sci 16(1–2):45–57
Dudek SM, Bear MF (1992) Homosynaptic long-term depression in area CA1 of hippocampus and effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89(10):4363–4367
Elger CE, Helmstaedter C, Kurthen M (2004) Chronic epilepsy and cognition. Lancet Neurol 3(11):663–672
Esmaeilpour K, Masoumi-Ardakani Y, Sheibani V, Shojaei A, Harandi SH, Mirnajafi-Zadeh J (2013) Comparing the anticonvulsant effects of low frequency stimulation of different brain sites on the amygdala kindling acquisition in rats. Basic Clin Neurosci 4(3):250–256
Feasey-Truger KL, Kargl G (1993) Differential effects of dentate kindling on working and reference spatial memory in the rat. Neurosci Lett 151(1):25–28
Gilbert TH, McNamara RK, Corcoran ME (1996) Kindling of hippocampal field CA1 impairs spatial learning and retention in the Morris water maze. Behav Brain Res 82(1):57–66
Gomez-Alonso JC, Andrade A (2005) On the definition of epileptic seizures and epilepsy. Epilepsia 46(10):1699–1700
Gomez-Alonso J, Giraldez B (2006) Epilepsy: a new definition for an old disease. Rev Neurol 45(2):126–127
Goodman JH, Berger RE, Tcheng TK (2005) Preemptive low-frequency stimulation decreases the incidence of amygdala-kindled seizures. Epilepsia 46(1):1–7
Gubellini P, Salin P, Kerkerian-Le Goff L, Baunez C (2009) Deep brain stimulation in neurological diseases and experimental models: from molecule to complex behavior. Prog Neurobiol 89(1):79–123
Hamed SA (2009) The aspects and mechanisms of cognitive alterations in epilepsy: the role of antiepileptic medications. CNS Neurosci Ther 15(2):134–156
Howland JG, Wang YT (2008) Synaptic plasticity in learning and memory: stress effects in the hippocampus. Prog Brain Res 169:145–158
Kirkwood A, Dudek SM, Gold JT, Aizenman CD, Bear MF (1993) Common forms of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus and neocortex in vitro. Science 260(5113):1518–1521
Klavir O, Genud-Gabai R, Paz R (2012) Low-frequency stimulation depresses the primate anterior-cingulate-cortex and prevents spontaneous recovery of aversive memories. J Neurosci 32(25):8589–8597
Leite JP, Neder L, Arisi GM, Carlotti CG Jr, Assirati JA, Moreira JE (2005) Plasticity, synaptic strength, and epilepsy: what can we learn from ultrastructural data? Epilepsia 46(5):134–141
Letty SM, Rondouin G (1995) Differential impairments of spatial memory and social behavior in two models of limbic epilepsy. Epilepsia 36(10):973–982
Leung LS, Shen B (1991) Hippocampal CA1 evoked response and radial 8-arm maze performance after hippocampal kindling. Brain Res 555(2):353–357
Leung LS, Shen B (2006) Hippocampal CA1 kindling but not long-term potentiation disrupts spatial memory performance. Learn Mem 13(1):18–26
Leung LS, Boon K, Kaibara T, Innis N (1990) Radial maze performance following hippocampal kindling. Behav Brain Res 40(2):119–129
Leung LS, Brzozowski D, Shen B (1996) Partial hippocampal kindling affects retention but not acquisition and place but not cue tasks on the radial arm maze. Behav Neurosci 110(5):1017–1024
Leung LS, Shen B, Sutherland R, Wu C, Wu K, Zhao D (1998) Long-lasting behavioral and electrophysiological effects induced by partial hippocampal kindling, in Kindling. Springer. 395–408
Malenka RC (1994) Synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus: LTP and LTD. Cell 78(4):535–538
McNamara RK, Kirkby RD, Corcoran ME (1992) Limbic seizures, but not kindling, reversibly impair place learning in the Morris water maze. Behav Brain Res 50(1):167–175
McNamara RK, Duncan Kirkby R, dePape GE, Skelton RW, Corcoran ME (1993) Differential effects of kindling and kindled seizures on place learning in the Morris water maze. Hippocampus 3(2):149–152
Mody I (1998) Synaptic plasticity in kindling. Adv Neurol 79:631–643
Motamedi G, Meador K (2003) Epilepsy and cognition. Epilepsy Behav 4:25–38
Najm I, Wang Y, Shedid D, Lüders HO, Ng TC, Comair YG (1998) MRS metabolic markers of seizures and seizure-induced neuronal damage. Epilepsia 39(3):244–250
Olton DS, Wolf WA (1981) Hippocampal seizures produce retrograde amnesia without a temporal gradient when they reset working memory. Behav Neural Biol 33(4):437–452
Ozen LJ, Young NA, Koshimori Y, Teskey GC (2008) Low-frequency stimulation reverses kindling-induced neocortical motor map expansion. Neuroscience 153(1):300–307
Pascual-Leone A, Tormos JM, Keenan J, Tarazona F, Cañete C, Catalá MD (1998) Study and modulation of human cortical excitability with transcranial magnetic stimulation. J Clin Neurophysiol 15(4):333–343
Robinson GB, McNeill HA, Reed GD (1993) Comparison of the short-and long-lasting effects of perforant path kindling on radial maze learning. Behav Neurosci 107(6):988–995
Silva FL, Blanes W, Kalitzin SN, Parra J, Suffczynski P, Velis DN (2003) Epilepsies as dynamical diseases of brain systems: basic models of the transition between normal and epileptic activity. Epilepsia 44(12):72–83
Stan Leung LD, Shen B (1994) Long-lasting effects of partial hippocampal kindling on hippocampal physiology and function. Hippocampus 4(6):696–704
Velı́šek L, Velı́šková J, Stanton PK (2002) Low-frequency stimulation of the kindling focus delays basolateral amygdala kindling in immature rats. Neurosci Lett 326(1):61–63
Weiss SR, Eidsath A, Li XL, Heynen T, Post RM (1998) Quenching revisited: low level direct current inhibits amygdala-kindled seizures. Exp Neurol 154(1):185–192
Wichmann T, DeLong MR (2006) Deep brain stimulation for neurologic and neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuron 52(1):197–204
Willment KC, Golby A (2013) Hemispheric lateralization interrupted: material-specific memory deficits in temporal lobe epilepsy. Front Hum Neurosci 7:1–33
Winawer MR (2006) Phenotype definition in epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 8(3):462–476
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghotbeddin, Z., Moazedi, A.A., Yadollahpour, A. et al. Improving cognitive task in kindled rats by using low frequency stimulation during epileptogenesis. Metab Brain Dis 33, 1525–1531 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0260-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0260-0