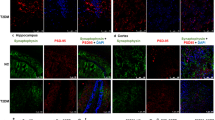
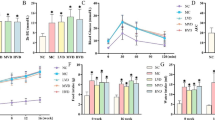
Abstract
Neuroinflammation is a key feature of cerebral complication which is associated with diabetes mellitus (DM). Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is implicated in the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation. However, how iNOS facilitates the development of inflammation in brain is still unidentified. The aim of the present study was to investigate the association of iNOS and neuroinflammation in diabetic mice, and elucidate the potential mechanisms underlying aminoguanidine (AG), the selective inhibitor of iNOS, protected neurons against inflammation in diabetic mice. In present experiment, diabetic mice model were established by a single intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin (STZ). AG was administered to diabetic mice for ten weeks after this disease induction. Then we measured iNOS activity in the serum and brain, detected the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ionised calcium binding adaptor molecule-1 (Iba-1) expressions in the brain. Moreover, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) in cytoplasm and nucleus were tested by IP and WB. Results revealed that high expression of iNOS in serum and brain could be reversed by AG treatment. Furthermore, AG could also inhibit GFAP and Iba-1 expressions, and NF-κB nuclear translocation by inhibiting it from binding to iNOS in cytoplasm. Our findings indicated that iNOS can combine with NF-κB in cytoplasm and promote its nuclear transfer in diabetic mice. Furthermore, AG decreased neuroinflammation through inhibiting iNOS activity and reducing NF-κB nuclear translocation by promoting its dissociation with iNOS in cytoplasm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellaver B, Souza DG, Souza DO, Quincozes-Santos A (2016) Hippocampal astrocyte cultures from adult and aged rats reproduce changes in glial functionality observed in the aging brain. Mol Neurobiol 54:2969–2985
Bloch K, Gil-Ad I, Tarasenko I, Vanichkin A, Taler M, Hornfeld SH, Vardi P, Weizman A (2015) Intracranial pancreatic islet transplantation increases islet hormone expression in the rat brain and attenuates behavioral dysfunctions induced by MK-801 (dizocilpine). Horm Behav 72:1–11
Cai Z, Zhao Y, Yao S, Bin Zhao B (2011) Increases in beta-amyloid protein in the hippocampus caused by diabetic metabolic disorder are blocked by minocycline through inhibition of NF-kappaB pathway activation. Pharmacol Rep 63:381–391
Cheng YS, Cong XD, Dai DZ, Zhang Y, Dai Y (2013) Argirein alleviates corpus cavernosum dysfunction by suppressing pro-inflammatory factors p66Shc and ER stress chaperone Bip in diabetic rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 65:94–101
Cheong MH, Lee SR, Yoo HS, Jeong JW, Kim GY, Kim WJ, Jung IC, Choi YH (2011) Anti-inflammatory effects of Polygala Tenuifolia root through inhibition of NF-kappaB activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells. J Ethnopharmacol 137:1402–1408
Chougala MB, Bhaskar JJ, Rajan MG, Salimath PV (2012) Effect of curcumin and quercetin on lysosomal enzyme activities in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Clin Nutr 31749-755
Datusalia AK, Sharma SS (2016) NF-kappaB inhibition resolves cognitive deficits in experimental type 2 diabetes mellitus through CREB and glutamate/GABA neurotransmitters pathway. Curr Neurovasc Res 13:22–32
Di Naso FC, Rodrigues G, Simoes Dias A, Porawski M, Fillmann H, Marroni NP (2012) Hepatic nitrosative stress in experimental diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat 26:378–381
Elahi M, Hasan Z, Motoi Y, Matsumoto SE, Ishiguro K, Hattori N (2016) Region-specific vulnerability to oxidative stress, Neuroinflammation, and tau hyperphosphorylation in experimental diabetes mellitus mice. J Alzheimers Dis 51:1209–1224
Fan J, Fan X, Li Y, Guo J, Xia D, Ding L, Zheng Q, Wang W, Xue F, Chen R, Liu S, Hu L, Gong Y (2016) Blunted inflammation mediated by NF-kappaB activation in hippocampus alleviates chronic normobaric hypoxia-induced anxiety-like behavior in rats. Brain Res Bull 122:54–61
Firouzjaei MA, Jafari MR, Eskandari M, Anarkoli IJ, Alipour M (2014) Aminoguanidine changes hippocampal expression of apoptosis-related genes, improves passive avoidance learning and memory in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34:343–350
Gu SM, Park MH, Hwang CJ, Song HS, Lee US, Han SB, Oh KW, Ham YW, Song MJ, Son DJ, Hong JT (2015) Bee venom ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced memory loss by preventing NF-kappaB pathway. J Neuroinflammation 12:124
Han L, Holscher C, Xue GF, Li G, Li D (2016) A novel dual-glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor agonist is neuroprotective in transient focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neuroreport 27:23–32
Hansen F, Battu CE, Dutra MF, Galland F, Lirio F, Broetto N, Nardin P, Gonçalves CA (2016) Methylglyoxal and carboxyethyllysine reduce glutamate uptake and S100B secretion in the hippocampus independently of RAGE activation. Amino Acids 48:375–385
Hu P, Thinschmidt JS, Caballero S, Adamson S, Cole L, Chan-Ling T, Grant MB (2015) Loss of survival factors and activation of inflammatory cascades in brain sympathetic centers in type 1 diabetic mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 308:E688–E698
Huang C, Lu X, Tong L, Wang J, Zhang W, Jiang B, Yang R (2015) Requirement for endogenous heat shock factor 1 in inducible nitric oxide synthase induction in murine microglia. J Neuroinflammation 12:189
Iizumi T, Takahashi S, Mashima K, Minami K, Izawa Y, Abe T, Hishiki T, Suematsu M, Kajimura M, Suzuki N (2016) A possible role of microglia-derived nitric oxide by lipopolysaccharide in activation of astroglial pentose-phosphate pathway via the Keap1/Nrf2 system. J Neuroinflammation 13:99
Jing L, He Q, Zhang JZ, Li PA (2013) Temporal profile of astrocytes and changes of oligodendrocyte-based myelin following middle cerebral artery occlusion in diabetic and non-diabetic rats. Int J Biol Sci 9:190–199
Li MY, Wang YY, Cao R, Hou XH, Zhang L, Yang RH, Wang F (2015) Dietary fish oil inhibits mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in diabetic rats by blocking nuclear factor-kappaB-mediated inflammatory pathways. J Nutr Biochem 26:1147–1155
Lind KR, Ball KK, Cruz NF, Dienel GA (2013) The unfolded protein response to endoplasmic reticulum stress in cultured astrocytes and rat brain during experimental diabetes. Neurochem Int 62:784–795
Liu YW, Zhu X, Zhang L, Lu Q, Zhang F, Guo H, Yin XX (2014) Cerebroprotective effects of ibuprofen on diabetic encephalopathy in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 117:128–136
Moreira TJ, Cebere A, Cebers G, Ostenson CG, Efendic S, Liljequist S (2007) Reduced HO-1 protein expression is associated with more severe neurodegeneration after transient ischemia induced by cortical compression in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1710–1723
Nardin P, Zanotto C, Hansen F, Batassini C, Gasparin MS, Sesterheim P, Gonçalves CA (2016) Peripheral levels of AGEs and astrocyte alterations in the hippocampus of STZ-diabetic rats. Neurochem Res 41:2006–2016
Park SB, Jung WH, Kang NS, Park JS, Bae GH, Kim HY, Rhee SD, Kang SK, Ahn JH, Jeong HG, Kim KY (2013) Anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effect of a novel selective 11beta-HSD1 inhibitor in the diet-induced obese mice. Eur J Pharmacol 721:70–79
Parthsarathy V, Holscher C (2013) The type 2 diabetes drug liraglutide reduces chronic inflammation induced by irradiation in the mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol 700:42–50
Quan Y, Du J, Wang X (2007) High glucose stimulates GRO secretion from rat microglia via ROS, PKC, and NF-kappaB pathways. J Neurosci Res 85:3150–3159
Reus GZ, Bernardini Dos Santos MA, Abelaira HM, Maciel AL, Arent CO, Matias BI, Bruchchen L, Ignácio ZM, Michels M, Dal-Pizzol F, Carvalho AF, Zugno AI, Quevedo J (2016) Antioxidant therapy alters brain MAPK-JNK and BDNF signaling path-ways in experimental diabetes mellitus. Curr Neurovasc Res 13:107–114
Richa R, Yadawa AK, Chaturvedi CM (2016) Hyperglycemia and high nitric oxide level induced oxidative stress in the brain and molecular alteration in the neurons and glial cells of laboratory mouse, Mus musculus. Neurochem Int S0197-0186:30505–30508
Salat K, Gdula-Argasinska J, Malikowska N, Podkowa A, Lipkowska A, Librowski T (2016) Effect of pregabalin on contextual memory deficits and inflammatory state-related protein expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 389:613–623
Shi S, Liang D, Chen Y, Xie Y, Wang Y, Wang L, Wang Z, Qiao Z (2016) Gx-50 reduces beta-amyloid-induced TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, NO, and PGE2 expression and inhibits NF-kappaB signaling in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Immunol 46:665–676
Valsecchi AE, Franchi S, Panerai AE, Rossi A, Sacerdote P, Colleoni M (2011) The soy isoflavone genistein reverses oxidative and inflammatory state, neuropathic pain, neurotrophic and vasculature deficits in diabetes mouse model. Eur J Pharmacol 650:694–702
van der Harg JM, Eggels L, Ruigrok SR, Hoozemans JJ, la Fleur SE, Scheper W (2015) Neuroinflammation is not a prerequisite for diabetes-induced tau phosphorylation. Front Neurosci 9:432
Wang L, Chen K, Liu K, Zhou Y, Zhang T, Wang B, Mi M (2015) DHA inhibited AGEs-induced retinal microglia activation via suppression of the PPARγ/NFκB pathway and reduction of signal transducers in the AGEs/RAGE axis recruitment into lipid rafts. Neurochem Res 40:713–722
Wang YY, Lin SY, Chuang YH, Sheu WH, Tung KC, Chen CJ (2014) Activation of hepatic inflammatory pathways by catecholamines is associated with hepatic insulin resistance in male ischemic stroke rats. Endocrinology 155:1235–1246
Wang SH, Sun ZL, Guo YJ, Yuan Y, Yang BQ (2009) Diabetes impairs hippocampal function via advanced glycation end product mediated new neuron generation in animals with diabetes-related depression. Toxicol Sci 111:72–79
Wei X, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Li H, Cheng L, Zhao X, Yin J, Wang G (2015) Hydrogen sulfide inhalation improves neurological outcome via NF-kappaB-mediated inflammatory pathway in a rat model of cardiac arrest and resuscitation. Cell Physiol Biochem 36:1527–1538
Wu WY, Wu YY, Huang H, He C, Li WZ, Wang HL, Chen HQ, Yin YY (2015) Biochanin a attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses and inhibits the activation of the MAPK pathway in BV2 microglial cells. Int J Mol Med 35:391–398
Xu L, Zhu J, Yin W, Ding X (2015) Astaxanthin improves cognitive deficits from oxidative stress, nitric oxide synthase and inflammation through upregulation of PI3K/Akt in diabetes rat. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:6083–6094
Yang CM, Lin CC, Hsieh HL (2016) High-glucose-derived oxidative stress-dependent Heme Oxygenase-1 expression from astrocytes contributes to the neuronal apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol 54:470–483
Yin Z, Yu H, Chen S, Ma C, Ma X, Xu L, Ma Z, Qu R, Ma S (2015) Asiaticoside attenuates diabetes-induced cognition deficits by regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway. Behav Brain Res 292:288–299
Ying CJ, Zhang F, Zhou XY, Hu XT, Chen J, Wen XR, Sun Y, Zheng KY, Tang RX, Song YJ (2015) Anti-inflammatory effect of Astaxanthin on the sickness behavior induced by diabetes mellitus. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35:1027–1037
Zhao L, Xu J, Wang Q, Qian Z, Feng W, Yin X, Fang Y (2015) Protective effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on brain ischemia/reperfusion damage in diabetic rats. Brain Res 1602:153–159
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81371300, 81501042, 81671208), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20150218), Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) and the Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province. The experiments in this article were completed in Research Facility Center for Morphology, and thanks the teachers Hongyan Dong, Ting Li, Honghua Yuan, Hongli Yu, Fuxing Dong, Zhiwei Liu, Qingli Huang and Meng Wang for their support and help during the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors state that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Zhang, F., Ying, C. et al. Inhibition of NF-κB activity by aminoguanidine alleviates neuroinflammation induced by hyperglycemia. Metab Brain Dis 32, 1627–1637 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0013-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-0013-5