Abstract
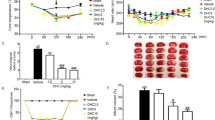
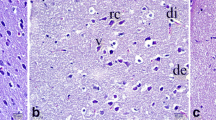
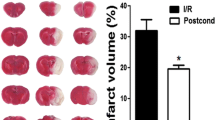
The aim of the study reported here was to evaluate whether the mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium (mitoKATP) channel could participate in the effect of dexmedetomidine on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) rats. Forty rats were randomly assigned into 5 groups: sham operation (S) group; cerebral I/R group; dexmedetomidine (D) group; 5-hydroxydecanoate (5-HD) group; 5-HD + D group. The cerebral I/R were produced by 2 h right middle cerebral artery occlusion followed by 24 h reperfusion. Dexmedetomidine (50μg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally before ischemia and after the onset of reperfusion. 5-HD (30 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally at 1 h before ischemia. The neurological deficit score (NDS) and the levels of super oxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), myeloperoxidase (MPO), Interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were evaluated. Compared to group S, NDS and the levels of MDA, MPO, IL-6 and TNF-α were significantly higher, and SOD levels were significantly lower in the other groups (P < 0.05). Compared to group I/R,NDS and the levels of MDA, MPO, IL-6 and TNF-α were significantly lower, and SOD level was significantly higher in group D (P < 0.05). Compared to group D, NDS and the levels of MDA, MPO, IL-6 and TNF-α were significantly higher, and SOD level was significantly lower in group5-HD + D (P < 0.05). The activation of the mitoKATP channel could contribute to the protective effect of dexmedetomidine on rats induced by focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Ahn MJ, Sherwood ER, Prough DS, Lin CY, DeWitt DS (2004) The effects of traumatic brain injury on cerebral blood flow and brain tissue nitric oxide levels and cytokine expression. J Neurotrauma 21:1431–1442
Bajgar R, Seetharaman S, Kowaltowski AJ, Garlid KD, Paucek P (2001) Identification and properties of a novel intracellular (mitochondrial) ATP-sensitive potassium channel in brain. J Biol Chem 276:33369–33374. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103320200
Barone FC, Arvin B, White RF, Miller A, Webb CL, Willette RN, Lysko PG, Feuerstein GZ (1997) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke 28:1233–1244. doi:10.1161/01.STR.28.6.1233
Bates B et al (2002) Neurotrophin-3 promotes cell death induced in cerebral ischemia, oxygen-glucose deprivation, and oxidative stress: possible involvement of oxygen free radicals. Neurobiol Dis 9:24–37. doi:10.1006/nbdi.2001.0458
Bradley PP, Priebat DA, Christensen RD, Rothstein G (1982) Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol 78:206–209
Clark WM, Rinker LG, Lessov NS, Hazel K, Eckenstein F (1999) Time course of IL-6 expression in experimental CNS ischemia. Neurol Res 21:287–292
Debska G, May R, Kicinska A, Szewczyk A, Elger CE, Kunz WS (2001) Potassium channel openers depolarize hippocampal mitochondria. Brain Res 892:42–50
del Zoppo GJ (2009) Inflammation and the neurovascular unit in the setting of focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 158:972–982. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.08.028
Graham SH, Chen J (2001) Programmed cell death in cerebral ischemia. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism : Official Journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 21:99–109. doi:10.1097/00004647-200102000-00001
Hagar H, Al Malki W (2014) Betaine supplementation protects against renal injury induced by cadmium intoxication in rats: role of oxidative stress and caspase-3. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:803–811. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2014.02.013
Halestrap AP (1994) Regulation of mitochondrial metabolism through changes in matrix volume. Biochem Soc Trans 22:522–529
Hanley PJ, Daut J (2005) K(ATP) channels and preconditioning: a re-examination of the role of mitochondrial K(ATP) channels and an overview of alternative mechanisms. J Mol Cell Cardiol 39:17–50. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2005.04.002
Hanley PJ et al (2005) 5-hydroxydecanoate is metabolised in mitochondria and creates a rate-limiting bottleneck for beta-oxidation of fatty acids. J Physiol 562:307–318. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2004.073932
Hoffman WE, Kochs E, Werner C, Thomas C, Albrecht RF (1991) Dexmedetomidine improves neurologic outcome from incomplete ischemia in the rat. Reversal by the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist atipamezole. Anesthesiology 75:328–332
Huang J, Upadhyay UM, Tamargo RJ (2006) Inflammation in stroke and focal cerebral ischemia. Surg Neurol 66:232–245. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2005.12.028
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M, Korthuis RJ (2012) Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 298:229–317. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-394309-5.00006-7
Kitamoto M et al (2011) Sairei-to ameliorates rat peritoneal fibrosis partly through suppression of oxidative stress nephron. Exp Nephrol 117:e71–e81. doi:10.1159/000321147
Kleemann R et al (2003) Rosuvastatin reduces atherosclerosis development beyond and independent of its plasma cholesterol-lowering effect in APOE*3-Leiden transgenic mice: evidence for antiinflammatory effects of rosuvastatin. Circulation 108:1368–1374. doi:10.1161/01.cir.0000086460.55494.af
Kontos HA (2001) Oxygen radicals in cerebral ischemia: the 2001 Willis lecture. Stroke; A J Cereb Circ 32:2712–2716
Liu T, Clark RK, McDonnell PC, Young PR, White RF, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (1994) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke; J Cereb Circ 25:1481–1488
Lu DQ, Chen Y, Li T, Li BL (2010) Role of protein kinase C in protecting rats against pulmonary ischemia reperfusion injury through opening of mitochondrial ATP sensitive potassium channel. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 41:436–440
Mao GX et al (2010) Salidroside protects human fibroblast cells from premature senescence induced by H(2)O(2) partly through modulating oxidative status. Mech Ageing Dev 131:723–731. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2010.10.003
Mao GX et al (2012) Antiaging effect of pine pollen in human diploid fibroblasts and in a mouse model induced by D-galactose. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2012:750963. doi:10.1155/2012/750963
Matsuo Y, Onodera H, Shiga Y, Nakamura M, Ninomiya M, Kihara T, Kogure K (1994) Correlation between myeloperoxidase-quantified neutrophil accumulation and ischemic brain injury in the rat. Effects of Neutrophil Depletion Stroke; J Cereb Circ 25:1469–1475
Pac-Soo CK, Mathew H, Ma D (2015) Ischaemic conditioning strategies reduce ischaemia/reperfusion-induced organ injury. Br J Anaesth 114:204–216. doi:10.1093/bja/aeu302
Rajapakse N, Shimizu K, Kis B, Snipes J, Lacza Z, Busija D (2002) Activation of mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels prevents neuronal cell death after ischemia in neonatal rats. Neurosci Lett 327:208–212
Rodriguez MJ, Martinez-Moreno M, Ortega FJ, Mahy N (2013) Targeting microglial K(ATP) channels to treat neurodegenerative diseases: a mitochondrial issue. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2013:194546. doi:10.1155/2013/194546
Sanderson TH, Reynolds CA, Kumar R, Przyklenk K, Huttemann M (2013) Molecular mechanisms of ischemia-reperfusion injury in brain: pivotal role of the mitochondrial membrane potential in reactive oxygen species generation. Mol Neurobiol 47:9–23. doi:10.1007/s12035-012-8344-z
Sheng H, Bart RD, Oury TD, Pearlstein RD, Crapo JD, Warner DS (1999) Mice overexpressing extracellular superoxide dismutase have increased resistance to focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 88:185–191
Sun H-s, Feng Z-p (2013) Neuroprotective role of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in cerebral ischemia. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34:24–32
Sun GY, Hu ZY (1995) Stimulation of phospholipase A2 expression in rat cultured astrocytes by LPS, TNF alpha and IL-1 beta. Prog Brain Res 105:231–238
Szewczyk A, Marbán E (1999) Mitochondria: a new target for K+ channel openers? Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:157–161. doi:10.1016/S0165-6147(99)01301-2
Tessier PA, Naccache PH, Clark-Lewis I, Gladue RP, Neote KS, McColl SR (1997) Chemokine networks in vivo: involvement of C-X-C and C-C chemokines in neutrophil extravasation in vivo in response to TNF-alpha. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 159:3595–3602
Uysal HY et al (2012) Preventive effect of dexmedetomidine in ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Craniofac Surg 23:1287–1291. doi:10.1097/SCS.0b013e3182519f24
Wang Q, Tang XN, Yenari MA (2007) The inflammatory response in stroke. J Neuroimmunol 184:53–68. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.11.014
Weston RM, Jones NM, Jarrott B, Callaway JK (2007) Inflammatory cell infiltration after endothelin-1-induced cerebral ischemia: histochemical and myeloperoxidase correlation with temporal changes in brain injury. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism : Official Journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 27:100–114. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600324
Wu L, Shen F, Lin L, Zhang X, Bruce IC, Xia Q (2006) The neuroprotection conferred by activating the mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channel is mediated by inhibiting the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Neurosci Lett 402:184–189. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2006.04.001
Xiong L, Zheng Y, Wu M, Hou L, Zhu Z, Zhang X, Lu Z (2003) Preconditioning with isoflurane produces dose-dependent neuroprotection via activation of adenosine triphosphateSS-regulated potassium channels after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Anesth Analg 96:233–237
Yang Z, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Jiang Y, Fang X, Xu J (2014) Sevoflurane postconditioning against cerebral ischemic neuronal injury is abolished in diet-induced obesity: role of brain mitochondrial KATP channels. Mol Med Rep 9:843–850. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.1912
Yilmaz G, Granger DN (2010) Leukocyte recruitment and ischemic brain injury. Neruomol Med 12:193–204. doi:10.1007/s12017-009-8074-1
Yu C, Mei XT, Zheng YP, Xu DH (2014) Zn(II)-curcumin protects against hemorheological alterations, oxidative stress and liver injury in a rat model of acute alcoholism. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:729–737. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2014.02.011
Zhao Z et al (2015) Pre-treatment of a single high-dose of atorvastatin provided cardioprotection in different ischaemia/reperfusion models via activating mitochondrial KATP channel. Eur J Pharmacol 751:89–98. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.01.036
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Department of Anesthesia, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, F., Fu, H., Sun, K. et al. Effect of dexmedetomidine on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats by activating mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Metab Brain Dis 32, 539–546 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9945-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9945-4