Abstract
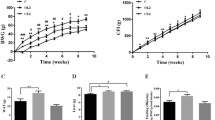
Mood disorder patients that are on long-term atypical antipsychotics treatment frequently experience metabolic dysfunctions. In addition to this, accumulating evidences points to increased risk of structural abnormalities, brain volume changes, altered neuroplasticity and behavioral depression with long-term antipsychotics use. However, there is paucity of preclinical evidences for long-term antipsychotic associated depression-like behavior. The objectives of the present study were: (1) to evaluate influence of long-term antipsychotic (olanzapine) treatment on rat behavior in forced swim test (FST) as a model for depression and; (2) to examine impact of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist liraglutide - an antidiabetic medication for type II diabetes, on long-term olanzapine associated metabolic and behavioral changes in rats. Daily olanzapine treatment (0.5 mg/kg; p.o.) for 8-9 weeks significantly increased body weights, food and water intake, plasma cholesterol and triglycerides and immobility time in FST with parallel reduction in plasma HDL cholesterol levels. These results points to development of metabolic abnormalities and depression-like behavior with long-term olanzapine treatment. Acute liraglutide (50 μg/kg; i.p.) and imipramine (10 mg/kg, i. p.) treatment per se significantly decreased duration of immobility in FST compared to vehicle treated rats. Additionally, 3-week liraglutide treatment (50 μg/kg; i.p., daily) partially reversed metabolic abnormalities and depression-like behavior with long-term olanzapine-treatment in rats. None of these treatment regimens affected locomotor behavior of rats. In summary, add-on GLP-1 receptor agonists promise novel alternatives to counteract long-term antipsychotics associated behavioral and metabolic complications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuirmeileh A, Harkavyi A, Rampersaud N, Lever R, Tadross JA, Bloom SR, Whitton PS (2012) Exendin-4 treatment enhances L-DOPA evoked release of striatal dopamine and decreases dyskinetic movements in the 6-hydoxydopamine lesioned rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 64:637–643
Agerso H, Jensen LB, Elbrond B, Rolan P, Zdravkovic M (2002) The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety and tolerability of NN2211, a new long-acting GLP-1 derivative, in healthy men. Diabetologia 45:195–202
Barnes TR, McPhillips MA (1995) How to distinguish between the neuroleptic-induced deficit syndrome, depression and disease-related negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 10(Suppl 3):115–121
Benedict C, Barclay JL, Ott V, Oster H, Hallschmid M (2013) Acute sleep deprivation delays the glucagon-like peptide 1 peak response to breakfast in healthy men. Nutr Diabetes 3:e78
Brunetti L, Orlando G, Recinella L, Leone S, Ferrante C, Chiavaroli A, Lazzarin F, Vacca M (2008) Glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36) amide (GLP-1) and exendin-4 stimulate serotonin release in rat hypothalamus. Peptides 29:1377–1381
Buckley PF (2001) Broad therapeutic uses of atypical antipsychotic medications. Biol Psychiatry 50:912–924
Caldwell CB, Gottesman II (1990) Schizophrenics kill themselves too: a review of risk factors for suicide. Schizophr Bull 16:571–589
Coccurello, R., Moles, A., 2010. A murine model of atypical antipsychotic-induced weight gain and metabolic dysregulation. Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. Chapter 9, Unit9.
Cohen D, Stolk RP, Grobbee DE, Gispen-de Wied CC (2006) Hyperglycemia and diabetes in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorders. Diabetes Care 29:786–791
De AR, Carney MW (1969) Severe depressive mood changes following slow-release intramuscular fluphenazine injection. Br Med J 3:564–567
De HM, Correll CU, Cohen D (2010) Do antipsychotic medications reduce or increase mortality in schizophrenia? a critical appraisal of the FIN-11 study. Schizophr Res 117:68–74
De HM, Dobbelaere M, Sheridan EM, Cohen D, Correll CU (2011) Metabolic and endocrine adverse effects of second-generation antipsychotics in children and adolescents: a systematic review of randomized, placebo controlled trials and guidelines for clinical practice. Eur Psychiatry 26:144–158
De HM, Detraux J, van WR, Yu W, Correll CU (2012) Metabolic and cardiovascular adverse effects associated with antipsychotic drugs. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8:114–126
Dean CE (2006) Antipsychotic-associated neuronal changes in the brain: toxic, therapeutic, or irrelevant to the long-term outcome of schizophrenia? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 30:174–189
Dickerson F, Brown CH, Fang L, Goldberg RW, Kreyenbuhl J, Wohlheiter K, Dixon L (2008) Quality of life in individuals with serious mental illness and type 2 diabetes. Psychosomatics 49:109–114
Dixit TS, Sharma AN, Lucot JB, Elased KM (2013) Antipsychotic-like effect of GLP-1 agonist liraglutide but not DPP-IV inhibitor sitagliptin in mouse model for psychosis. Physiol Behav 114–115:38–41
Ebdrup BH, Knop FK, Ishoy PL, Rostrup E, Fagerlund B, Lublin H, Glenthoj B (2012) Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs against antipsychotic-induced weight gain: potential physiological benefits. BMC Med 10:92
Egecioglu E, Steensland P, Fredriksson I, Feltmann K, Engel JA, Jerlhag E (2013) The glucagon-like peptide 1 analogue Exendin-4 attenuates alcohol mediated behaviors in rodents. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38:1259–1270
Erreger K, Davis AR, Poe AM, Greig NH, Stanwood GD, Galli A (2012) Exendin-4 decreases amphetamine-induced locomotor activity. Physiol Behav 106:574–578
Farilla L, Hui H, Bertolotto C, Kang E, Bulotta A, Di MU, Perfetti R (2002) Glucagon-like peptide-1 promotes islet cell growth and inhibits apoptosis in Zucker diabetic rats. Endocrinology 143:4397–4408
Farwell WR, Stump TE, Wang J, Tafesse E, L’Italien G, Tierney WM (2004) Weight gain and new onset diabetes associated with olanzapine and risperidone. J Gen Intern Med 19:1200–1205
Fell MJ, Anjum N, Dickinson K, Marshall KM, Peltola LM, Vickers S, Cheetham S, Neill JC (2007) The distinct effects of subchronic antipsychotic drug treatment on macronutrient selection, body weight, adiposity, and metabolism in female rats. Psychopharmacol Berl 194:221–231
Glick ID, Murray SR, Vasudevan P, Marder SR, Hu RJ (2001) Treatment with atypical antipsychotics: new indications and new populations. J Psychiatr Res 35:187–191
Gromada J, Holst JJ, Rorsman P (1998) Cellular regulation of islet hormone secretion by the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide 1. Pflugers Arch 435:583–594
Guedes EP, Madeira E, Mafort TT, Madeira M, Moreira RO, Mendonca LM, Godoy-Matos AF, Lopes AJ, Farias ML (2013) Body composition and depressive/anxiety symptoms in overweight and obese individuals with metabolic syndrome. Diabetol Metab Syndr 5:82
Harrow M, Grinker RR, Holzman PS, Kayton L (1977) Anhedonia and schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 134:794–797
Harrow M, Yonan CA, Sands JR, Marengo J (1994) Depression in schizophrenia: are neuroleptics, akinesia, or anhedonia involved? Schizophr Bull 20:327–338
Herbener ES, Harrow M (2002) The course of anhedonia during 10 years of schizophrenic illness. J Abnorm Psychol 111:237–248
Ho BC, Andreasen NC, Ziebell S, Pierson R, Magnotta V (2011) Long-term antipsychotic treatment and brain volumes: a longitudinal study of first-episode schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 68:128–137
Hoare E, Skouteris H, Fuller-Tyszkiewicz M, Millar L, Allender S (2014) Associations between obesogenic risk factors and depression among adolescents: a systematic review. Obes Rev 15:40–51
Isacson R, Nielsen E, Dannaeus K, Bertilsson G, Patrone C, Zachrisson O, Wikström L (2011) The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist exendin-4 improves reference memory performance and decreases immobility in the forced swim test. Eur J Pharmacol 650(1):249–255
Ishoy PL, Knop FK, Vilsboll T, Glenthoj BY, Ebdrup BH (2013) Sustained weight loss after treatment with a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist in an obese patient with schizophrenia and type 2 diabetes. Am J Psychiatry 170:681–682
Ishoy PL, Knop FK, Broberg BV, Baandrup L, Fagerlund B, Jorgensen NR, Andersen UB, Rostrup E, Glenthoj BY, Ebdrup BH (2014) Treatment of antipsychotic-associated obesity with a GLP-1 receptor agonist–protocol for an investigator-initiated prospective, randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blinded intervention study: the TAO study protocol. BMJ Open 4:e004158
Kalinichev M, Rourke C, Daniels AJ, Grizzle MK, Britt CS, Ignar DM, Jones DN (2005) Characterisation of olanzapine-induced weight gain and effect of aripiprazole vs olanzapine on body weight and prolactin secretion in female rats. Psychopharmacol Berl 182:220–231
Kim S, Moon M, Park S (2009) Exendin-4 protects dopaminergic neurons by inhibition of microglial activation and matrix metalloproteinase-3 expression in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. J Endocrinol 202:431–439
Koreen AR, Siris SG, Chakos M, Alvir J, Mayerhoff D, Lieberman J (1993) Depression in first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 150:1643–1648
Lando HM, Alattar M, Dua AP (2012) Elevated amylase and lipase levels in patients using glucagonlike peptide-1 receptor agonists or dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitors in the outpatient setting. Endocr Pract 18:472–477
Levitt Katz LE, Swami S, Abraham M, Murphy KM, Jawad AF, McKnight-Menci H, Berkowitz R (2005) Neuropsychiatric disorders at the presentation of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children. Pediatr Diabetes 6:84–89
Lin PI, Shuldiner AR (2010) Rethinking the genetic basis for comorbidity of schizophrenia and type 2 diabetes. Schizophr Res 123:234–243
Liu WJ, Jin HY, Lee KA, Xie SH, Baek HS, Park TS (2011) Neuroprotective effect of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, synthetic exendin-4, in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 164:1410–1420
Lykkegaard K, Larsen PJ, Vrang N, Bock C, Bock T, Knudsen LB (2008) The once-daily human GLP-1 analog, liraglutide, reduces olanzapine-induced weight gain and glucose intolerance. Schizophr Res 103:94–103
Marmorstein, N.R., Iacono, W.G., Legrand, L., 2014. Obesity and depression in adolescence and beyond: reciprocal risks. Int. J. Obes. (Lond).
Newcomer JW, Haupt DW, Fucetola R, Melson AK, Schweiger JA, Cooper BP, Selke G (2002) Abnormalities in glucose regulation during antipsychotic treatment of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:337–345
Perry T, Lahiri DK, Sambamurti K, Chen D, Mattson MP, Egan JM, Greig NH (2003) Glucagon-like peptide-1 decreases endogenous amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta) levels and protects hippocampal neurons from death induced by abeta and iron. J Neurosci Res 72:603–612
Porsolt RD (1979) Animal model of depression. Biomedicine 30:139–140
Rampersaud N, Harkavyi A, Giordano G, Lever R, Whitton J, Whitton P (2012a) Exendin-4 reverts behavioural and neurochemical dysfunction in a pre-motor rodent model of Parkinson’s disease with noradrenergic deficit. Br J Pharmacol 167:1467–1479
Rampersaud N, Harkavyi A, Giordano G, Lever R, Whitton J, Whitton PS (2012b) Exendin-4 reverses biochemical and behavioral deficits in a pre-motor rodent model of Parkinson’s disease with combined noradrenergic and serotonergic lesions. Neuropeptides 46:183–193
Rummel C, Kissling W, Leucht S (2005) Antidepressants as add-on treatment to antipsychotics for people with schizophrenia and pronounced negative symptoms: a systematic review of randomized trials. Schizophr Res 80:85–97
Sharma AN, Elased KM, Garrett TL, Lucot JB (2010) Neurobehavioral deficits in db/db diabetic mice. Physiol Behav 101:381–388
Sharma AN, Elased KM, Lucot JB (2012) Rosiglitazone treatment reversed depression- but not psychosis-like behavior of db/db diabetic mice. J Psychopharmacol 26:724–732
Siris SG (2000) Depression in schizophrenia: perspective in the era of “atypical” antipsychotic agents. Am J Psychiatry 157:1379–1389
Smith GC, Vickers MH, Shepherd PR (2011) Olanzapine effects on body composition, food preference, glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in the rat. Arch Physiol Biochem 117:241–249
Stonehouse AH, Darsow T, Maggs DG (2012) Incretin-based therapies. J Diabetes 4:55–67
Teramoto S, Miyamoto N, Yatomi K, Tanaka Y, Oishi H, Arai H, Hattori N, Urabe T (2011) Exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, provides neuroprotection in mice transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1696–1705
Tolessa T, Gutniak M, Holst JJ, Efendic S, Hellstrom PM (1998) Glucagon-like peptide-1 retards gastric emptying and small bowel transit in the rat: effect mediated through central or enteric nervous mechanisms. Dig Dis Sci 43:2284–2290
Volavka J, Citrome L (2004) Olanzapine vs haloperidol for treatment of schizophrenia. JAMA 291:1064–1066
Whitehead C, Moss S, Cardno A, Lewis G (2003) Antidepressants for the treatment of depression in people with schizophrenia: a systematic review. Psychol Med 33:589–599
Wise RA, Spindler J, deWit H, Gerberg GJ (1978) Neuroleptic-induced “anhedonia” in rats: pimozide blocks reward quality of food. Science 201:262–264
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A.N., Ligade, S.S., Sharma, J.N. et al. GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide reverses long-term atypical antipsychotic treatment associated behavioral depression and metabolic abnormalities in rats. Metab Brain Dis 30, 519–527 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9591-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9591-7