Abstract
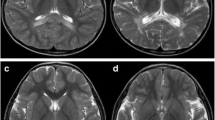
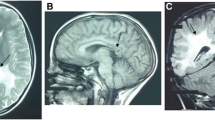
X linked adrenoleukodystrophy (X-ALD) is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive demyelination of the central nervous system, adrenocortical insufficiency and elevated levels of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs). It is caused by mutations in ABCD1 gene located at Xq28. More than 1,300 mutations have been identified to date which is unique to each patient. In this study we report the mutational analysis of 2 X-ALD patients (1 male and 1 female) showing variable clinical spectrum. The mutation analysis of the female patient revealed IVS5-6delC (c.1489-6delC) and p. P543L variations in compound heterozygous state. The male patient was found to be hemizygous for a novel mutation, p. R104P. In conclusion, while defining a novel mutation, the cases presented herein may contribute to the mutation and clinical spectrum of X-ALD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR (2010) A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 7(4):248–9
Bezman L, Moser AB, Raymond GV, Rinaldo P, Watkins PA, Smith KD, Kass NE, Moser HW (2001) Adrenoleukodystrophy: incidence, new mutation rate, and results of extended family screening. Ann Neurol 49:512–517
Chiu HC, Liang JS, Wang JS, Lu JF (2006) Mutational analyses of Taiwanese kindred with Xlinked adrenoleukodystrophy. Pediatr Neurol 35(4):250–6
Engelen M, Barbier M, Dijkstra IM, Schür R, de Bie RM, Verhamme C, Dijkgraaf MG, Aubourg PA, Wanders RJ, van Geel BM, de Visser M, Poll-The BT, Kemp S (2014) X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in women: a cross-sectional cohort study. Brain 137:693–706
Hershkovitz E, Narkis G, Shorer Z, Moser AB, Watkins PA, Moser HW, Manor E (2002) Cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy in a girl with Xq27-Ter deletion. Ann Neurol 52:234–237. 8
Horn MA, Retterstøl L, Abdelnoor M, Skjeldal OH, Tallaksen CM (2013) Adrenoleukodystrophy in Norway: high rate of de novo mutations and age-dependent penetrance. Pediatr Neurol 48:212–219
Kemp S, Pujol A, Waterham HR, van Geel BM, Boehm CD, Raymond GV, Cutting GR, Wanders RJ, Moser HW (2001) ABCD1 mutations and the X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy mutation database: role in diagnosis and clinical correlations. Hum Mutat 18(6):499–515
Lachtermacher MB, Seuánez HN, Moser AB, Moser HW, Smith KD (2000) Determination of 30 X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy mutations, including 15 not previously described. Hum Mutat 15(4):348–53
Moser HW, Mahmood A, Raymond GV (2007) X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 3:140e51
Mosser J, Douar AM, Sarde CO, Kioschis P, Feil R, Moser H, Poustka AM, Mandel JL, Aubourg P (1993) Putative X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy gene shares unexpected homology with ABC transporters. Nature 361:726–730
Neumann S, Topper A, Mandel H, Shapira I, Golan O, Gazit E, Loewenthal R (2001) Identification of new mutations in Israeli patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Genet Test Spring 5(1):65–8
Ng PC, Henikoff S (2006) Predicting the effects of amino acid substitutions on protein function. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7:61–80
Pereira Fdos S, Matte U, Habekost CT, de Castilhos RM, El Husny AS, Lourenço CM, Vianna–Morgante AM, Giuliani L, Galera MF, Honjo R, Kim CA, Politei J, Vargas CR, Jardim LB (2012) Mutations, clinical findings and survival estimates in South American patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. PLoS One 7(3):e34195. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0034195. Epub 2012 Mar 29
Singh I, Pujol A (2010) Pathomechanisms underlying X-Adrenoleukodystrophy: a three-hit hypothesis. Brain Pathol 20:838–844
Takano H, Koike R, Onodera O, Sasaki R, Tsuji S (1999) Mutational analysis and genotypephenotype correlation of 29 unrelated Japanese patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Arch Neurol 56(3):295–300
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Durmaz, A., Atik, T., Onay, H. et al. Molecular analysis in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy patients: identification of a novel mutation. Metab Brain Dis 29, 809–812 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9552-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9552-1