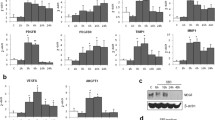
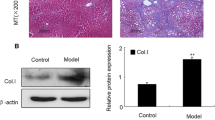
Abstract
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are known to play a key role in the progression of liver fibrosis by producing excessive extracellular matrix (ECM). Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) belong to a family of endopeptidases, which have a well-established role in the degradation of ECM. Our study suggests that, besides the degradation of the extracellular matrix, matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) has a non-canonical role in activating the quiescent HSCs to myofibroblasts by regulating the expression of Col1A1 and αSMA. We have identified that MMP-8 secreted from macrophages as a response to LPS stimulation activates HSCs via ERK1/2-dependent pathway. In addition to this, we determined that MMP-8 may regulate the homodimerization of c-Jun in LX-2 cells, during the trans-differentiation process from quiescent HSC to activate myofibroblasts. Macrophage-released MMP-8 plays a master role in activating the dormant HSCs to activate myofibroblasts through the Erk-mediated pathway and Jun cellular translocation leading to liver fibrosis. Significance MMP-8 can be used as a therapeutic target against liver fibrosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang JX, Török NJ (2013) Liver injury and the activation of the hepatic myofibroblasts. Curr Pathobiol Rep 1:215–223
Iwaisako K, Brenner DA, Kisseleva T (2012) What's new in liver fibrosis? The origin of myofibroblasts in liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27:65–68
Mederacke I, Hsu CC, Troeger JS, Huebener P, Mu X, Dapito DH, Pradere J-P, Schwabe RF (2013) Fate tracing reveals hepatic stellate cells as dominant contributors to liver fibrosis independent of its aetiology. Nat Commun 4:2823
Terai S, Tsuchiya A (2017) Status of and candidates for cell therapy in liver cirrhosis: overcoming the “point of no return” in advanced liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol 52:129–140
Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM, Werb Z (2011) Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a005058
PageMcCaw A, Ewald AJ, Werb Z (2007) Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:221
Duarte S, Baber J, Fujii T, Coito AJ (2015) Matrix metalloproteinases in liver injury, repair and fibrosis. Matrix Biol 44:147–156
Heino J (2007) The collagen family members as cell adhesion proteins. BioEssays 29:1001–1010
Zitka O, Kukacka J, Krizkov S, Huska D, Adam V, Masarik M, Prusa R, Kizek R (2010) Matrix metalloproteinases. Curr Med Chem 17:3751–3768
Koyama H, Iwata H, Kuwabara Y, Iwase H, Kobayashi S, Fujii Y (2000) Gelatinolytic activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and-9 in oesophageal carcinoma; a study using in situ zymography. Eur J Cancer 36:2164–2170
Woessner JF, Nagase H (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Oxford University Press, New York
Itoh Y (2015) Membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases: their functions and regulations. Matrix Biol 44:207–223
Huang C-C, Chuang J-H, Chou M-H, Wu C-L, Chen C-M, Wang C-C, Chen Y-S, Chen C-L, Tai M-H (2005) Matrilysin (MMP-7) is a major matrix metalloproteinase upregulated in biliary atresia-associated liver fibrosis. Mod Pathol 18:941
Belaaouaj A, Shipley JM, Kobayashi DK, Zimonjic DB, Popescu N, Silverman GA, Shapiro SD (1995) Human macrophage metalloelastase. Genomic organization, chromosomal location, gene linkage, and tissue-specific expression. J Biol Chem 270:14568–14575
Nagase H, Visse R, Murphy G (2006) Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc Res 69:562–573
Giannandrea M, Parks WC (2014) Diverse functions of matrix metalloproteinases during fibrosis. Dis Model Mech 7:193–203
Gill SE, Parks WC (2008) Metalloproteinases and their inhibitors: regulators of wound healing. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:1334–1347
Parks WC, Wilson CL, López-Boado YS (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4:617
Hadler-Olsen E, Fadnes B, Sylte I, Uhlin-Hansen L, Winberg JO (2011) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase activity in health and disease. FEBS J 278:28–45
Amălinei C, Căruntu I-D, Bălan RA (2007) Biology of metalloproteinases. Rom J Morphol Embryol 48:323–334
Arriazu E, Ruiz de Galarreta M, Cubero FJ, Varela-Rey M, Perez de Obanos MP, Leung TM, Lopategi A, Benedicto A, Abraham-Enachescu I, Nieto N (2014) Extracellular matrix and liver disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 21:1078–1097
Chen G, Qin G-H, Dang Y-W, Yang J (2017) The prospective role of matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 and transforming growth factor beta 1 in accelerating the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl Cancer Res 6:S229–S231
Iredale JP (2004) A cut above the rest? MMP-8 and liver fibrosis gene therapy. Gastroenterology 126:1199–1201
García-Prieto E, González-López A, Cabrera S, Astudillo A, Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Fanjul-Fernandez M, Batalla-Solís E, Puente XS, Fueyo A, López-Otín C (2010) Resistance to bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in MMP-8 deficient mice is mediated by interleukin-10. PLoS ONE 5:e13242
Craig VJ, Quintero PA, Fyfe SE, Patel AS, Knolle MD, Kobzik L, Owen CA (2013) Profibrotic activities for matrix metalloproteinase-8 during bleomycin-mediated lung injury. J Immunol 190(8):4283–4296
Baig MS, Yaqoob U, Cao S, Saqib U, Shah VH (2016) Non-canonical role of matrix metalloprotease (MMP) in activation and migration of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Life Sci 155:155–160
Han Y-P, Tuan T-L, Hughes M, Wu H, Garner WL (2001) Transforming growth factor-β- and tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated induction and proteolytic activation of MMP-9 in human skin. J Biol Chem 276:22341–22350
Smart DE, Vincent KJ, Arthur MJ, Eickelberg O, Castellazzi M, Mann J, Mann DA (2001) JunD regulates transcription of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 and interleukin-6 genes in activated hepatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem 276:24414–24421
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to Imagej: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2089
Zhang C-Y, Yuan W-G, He P, Lei J-H, Wang C-X (2016) Liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cells: etiology, pathological hallmarks and therapeutic targets. World J Gastroenterol 22:10512
Lee UE, Friedman SL (2011) Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 25:195–206
Naim A, Pan Q, Baig MS (2017) Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in liver diseases. J Clin Exp Hepatol 7:367–372
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for providing financial assistance through the grant (37/1664/15/EMR-11). The authors also gratefully acknowledge the Indian Institute of Technology Indore (IITI) for providing facilities and other support. We are thankful to Sajjan Rajpoot and Anjali Roy for their contribution in making reviewing the revised manuscript figures and text. Authors are thankful to Institute of Liver and Biliary Sciences (ILBS), New Delhi, for providing human hepatic stellate cells lines (LX-2).
Funding
Financial assistance for this work was provided by the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) through the grant (37/1664/15/EMR-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MSB conceived the study. AN did the experimental work. MSB wrote and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors expressed no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2020_3705_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. 1—Expression of IL-12 and IL-23 in LX-2 cells post-stimulation with LPS conditioned media. (A) Expression of IL-12 in LX-2 cells cultured in LPS stimulated conditioned media and in the presence of MMP-8 and ERK inhibitor. (B) Expression of IL-23 in LX-2 cells cultured in LPS stimulated conditioned media and in the presence of MMP-8 and ERK inhibitor. (JPG 68 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naim, A., Baig, M.S. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) through the ERK-mediated pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 467, 107–116 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03705-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03705-x