Abstract
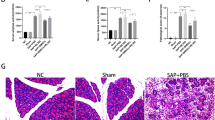
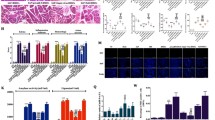
The treatment and prognosis for severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) is currently unsatisfactory showing a high incidence of morbidity and mortality. Here, we investigated the effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) on SAP in rats and explored the possible mechanisms. The common bile duct of each model rat was occluded at the liver hilum, and the induction of SAP was achieved by retrograde perfusion of 3% sodium taurocholate (NaT). Prepared BMSCs were intravenously injected via the tail vein. Pancreatic acinar cells (PACs) were isolated from rat pancreas, and induced by TNF-α. In the present study, we found that necroptosis was activated in NaT-induced acute-necrotized pancreatitis, and transplanted BMSCs could inhibit necroptosis, repair pancreatic injury, and reduce systemic inflammatory response. In addition, necrostatin-1 (Nec-1), as the inhibitor of receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1), could also reduce SAP to some extent. Besides, we detected that BMSCs could also promote regeneration of damaged pancreatic tissues. Furthermore, in vitro, we also investigated that BMSCs could suppress TNF-α-induced necroptosis and improve the viability of PACs. In addition, Nec-1 and knockdown of receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) or mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) could also inhibit necrosis of PACs induced by TNF-α. BMSCs ameliorated SAP and reduced injury of PACs by suppressing the activation of the necroptosis signaling pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Qiu Z, Yu P, Bai B, Hao Y, Wang S, Zhao Z, Hang Z, Wang Q, Guo M, Feng Q, Zhao Q (2016) Regulatory B10 cells play a protective role in severe acute pancreatitis. Inflamm Res 65:647–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0947-9
Sellers ZM, Abu-El-Haija M, Husain SZ, Morinville V (2018) New management guidelines for both children and adults with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 155:234–235. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.068
Wu BU, Banks PA (2013) Clinical management of patients with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 144:1272–1281. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.075
Zhao Q, Wei Y, Pandol SJ, Li L, Habtezion A (2018) STING signaling promotes inflammation in experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 154(1822–1835):e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.01.065
Hegyi P, Pandol S, Venglovecz V, Rakonczay Z Jr (2011) The acinar-ductal tango in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Gut 60:544–552. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2010.218461
Kang R, Zhang Q, Hou W, Yan Z, Chen R, Bonaroti J, Bansal P, Billiar TR, Tsung A, Wang Q, Bartlett DL, Whitcomb DC, Chang EB, Zhu X, Wang H, Lu B, Tracey KJ, Cao L, Fan XG, Lotze MT, Zeh HJ III, Tang D (2014) Intracellular Hmgb1 inhibits inflammatory nucleosome release and limits acute pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 146:1097–1107. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.12.015
Kang R, Lotze MT, Zeh HJ, Billiar TR, Tang D (2014) Cell death and DAMPs in acute pancreatitis. Mol Med 20:466–477. https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2014.00117
Hoque R, Malik AF, Gorelick F, Mehal WZ (2012) Sterile inflammatory response in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 41:353–357. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182321500
Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P (2015) Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature 517:311–320. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14191
Wegner KW, Saleh D, Degterev A (2017) Complex pathologic roles of RIPK1 and RIPK3: moving beyond necroptosis. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38:202–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2016.12.005
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L, Wang X (2009) Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 137:1100–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.021
Wu J, Huang Z, Ren J, Zhang Z, He P, Li Y, Ma J, Chen W, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Yang Z, Wu SQ, Chen L, Han J (2013) Mlkl knockout mice demonstrate the indispensable role of Mlkl in necroptosis. Cell Res 23:994–1006. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2013.91
Degterev A, Maki JL, Yuan J (2013) Activity and specificity of necrostatin-1, small-molecule inhibitor of RIP1 kinase. Cell Death Differ 20:366. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.133
Vandenabeele P, Grootjans S, Callewaert N, Takahashi N (2013) Necrostatin-1 blocks both RIPK1 and IDO: consequences for the study of cell death in experimental disease models. Cell Death Differ 20:185–187. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2012.151
Gong J, Meng HB, Hua J, Song ZS, He ZG, Zhou B, Qian MP (2014) The SDF-1/CXCR15 axis regulates migration of transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells towards the pancreas in rats with acute pancreatitis. Mol Med Rep 9:1575–1582. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2053
Qian D, Gong J, He Z, Hua J, Lin S, Xu C, Meng H, Song Z (2015) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair necrotic pancreatic tissue and promote angiogenesis by secreting cellular growth factors involved in the SDF-1 alpha/CXCR16 axis in rats. Stem Cells Int 2015:306836. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/306836
He Z, Hua J, Qian D, Gong J, Lin S, Xu C, Wei G, Meng H, Yang T, Zhou B, Song Z (2016) Intravenous hMSCs ameliorate acute pancreatitis in mice via secretion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulated gene/protein 6. Sci Rep 6:38438. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38438
Qian D, Wei G, Xu C, He Z, Hua J, Li J, Hu Q, Lin S, Gong J, Meng H, Zhou B, Teng H, Song Z (2017) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) repair acute necrotized pancreatitis by secreting microRNA-9 to target the NF-kappaB1/p50 gene in rats. Sci Rep 7:581. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00629-3
Zhang L, Wei J, Ren L, Zhang J, Yang M, Jing L, Wang J, Sun Z, Zhou X (2017) Endosulfan inducing apoptosis and necroptosis through activation RIPK signaling pathway in human umbilical vascular endothelial cells. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:215–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7652-7
Yu G, Wan R, Hu Y, Ni J, Yin G, Xing M, Shen J, Tang M, Chen C, Fan Y, Xiao W, Zhao Y, Wang X, Hu G (2014) Pancreatic acinar cells-derived cyclophilin A promotes pancreatic damage by activating NF-kappaB pathway in experimental pancreatitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 444:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.015
Hu G, Shen J, Cheng L, Guo C, Xu X, Wang F, Huang L, Yang L, He M, Xiang D, Zhu S, Wu M, Yu Y, Han W, Wang X (2011) Reg4 protects against acinar cell necrosis in experimental pancreatitis. Gut 60:820–828. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2010.215178
Chugh S, Barkeer S, Rachagani S, Nimmakayala RK, Perumal N, Pothuraju R, Atri P, Mahapatra S, Thapa I, Talmon GA, Smith LM, Yu X, Neelamegham S, Fu J, Xia L, Ponnusamy MP, Batra SK (2018) Disruption of C1galt1 gene promotes development and metastasis of pancreatic adenocarcinomas in mice. Gastroenterology 155:1608–1624. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.007
Weedon MN, Cebola I, Patch AM, Flanagan SE, De Franco E, Caswell R, Rodriguez-Segui SA, Shaw-Smith C, Cho CH, Allen HL, Houghton JA, Roth CL, Chen R, Hussain K, Marsh P, Vallier L, Murray A, International Pancreatic Agenesis C, Ellard S, Ferrer J, Hattersley AT (2014) Recessive mutations in a distal PTF1A enhancer cause isolated pancreatic agenesis. Nat Genet 46:61–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2826
Munigala S, Yadav D (2016) Case-fatality from acute pancreatitis is decreasing but its population mortality shows little change. Pancreatology 16:542–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2016.04.008
Jung KH, Song SU, Yi T, Jeon MS, Hong SW, Zheng HM, Lee HS, Choi MJ, Lee DH, Hong SS (2011) Human bone marrow-derived clonal mesenchymal stem cells inhibit inflammation and reduce acute pancreatitis in rats. Gastroenterology 140:998–1008. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2010.11.047
Kanou T, Ohsumi A, Kim H, Chen M, Bai X, Guan Z, Hwang D, Cypel M, Keshavjee S, Liu M (2018) Inhibition of regulated necrosis attenuates receptor-interacting protein kinase 1-mediated ischemia-reperfusion injury after lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 37:1261–1270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2018.04.005
Liu Y, Liao R, Qiang Z, Zhang C (2017) Pro-inflammatory cytokine-driven PI3 K/Akt/Sp1 signalling and H2S production facilitates the pathogenesis of severe acute pancreatitis. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20160483
Plugis NM, Weng N, Zhao Q, Palanski BA, Maecker HT, Habtezion A, Khosla C (2018) Interleukin 4 is inactivated via selective disulfide-bond reduction by extracellular thioredoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:8781–8786. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1805288115
Liu Z, Lai K, Xie Y, He X, Zhou X (2018) Gli2 mediated activation of hedgehog signaling attenuates acute pancreatitis via balancing inflammatory cytokines in mice. Cell Physiol Biochem 48:120–130. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491668
Wu J, Mulatibieke T, Ni J, Han X, Li B, Zeng Y, Wan R, Wang X, Hu G (2017) Dichotomy between receptor-interacting protein 1- and receptor-interacting protein 3-mediated necroptosis in experimental pancreatitis. Am J Pathol 187:1035–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.12.021
Barlass U, Dutta R, Cheema H, George J, Sareen A, Dixit A, Yuan Z, Giri B, Meng J, Banerjee S, Banerjee S, Dudeja V, Dawra RK, Roy S, Saluja AK (2018) Morphine worsens the severity and prevents pancreatic regeneration in mouse models of acute pancreatitis. Gut 67:600–602. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-313717
Wang X, Zhou G, Liu C, Wei R, Zhu S, Xu Y, Wu M, Miao Q (2016) Acanthopanax versus 3-methyladenine ameliorates sodium taurocholate-induced severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting the autophagic pathway in rats. Mediat Inflamm 2016:8369704. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/8369704
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81670582), the College Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (Grant No. KJ2017A271), and the Talent Introduction Fund of Yijishan Hospital of Wannan Medical School (Grant No. YR201601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, G., Ma, Z., Liu, D. et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate severe acute pancreatitis by inhibiting necroptosis in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 459, 7–19 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03546-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03546-3