Abstract
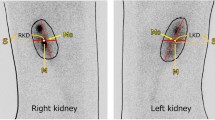
Biochemical and histological assays are currently used for the diagnosis and characterization of kidney injury. The purpose of this study was to compare technetium-99m-labeled dimercaptosuccinic acid (99mTc-DMSA) renal scintigraphy, as a non-invasive method, with common biochemical and histopathological methods in two animal models of acute kidney injury. Nephrotoxicity was induced either by gentamicin (100 mg/kg/day for one week) or unilateral ureteral ligation (UUO). Renal scintigraphy was performed 1 h after intravenous injection of 99mTc-DMSA (3 mCi). Furthermore, plasma levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, sodium, and potassium were determined using an autoanalyzer. At the end of experiments, kidneys were excised for the measurement of activity uptake (mCi/gr) using a dose calibrator as well as histopathological examinations with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. There was a significant decrease in 99mTc-DMSA uptake in both gentamicin (P value = 0.049) and UUO (P value = 0.034) groups, and it was more significant in the former. The levels of BUN and creatinine increased in both gentamicin and UUO groups, while the levels of sodium and potassium remained unchanged. Furthermore, a strong correlation was found between DMSA uptake and histopathological findings. Scintigraphy with 99mTc-DMSA is capable of detection of kidney injury in both gentamicin and UUO groups. Moreover, a significant correlation was found between scintigraphy parameters and histopathological findings. This suggests 99mTc-DMSA as a non-invasive method for the evaluation of kidney injury induced by drugs or anatomical disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellomo R, Kellum JA, Ronco C (2012) Acute kidney injury. Lancet 380(9843):756–766
Lieberthal W, Nigam SK (2000) Acute renal failure. II. Experimental models of acute renal failure: imperfect but indispensable. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278(1):F1–F12
Ramesh G, Ranganathan P (2014) Mouse models and methods for studying human disease, acute kidney injury (AKI). In: Mouse Genetics. Springer, New York, pp 421–436
Dai C, Kiss LP, Liu Y (2008) Animal models of kidney diseases. In: Sourcebook of models for biomedical research. Springer, Berlin, pp 657–664
Singh AP, Muthuraman A, Jaggi AS, Singh N, Grover K, Dhawan R (2012) Animal models of acute renal failure. Pharmacol Rep 64(1):31–44
Najafi H, Owji SM, Kamali-Sarvestani E, Moosavi SMS (2016) A1-Adenosine receptor activation has biphasic roles in development of acute kidney injury at 4 and 24 h of reperfusion following ischaemia in rats. Exp Physiol 101(7):913–931
Nuransoy A, Beytur A, Polat A, Samdanci E, Sagir M, Parlakpinar H (2015) Protective effect of sitagliptin against renal ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Ren Fail 37(4):687–693
Edelstein CL (2008) Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 15(3):222–234
Krawiec D, Badertscher R 2nd, Twardock A, Rubin S, Gelberg H (1986) Evaluation of 99mTc-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid nuclear imaging for quantitative determination of the glomerular filtration rate of dogs. Am J Vet Res 47(10):2175–2179
Labato M, Ross L (1991) Plasma disappearance of creatinine as a renal function test in the dog. Res Vet Sci 50(3):253–258
Kwak W, Jang H-S, Belay T, Kim J, Ha YS, Lee SW, Ahn B-C, Lee J, Park KM, Yoo J (2011) Evaluation of kidney repair capacity using 99m Tc-DMSA in ischemia/reperfusion injury models. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 406(1):7–12
Silva-Rodríguez J, Cortés J, Pardo-Montero J, Pérez-Fentes D, Herranz M, Ruibal Á, Aguiar P (2015) In vivo quantification of renal function in mice using clinical gamma cameras. Phys Med 31(3):242–247
Melis M, de Swart J, de Visser M, Berndsen SC, Koelewijn S, Valkema R, Boerman OC, Krenning EP, de Jong M (2010) Dynamic and static small-animal SPECT in rats for monitoring renal function after 177Lu-labeled Tyr3-octreotate radionuclide therapy. J Nucl Med 51(12):1962–1968
Lee WG, Kim J-H, Kim JM, Shim KM, Kang SS, Chae HI, Choi SH (2010) Renal uptakes of 99mTc-MAG3, 99mTc-DTPA, and 99mTc-DMSA in rabbits with unilateral ureteral obstruction. Vivo 24(2):137–139
Cabuk M, Gurel A, Sen F, Demircan N (2008) Renoprotective effect of erdosteine in rats against gentamicin nephrotoxicity: a comparison of 99mTc-DMSA uptake with biochemical studies. Mol Cell Biochem 308(1–2):35–42
Weyer K, Nielsen R, Petersen SV, Christensen EI, Rehling M, Birn H (2013) Renal uptake of 99mTc-dimercaptosuccinic acid is dependent on normal proximal tubule receptor-mediated endocytosis. J Nucl Med 54(1):159–165
Daniel GB, Mitchell SK, Mawby D, Sackman JE, Schmidt D (1999) Renal nuclear medicine: a review. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 40(6):572–587
Yürekli Y, Ünak P, Yenisey Ç, Ertay T, Müftüler FZB, Medine Eİ (2011) l-carnitine protection against cisplatin nephrotoxicity in rats: comparison with amifostin using quantitative renal Tc 99m DMSA uptake. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther 20(1):1
Pérez-Fentes D, Cortés J, Gude F, García C, Ruibal Á, Aguiar P (2014) Does percutaneous nephrolithotomy and its outcomes have an impact on renal function? Quantitative analysis using SPECT-CT DMSA. Urolithiasis 42(5):461–467
Aguiar P, Perez-Fentes D, Garrido M, García C, Ruibal A, Cortes J (2016) A method for estimating DMSA SPECT renal function for assessing the effect of percutaneous nephrolithotripsy on the treated pole. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 60(2):154–162
Yamada M (1991) Assessment of 99mTc-DMSA renography and uptake compared with creatinine clearance in rats with drug-induced nephrotoxicity–II. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Kaku Igaku 28(4):347–354
Kawamura J, Hosokawa S, Yoshida O (1979) Renal function studies using 99mTc-dimercaptosuccinic acid. Clin Nucl Med 4(1):39–46
Taylor A (1982) Quantitation of renal function with static imaging agents. Semin Nucl Med 4:330–344
Kolar R (2006) Animal experimentation. Sci Eng Ethics 12(1):111–122
Baradaran A, Rafieian-kopaei M (2013) Histopathological study of the combination of metformin and garlic juice for the attenuation of gentamicin renal toxicity in rats. J Renal Inj Prev 2(1):15–21
Tavafi M, Ahmadvand H, Tamjidipour A, Rasolian B (2014) Effect of normobaric hyperoxia on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 17(4):287
Wu M, Wen M, Chiu Y, Chiou Y, Shu K, Tang M-J (2006) Rapamycin attenuates unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis. Kidney Int 69(11):2029–2036
Tantawy MN, Jiang R, Wang F, Takahashi K, Peterson TE, Zemel D, Hao C-M, Fujita H, Harris RC, Quarles CC (2012) Assessment of renal function in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction using 99m Tc-MAG3 dynamic scintigraphy. BMC Nephrol 13(1):1
Maeshima A, Mishima K, Yamashita S, Nakasatomi M, Miya M, Sakurai N, Sakairi T, Ikeuchi H, Hiromura K, Hasegawa Y (2014) Follistatin, an activin antagonist, ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis in a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction. BioMed Res Int 2014:1–10
Pashazadeh A, Tanha K, Jafarian-Dehkordi F, Assadi M, Moji V, Zeraatkar N, Ay M (2015) Experimental evaluation of the performance of HiReSPECT scanner: a high-resolution SPECT system for small animal imaging. Front Biomed Technol 1(3):222–227
Moji V, Zeratkar N, Farahani MH, Aghamiri MR, Sajedi S, Teimourian B, Ghafarian P, Sarkar S, Ay MR (2014) Performance evaluation of a newly developed high-resolution, dual-head animal SPECT system based on the NEMA NU1-2007 standard. J Appl Clin Med Phys 15(6):267–278
Tanha K, Fatemikia H, Assadi M, Seyedabadi M (2017) Assessment of the maximum uptake time of 99mTc-DMSA in renal scintigraphy in rat. Iran J Nucl Med (in press)
Moosavi S, Bayat G, Owji S, Panjehshahin M (2009) Early renal post-ischaemic tissue damage and dysfunction with contribution of A1-adenosine receptor activation in rat. Nephrology 14(2):179–188
Karimi Z, Ketabchi F, Alebrahimdehkordi N, Fatemikia H, Owji SM, Moosavi SMS (2016) Renal ischemia/reperfusion against nephrectomy for induction of acute lung injury in rats. Ren Fail 38(9):1503–1515
Nagai J, Takano M (2004) Molecular aspects of renal handling of aminoglycosides and strategies for preventing the nephrotoxicity. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 19(3):159–170
Wargo KA, Edwards JD (2014) Aminoglycoside-induced nephrotoxicity. J Pharm Pract 27(6):573–577
Priuska EM, Schacht J (1995) Formation of free radicals by gentamicin and iron and evidence for an iron/gentamicin complex. Biochem Pharmacol 50(11):1749–1752
Lora-Michiels M, Anzola K, Amaya G, Solano M (2001) Quantitative and qualitative scintigraphic measurement of renal function in dogs exposed to toxic doses of Gentamicin. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 42(6):553–561
Finco D, Tabaru H, Brown S, Barsanti J (1993) Endogenous creatinine clearance measurement of glomerular filtration rate in dogs. Am J Vet Res 54(10):1575–1578
Yen TC, Chen WP, Chang SL, Liu RS, Yeh SH, Lin CY (1996) Technetium-99m-DMSA renal SPECT in diagnosing and monitoring pediatric acute pyelonephritis. J Nucl Med 37(8):1349–1353
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Grant No. 9228 to K. Tanha from the deputy of research of Bushehr University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatemikia, H., Seyedabadi, M., Karimi, Z. et al. Comparison of 99mTc-DMSA renal scintigraphy with biochemical and histopathological findings in animal models of acute kidney injury. Mol Cell Biochem 434, 163–169 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3046-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3046-5