Abstract
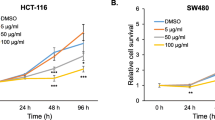
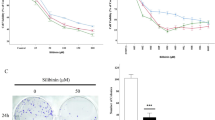
Cryptotanshinone (CPT) is a natural compound extracted from herbal medicine that has been previously shown to possess antitumor properties in various types of human cancer cells. In the present study, we examined the potential role of CPT in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Using SW480, HCT116, and LOVO colorectal cancer cell lines, the effects of CPT on cell viability, apoptosis, and tumorigenicity were evaluated. The results showed that CPT significantly inhibited the growth and viability of SW480, HCT116, and LOVO cell lines by inducing apoptosis and prevented anchorage dependent growth on agar. In addition, CPT inhibited the activation of Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) pathways in colorectal cancer cells. Stat3 is a transcription factor that mediates the expression of various genes associated with many cellular processes, such as inflammation and cell growth, and has been shown to promote several cancer types, including colorectal cancer. These findings indicate that CPT may be a potential candidate for the treatment and prevention of colorectal cancer in part by inhibiting the activation of Stat3.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Inoue-Choi M, Lazovich D, Prizment AE, Robien K (2013) Adherence to the World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research recommendations for cancer prevention is associated with better health-related quality of life among elderly female cancer survivors. J Clin Oncol 31:1758–1766. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.45.4462
Haggar FA, Boushey RP (2009) Colorectal cancer epidemiology: incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg 22:191–197. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242458
Garcia R, Bowman TL, Niu G, Yu H, Minton S, Muro-Cacho CA, Cox CE, Falcone R, Fairclough R, Parsons S, Laudano A, Gazit A, Levitzki A, Kraker A, Jove R (2001) Constitutive activation of Stat3 by the Src and JAK tyrosine kinases participates in growth regulation of human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene 20:2499–2513. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204349
Germain D, Frank DA (2007) Targeting the cytoplasmic and nuclear functions of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 13:5665–5669. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2491
Lau GK, Ye D (2010) STAT3 implicated in the development of colon cancer: a step closer for targeted therapy? Gastroenterology 139:353–355. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.05.030
Chen X, Du Y, Nan J, Zhang X, Qin X, Wang Y, Hou J, Wang Q, Yang J (2013) Brevilin A, a novel natural product, inhibits janus kinase activity and blocks STAT3 signaling in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 8:e63697. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063697
Morikawa T, Baba Y, Yamauchi M, Kuchiba A, Nosho K, Shima K, Tanaka N, Huttenhower C, Frank DA, Fuchs CS, Ogino S (2011) STAT3 expression, molecular features, inflammation patterns, and prognosis in a database of 724 colorectal cancers. Clin Cancer Res 17:1452–1462. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2694
Ma Y, Li H, Yue Z, Guo J, Xu S, Xu J, Jia Y, Yu N, Zhang B, Liu S, Liu M, Shao W, Chen S, Liu P (2014) Cryptotanshinone attenuates cardiac fibrosis via downregulation of COX-2, NOX-2 and NOX-4. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. doi:10.1097/FJC.0000000000000086
Tang Y, Chen Y, Chu Z, Yan B, Xu L (2014) Protective effect of cryptotanshinone on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 723:494–500. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.10.019
Zheng FL, Chang Y, Jia XY, Huang M, Wei W (2011) Effects and mechanisms of Cryptotanshinone on rats with adjuvant arthritis. Chin Med J (Engl) 124:4293–4298
Chen W, Liu L, Luo Y, Odaka Y, Awate S, Zhou H, Shen T, Zheng S, Lu Y, Huang S (2012) Cryptotanshinone activates p38/JNK and inhibits Erk1/2 leading to caspase-independent cell death in tumor cells. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 5:778–787. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0551
Chen W, Luo Y, Liu L, Zhou H, Xu B, Han X, Shen T, Liu Z, Lu Y, Huang S (2010) Cryptotanshinone inhibits cancer cell proliferation by suppressing Mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated cyclin D1 expression and Rb phosphorylation. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 3:1015–1025. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0020
Shin DS, Kim HN, Shin KD, Yoon YJ, Kim SJ, Han DC, Kwon BM (2009) Cryptotanshinone inhibits constitutive signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 function through blocking the dimerization in DU145 prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:193–202. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2575
Ge Y, Cheng R, Zhou Y, Shen J, Peng L, Xu X, Dai Q, Liu P, Wang H, Ma X, Jia J, Chen Z (2012) Cryptotanshinone induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of multidrug resistant human chronic myeloid leukemia cells by inhibiting the activity of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Mol Cell Biochem 368:17–25. doi:10.1007/s11010-012-1338-3
Kim JH, Jeong SJ, Kwon TR, Yun SM, Jung JH, Kim M, Lee HJ, Lee MH, Ko SG, Chen CY, Kim SH (2011) Cryptotanshinone enhances TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia KBM-5 cells. Apoptosis 16:696–707. doi:10.1007/s10495-011-0605-1
Youle RJ, Strasser A (2008) The BCL-2 protein family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:47–59. doi:10.1038/nrm2308
Adams JM, Cory S (2007) The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 26:1324–1337. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210220
Bai L, Chen J, McEachern D, Liu L, Zhou H, Aguilar A, Wang S (2014) BM-1197: a novel and specific Bcl-2/Bcl-xL inhibitor inducing complete and long-lasting tumor regression in vivo. PLoS ONE 9:e99404. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099404
Lu L, Li C, Li D, Wang Y, Zhou C, Shao W, Peng J, You Y, Zhang X, Shen X (2013) Cryptotanshinone inhibits human glioma cell proliferation by suppressing STAT3 signaling. Mol Cell Biochem 381:273–282. doi:10.1007/s11010-013-1711-x
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C, Darnell JE Jr (1999) Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 98:295–303
Lin L, Liu A, Peng Z, Lin HJ, Li PK, Li C, Lin J (2011) STAT3 is necessary for proliferation and survival in colon cancer-initiating cells. Cancer Res 71:7226–7237. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4660
Lin L, Fuchs J, Li C, Olson V, Bekaii-Saab T, Lin J (2011) STAT3 signaling pathway is necessary for cell survival and tumorsphere forming capacity in ALDH(+)/CD133(+) stem cell-like human colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 416:246–251. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.10.112
Zheng Q, Han L, Dong Y, Tian J, Huang W, Liu Z, Jia X, Jiang T, Zhang J, Li X, Kang C, Ren H (2014) JAK2/STAT3 targeted therapy suppresses tumor invasion via disruption of the EGFRvIII/JAK2/STAT3 axis and associated focal adhesion in EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 16:1229–1243. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nou046
Klampfer L (2006) Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs): novel targets of chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 6:107–121
Kusaba T, Nakayama T, Yamazumi K, Yakata Y, Yoshizaki A, Inoue K, Nagayasu T, Sekine I (2006) Activation of STAT3 is a marker of poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep 15:1445–1451
Aoki Y, Feldman GM, Tosato G (2003) Inhibition of STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and decreases survivin expression in primary effusion lymphoma. Blood 101:1535–1542. doi:10.1182/blood-2002-07-2130
Li H, Xiao W, Ma J, Zhang Y, Li R, Ye J, Wang X, Zhong X, Wang S (2014) Dual high expression of STAT3 and cyclinD1 is associated with poor prognosis after curative resection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:7989–7998
Krecicki T, Smigiel R, Fraczek M, Kowalczyk M, Sasiadek MM (2004) Studies of the cell cycle regulatory proteins P16, cyclin D1 and retinoblastoma protein in laryngeal carcinoma tissue. J Laryngol Otol 118:676–680. doi:10.1258/0022215042244769
Alao JP (2007) The regulation of cyclin D1 degradation: roles in cancer development and the potential for therapeutic invention. Mol Cancer 6:24. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-6-24
Altieri DC (2008) Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 8:61–70. doi:10.1038/nrc2293
Abbas T, Dutta A (2009) p21 in cancer: intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer 9:400–414. doi:10.1038/nrc2657
Collado M, Serrano M (2010) Senescence in tumours: evidence from mice and humans. Nat Rev Cancer 10:51–57. doi:10.1038/nrc2772
Majumder PK, Grisanzio C, O’Connell F, Barry M, Brito JM, Xu Q, Guney I, Berger R, Herman P, Bikoff R, Fedele G, Baek WK, Wang S, Ellwood-Yen K, Wu H, Sawyers CL, Signoretti S, Hahn WC, Loda M, Sellers WR (2008) A prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia-dependent p27 Kip1 checkpoint induces senescence and inhibits cell proliferation and cancer progression. Cancer Cell 14:146–155. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2008.06.002
Freedman VH, Shin SI (1974) Cellular tumorigenicity in nude mice: correlation with cell growth in semi-solid medium. Cell 3:355–359
Zhou L, Zuo Z, Chow MS (2005) Danshen: an overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol 45:1345–1359. doi:10.1177/0091270005282630
Lee HJ, Jung DB, Sohn EJ, Kim HH, Park MN, Lew JH, Lee SG, Kim B, Kim SH (2012) Inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor alpha and astrocyte-elevated gene-1 mediates cryptotanshinone exerted antitumor activity in hypoxic PC-3 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2012:390957. doi:10.1155/2012/390957
Park IJ, Kim MJ, Park OJ, Park MG, Choe W, Kang I, Kim SS, Ha J (2010) Cryptotanshinone sensitizes DU145 prostate cancer cells to Fas(APO1/CD95)-mediated apoptosis through Bcl-2 and MAPK regulation. Cancer Lett 298:88–98. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2010.06.006
Chen L, Zheng SZ, Sun ZG, Wang AY, Huang CH, Punchard NA, Huang SL, Gao X, Lu Y (2011) Cryptotanshinone has diverse effects on cell cycle events in melanoma cell lines with different metastatic capacity. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68:17–27. doi:10.1007/s00280-010-1440-8
Xu D, Lin TH, Li S, Da J, Wen XQ, Ding J, Chang C, Yeh S (2012) Cryptotanshinone suppresses androgen receptor-mediated growth in androgen dependent and castration resistant prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett 316:11–22. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.10.006
Song M, Hang TJ, Zhang Z, Chen HY (2007) Effects of the coexisting diterpenoid tanshinones on the pharmacokinetics of cryptotanshinone and tanshinone IIA in rat. Eur J Pharm Sci 32:247–253. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2007.07.007
Liu Y, Li X, Li Y, Wang L, Xue M (2010) Simultaneous determination of danshensu, rosmarinic acid, cryptotanshinone, tanshinone IIA, tanshinone I and dihydrotanshinone I by liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometry and the application to pharmacokinetics in rats. J Pharm Biomed Anal 53:698–704. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2010.03.041
Xie MZ, Shen ZF (1983) Absorption, distribution, excretion and metabolism of cryptotanshinone. Yao Xue Xue Bao 18:90–96
Aggarwal BB, Kunnumakkara AB, Harikumar KB, Gupta SR, Tharakan ST, Koca C, Dey S, Sung B (2009) Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3, inflammation, and cancer: how intimate is the relationship? Ann NY Acad Sci 1171:59–76. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04911.x
Xu Q, Briggs J, Park S, Niu G, Kortylewski M, Zhang S, Gritsko T, Turkson J, Kay H, Semenza GL, Cheng JQ, Jove R, Yu H (2005) Targeting Stat3 blocks both HIF-1 and VEGF expression induced by multiple oncogenic growth signaling pathways. Oncogene 24:5552–5560. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208719
Xu JH, Zhang C, Tang B, Hao YX, Chen J, Liu T, Cui H (2010) Effect of JAK2/STAT3/vimentin signaling pathway on proliferation and migration of human colon cancer cells. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 13:282–285
Corvinus FM, Orth C, Moriggl R, Tsareva SA, Wagner S, Pfitzner EB, Baus D, Kaufmann R, Huber LA, Zatloukal K, Beug H, Ohlschlager P, Schutz A, Halbhuber KJ, Friedrich K (2005) Persistent Stat3 activation in colon cancer is associated with enhanced cell proliferation and tumor growth. Neoplasia 7:545–555
Chen L, Wang HJ, Xie W, Yao Y, Zhang YS, Wang H (2014) Cryptotanshinone inhibits lung tumorigenesis and induces apoptosis in cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep 9:2447–2452. doi:10.3892/mmr.2014.2093
Harada D, Takigawa N, Kiura K (2014) The role of STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel) 6:708–722. doi:10.3390/cancers6020708
Epling-Burnette PK, Liu JH, Catlett-Falcone R, Turkson J, Oshiro M, Kothapalli R, Li Y, Wang JM, Yang-Yen HF, Karras J, Jove R, Loughran TP Jr (2001) Inhibition of STAT3 signaling leads to apoptosis of leukemic large granular lymphocytes and decreased Mcl-1 expression. J Clin Invest 107:351–362. doi:10.1172/JCI9940
Shen Y, Devgan G, Darnell JE Jr, Bromberg JF (2001) Constitutively activated Stat3 protects fibroblasts from serum withdrawal and UV-induced apoptosis and antagonizes the proapoptotic effects of activated Stat1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1543–1548. doi:10.1073/pnas.041588198
Darnell JE Jr (2002) Transcription factors as targets for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2:740–749. doi:10.1038/nrc906
Kan WL, Yin C, Xu HX, Xu G, To KK, Cho CH, Rudd JA, Lin G (2013) Antitumor effects of novel compound, guttiferone K, on colon cancer by p21Waf1/Cip1-mediated G(0)/G(1) cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Int J Cancer 132:707–716. doi:10.1002/ijc.27694
Russo A, Esposito D, Catillo M, Pietropaolo C, Crescenzi E, Russo G (2013) Human rpL3 induces G(1)/S arrest or apoptosis by modulating p21 (waf1/cip1) levels in a p53-independent manner. Cell Cycle 12:76–787. doi:10.4161/cc.22963
Zhang M, Truscott J, Davie J (2013) Loss of MEF2D expression inhibits differentiation and contributes to oncogenesis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Mol Cancer 12:150. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-12-150
Huang L, Wang HY, Li JD, Wang JH, Zhou Y, Luo RZ, Yun JP, Zhang Y, Jia WH, Zheng M (2013) KPNA2 promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity in epithelial ovarian carcinoma through upregulation of c-Myc and downregulation of FOXO3a. Cell Death Dis 4:e745. doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.256
Lee WY, Cheung CC, Liu KW, Fung KP, Wong J, Lai PB, Yeung JH (2010) Cytotoxic effects of tanshinones from Salvia miltiorrhiza on doxorubicin-resistant human liver cancer cells. J Nat Prod 73:854–859. doi:10.1021/np900792p
Ye Y, Xu W, Zhong W (2010) Effects of cryptotanshinone on proliferation and apoptosis of Hela cell line of cervical cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 35:118–121
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Jeffrey D. White and Dr. Libin Jia from Office of Cancer Complementary and Alternative Medicine, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health for support of this study. We thank Dr. Yinling Hu from Cancer and Inflammation Program, Center for Cancer Research, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health for support of this study. This work was supported by National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health intramural funding (ZIA BC 011159), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81273718 and No.81102587), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2012T50199).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Weidong Li and Shakir M. Saud have contributed equally to the work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2015_2424_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig. S1 Cryptotanshinone does not inhibit non-tumor HEK293 cell viability 2 × 104 HEK293 cells were seeded into 96-well plates and after 24 h were treated with 5–100 µmol/L CPT or 0.1 % DMSO. At 24, 48, and 72 h after CPT treatment, the cell viability was determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay as described in “Materials and methods” section. Absorbance at 570 nm was detected with Microplate reader. The experiments were independently performed at least twice, each in triplicate. Crypotanshinone (CPT). Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 187 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Saud, S.M., Young, M.R. et al. Cryptotanshinone, a Stat3 inhibitor, suppresses colorectal cancer proliferation and growth in vitro. Mol Cell Biochem 406, 63–73 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2424-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2424-0