Abstract
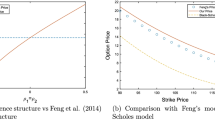
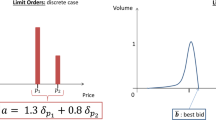
In this paper we build a discrete time model for the structure of the limit order book, so that the price per share depends on the size of the transaction. We deduce the value of a portfolio when the investor trades using market orders and a bank account with different interest rates for lending and borrowing. We also deduce conditions to rule out arbitrage and solve the problem of pricing and hedging an European call option with physical delivery. It is shown that contrary to the perfectly liquid setting, the price of a European call is not given by an expectation, but can be expressed as an optimization problem on a set of equivalent probability measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agliardi R, Gençay R (2014) Hedging through a limit order book with varying liquidity. J Deriv 22(23):32–49
Bank P, Baum D (2004) Hedging and portfolio optimization in illiquid financial markets with a large trader. Math Financ 14:1–18
Bayraktar E, Ludkovski M (2011) Optimal trade execution in illiquid markets. Math Financ 21(4):681–701
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L (2009) Convex optimization, 7th edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Cetin U, Jarrow R, Protter P (2004) Liquidity risk and arbitrage pricing theory. Finance Stochast 8:311–341
Çetin U, Rogers L (2007) Modeling liquidity effects in discrete time. Math Finance 17(1):15–29
Cetin U, Soner H, Touzi N (2010) Option hedging for small investors under liquidity costs. Finance Stochast 14:317–341
Cox J, Ross S, Rubinstein M (1979) Option pricing: A simplified approach. J Financ Econ 7:229–263
Cvitanić J, Ma J (1996) Hedging options for a large investor and forward-backward SDE’s. Ann Appl Probab 6:370–398
Delbaen F, Schachermayer W (1994) A general version of the fundamental theorem of asset pricing. Math Ann 300(3):463–520
Dolinsky Y, Soner H (2013) Duality and convergence for binomial markets with friction. Finance Stochast 17:447–475
Foucault T, Kadan O, Kendel E (2005) Limit order book as a market for liquidity. Rev Financ Stud 18(4):1171–1217
Gökay S, Soner HM (2012) Liquidity in a binomial market. Math Financ 22 (2):250–276
Gökay S, Soner HM (2013) Hedging in an illiquid binomial market. Nonlinear Anal: Real World Appl 16:1–16
Harrison J, Pliska S (1981) Martingales and stochastic integrals in the theory of continuous trading. Stochast Process Appl 11:215–260
Harrison JM, Kreps DM (1979) Martingales and arbitrage in multiperiod securities markets. J Econ Theory 20:381–408
Jarrow R (1994) Derivative security markets, market manipulation and option pricing. J Financ Quant Anal 29:241–261
Obizhaeva A, Wang J (2013) Optimal trading strategy and supply/demand dynamics. J Financ Mark 16:1–32
Predoiu S, Shaikhet G, Shreve S (2011) Optimal execution in a general one-sided limit-order book. SIAM J Financ Math 2:183–212
Roch A (2011) Liquidity risk, price impacts and the replication problem. Finance Stochast 15(3):399–419
Shreve SE (2004) Stochastic calculus for finance. II. Springer Finance. Springer, New York. Continuous-time models
Simard C (2014) General model for limit order books and market orders. Social Science Research Network. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2435198 or https://doi.org/10.2139/2435198.ssrn
Simard C, Rémillard B (2014) Option pricing in a discrete time model for the limit order book. Social Science Research Network. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2472410
Simard C, Rémillard B. (2016) Supplementary to option pricing in a discrete time model for the limit order book. Methodology and Computing in Applied Probability, Link to the supplementary material
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simard, C., Rémillard, B. Pricing European Options in a Discrete Time Model for the Limit Order Book. Methodol Comput Appl Probab 21, 985–1005 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-017-9610-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-017-9610-3