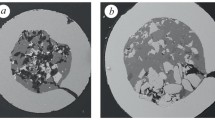
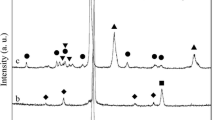
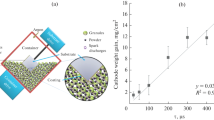
We investigate the influence of the chemical composition and modes of spraying of electric-arc coatings from powder wires of the Stein-Mesyfil series, in particular, 953V, 932V, 954V, and 957V, on their abrasive wear resistance and corrosion characteristics. It is established that all coatings obtained at a current of arc burning of 350 А, have the smallest porosity and largest resistance to abrasive wear resistance, and coatings obtained from 932V and 957V wires are most wear resistant. An influence of the chemical composition and spraying modes on the electrochemical properties of the coatings in a 3% solution of sodium chloride is not found.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Gedzevicius and A. V. Valiulis, “Analysis of wire arc spraying process variables on coatings properties,” J. Mater. Proc. Technol., 175, Nos. 1–3, 206–211 (2006).
V. І. Pokhmurs’kyi, М. М. Student, V. М. Dovhunyk, et al., Electric Arc Restorative and Protective Coatings [in Ukrainian], Karpenko Physicomechanical Institute, Ukrainian National Academy of Sciences, Lviv (2005).
R. C. Tucker, Jr. (editor), ASM Handbook, Volume 5A: Thermal Spray Technology, ASM Thermal Spray Society (2013).
Z. Babiak, T. Wenz, and L. Engl, “Fundamentals of thermal spraying, flame and arc spraying,” in: F.-W. Bach, A. Laarmann, and T. Wenz (editors), Modern Surface Technology, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim (2006), pp. 119–136.
N. Branland, E. Meillot, P. Fauchais, et al., “Relationships between microstructure and electrical properties of RV and DC plasma-sprayed titania coatings,” J. Therm. Spray Technol., 15 (1), 53–62 (2006).
A. Wank, B. Wielage, H. Pokhmurska, et al., “Comparison of hardmetal and hard chromium coatings under different tribological conditions,” Surf. Coat. Technol., 201, No. 5, 1975–1980 (2006).
L. Pawlowski, The Science and Engineering of Thermal Spray Coatings, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken (2008), pp. 79–105.
C. C. Berndt, J. Karthikeyan, R. Ratnaraj, et al., “Material property variation in thermally sprayed coatings”, in: Proc. of the 4th National Thermal Spray Conf. “Thermal Spray Coatings: Properties, Processes and Applications,” ASM International, Pittsburgh (1991), pp. 199–204.
“ASTM G65-94. Standard test method for measuring abrasion using the dry sand/rubber wheel apparatus,” in: Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 03.02, ASTM, Philadelphia (1994), pp. 245–256.
X. Ma, R. Liu, and D. Y. Li, “Abrasive wear behavior of D2 tool steel with respect to load and sliding speed under dry sand/rubber wheel abrasion condition,” Wear, 241, No. 1, 79–85 (2000).
ASTM G65-94. Test Method for Measuring Abrasion Using the Dry Sand/Rubber Wheel Apparatus (2000), pp. 239–250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Fizyko-Khimichna Mekhanika Materialiv, Vol. 50, No. 6, pp. 124–128, November–December, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gargasas, J., Gedzevicius, I., Pokhmurska, H. et al. Wear and Corrosion Resistance of Electric-ARC Coatings Sprayed from Powder Wires of the Stein-Mesyfil Series. Mater Sci 50, 912–916 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-015-9802-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11003-015-9802-3