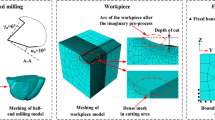
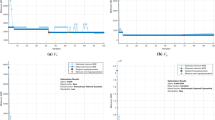
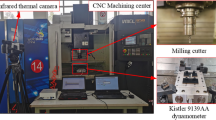
Abstract
This study delves into a Bayesian machine learning (ML) framework designed to comprehensively characterize cutting force and residual stress in the micro end milling process across a diverse range of aluminum alloys. The foundation of this investigation rested on acquiring dependable training data through finite element method simulations, encompassing material properties and processing parameters as inputs, while the output targets included residual stress in both the transverse and cutting directions, as well as cutting force divided into feed force and thrust force. The outcomes were remarkable, unveiling high predictive accuracy for both residual stress and cutting force, with a slight advantage in residual stress prediction. Moreover, the study revealed the significant influence of output target values on the weight functions of input parameters, highlighting distinct dependencies between each output target and the corresponding input features. This investigation elucidated that predicting residual stress and cutting force in micro end milling represents a multifaceted process contingent upon the interplay of material properties and processing parameters. The intricate nature of this process underscores the Bayesian ML model’s potential as a robust and highly accurate approach, adept at effectively encapsulating these complex objectives.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acerbi, L.: Variational Bayesian Monte Carlo. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 31 (2018).
Agrawal, S., Joshi, S.S.: Analytical modelling of residual stresses in orthogonal machining of AISI4340 steel. J. Manuf. Process. 15, 167–179 (2013)
Akram, S., Jaffery, S.H.I., Khan, M., Fahad, M., Mubashar, A., Ali, L.: Numerical and experimental investigation of Johnson–Cook material models for aluminum (Al 6061–T6) alloy using orthogonal machining approach. Adv. Mech. Eng. 10, 1687814018797794 (2018)
Alajmi, M.S., Almeshal, A.M.: Estimation and optimization of tool wear in conventional turning of 709M40 alloy steel using support vector machine (SVM) with Bayesian optimization. Materials (basel). 14, 3773 (2021)
Bagheri, B., Abbasi, M., Givi, M.: Effects of vibration on microstructure and thermal properties of friction stir spot welded (FSSW) aluminum alloy (Al5083). Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 20, 1219–1227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12541-019-00134-9
Caruso, S., Imbrogno, S., Rinaldi, S., Umbrello, D.: Finite element modeling of microstructural changes in Waspaloy dry machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 89, 227–240 (2017)
Chakradhar, B., Singaravel, B., Ugrasen, G., Kumar, A.K.: Prediction of cutting forces using MRA, GMDH and ANN techniques in micro end milling of titanium alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 72, 1943–1949 (2023)
Cheng, M., Jiao, L., Yan, P., Feng, L., Qiu, T., Wang, X., Zhang, B.: Prediction of surface residual stress in end milling with Gaussian process regression. Measurement 178, 109333 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109333
Chiba, N., Masuda, K., Uchida, K., Miura, Y.: Designing composition ratio of magnetic alloy multilayer for transverse thermoelectric conversion by Bayesian optimization. APL Mach. Learn. 1(2) (2023).
Daoud, M., Chatelain, J.F., Bouzid, A.: Effect of rake angle on Johnson–Cook material constants and their impact on cutting process parameters of Al2024-T3 alloy machining simulation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 81, 1987–1997 (2015)
Du, H., Wu, C., Li, D., Yip, W.S., Wang, Z., To, S.: Feasibility study on ultraprecision micro-milling of the additively manufactured NiTi alloy for generating microstructure arrays. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 25, 55–67 (2023)
Gao, X., Wang, H., Tan, H., Xing, L., Hu, Z.: Data-driven machine learning for alloy research: recent applications and prospects. Mater. Today Commun. 36, 106697 (2023)
Geng, X., Cheng, Z., Wang, S., Peng, C., Ullah, A., Wang, H., Wu, G.: A data-driven machine learning approach to predict the hardenability curve of boron steels and assist alloy design. J. Mater. Sci. 57, 10755–10768 (2022)
Huo, D., Lin, C., Choong, Z.J., Pancholi, K., Degenaar, P.: Surface and subsurface characterisation in micro-milling of monocrystalline silicon. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 81, 1319–1331 (2015)
Jia, Z., Lu, X., Gu, H., Ruan, F., Liang, S.Y.: Deflection prediction of micro-milling Inconel 718 thin-walled parts. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 291, 117003 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.117003
Jing, X., Lv, R., Chen, Y., Tian, Y., Li, H.: Modelling and experimental analysis of the effects of run out, minimum chip thickness and elastic recovery on the cutting force in micro-end-milling. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 176, 105540 (2020)
Kumari, N., Kumar, M.: Impact of ogival nosed Projectiles on Al 1100 H-12 thin Plates: numerical Study. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1248, 12046 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/1248/1/012046
Lalwani, D.I., Mehta, N.K., Jain, P.K.: Extension of Oxley’s predictive machining theory for Johnson and Cook flow stress model. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 5305–5312 (2009)
Liang, Z., Du, Y., Ma, Y., Su, Z., Chen, R., Yuan, H., Zhou, T., Wang, X.: Development of polycrystalline diamond micro end mill for milling-grinding combined machining of cemented carbide. J. Manuf. Process. 79, 844–853 (2022)
Liang, S.Y., Su, J.-C.: Residual stress modeling in orthogonal machining. CIRP Ann. 56, 65–68 (2007)
Liu, Q., Cheng, J., Liao, Z., Liu, M., Chen, M., Zhao, L., Lei, H., Ding, W.: Fractal analysis on machined surface morphologies of soft-brittle KDP crystals processed by micro ball-end milling. Materials (basel). 16, 1782 (2023)
Lu, J., Yue, C., Chen, Z., Liu, X., Li, M., Liang, S.Y.: Analytical modeling of milling residual stress under different tool wear conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 127, 4253–4269 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-023-11715-4
Mamedov, A., Lazoglu, I.: Thermal analysis of micro milling titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 229, 659–667 (2016)
Mamun, O., Wenzlick, M., Sathanur, A., Hawk, J., Devanathan, R.: Machine learning augmented predictive and generative model for rupture life in ferritic and austenitic steels. Npj Mater. Degrad. 5, 20 (2021)
Masmiati, N., Sarhan, A.A.D.: Optimizing cutting parameters in inclined end milling for minimum surface residual stress–Taguchi approach. Measurement 60, 267–275 (2015)
McDowell, D.L.: An approximate algorithm for elastic-plastic two-dimensional rolling/sliding contact. Wear 211, 237–246 (1997)
Meijer, A.L., Stangier, D., Tillmann, W., Biermann, D.: Induction of residual compressive stresses in the sub-surface by the adjustment of the micromilling process and the tool´s cutting edge. CIRP Ann. 71, 97–100 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2022.04.065
Mittelman, B., Priel, E., Navi, N.U.: A finite element study of thermo-mechanical fields and their relation to friction conditions in Al1050 ring compression tests. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2, 83 (2018)
Park, S.M., Lee, T., Lee, J.H., Kang, J.S., Kwon, M.S.: Gaussian process regression-based Bayesian optimization of the insulation-coating process for Fe–Si alloy sheets. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 22, 3294–3301 (2023)
Pei, X., Hong Zhao, Y., Chen, L., Guo, Q., Duan, Z., Pan, Y., Hou, H.: Robustness of machine learning to color, size change, normalization, and image enhancement on micrograph datasets with large sample differences. Mater. Des. 232, 112086 (2023)
Qasemi, M., Tahmasbi, V., Sheikhi, M.-M., Zolfaghari, M.: An effect of osteon orientation in end milling operation of cortical bone based on FEM and experiment. J. Manuf. Process. 81, 141–154 (2022)
Rahul, Y., Vipindas, K., Mathew, J.: Methodology for prediction of sub-surface residual stress in micro end milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 62, 600–612 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.12.031
Rahul, Y., Vipindas, K., Sekhar, K.M., Mathew, J.: Modeling of mechanical residual stresses in micro-end milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. In: Shunmugam, M., Kanthababu, M. (eds.) Advances in Micro and Nano Manufacturing and Surface Engineering. Lecture Notes on Multidisciplinary Industrial Engineering. Springer, Singapore (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-32-9425-7_36
Raju, C.T., Hussain, S.J., Yedukondalu, G., Galal, A.M.: Investigation of the cutting-edge radius size effect on dynamic forces in micro end milling of brass260. Mater. Today Proc. (2023).
Ruiz-Jacinto, V.-S., Gutiérrez-Valverde, K.-S., Aslla-Quispe, A.-P., Burga-Falla, J.-M., Alarcón-Sucasaca, A., Huamán-Romaní, Y.-L.: Low-cycle fatigue life assessment of SAC solder alloy through a FEM-data driven machine learning approach. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 36(2), 69–79. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1108/SSMT-08-2023-0045
Samavatian, V., Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M., Samavatian, M., Dehghanian, P., Blaabjerg, F.: Correlation-driven machine learning for accelerated reliability assessment of solder joints in electronics. Sci. Rep. 10, 14821 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71926-7
Samavatian, M., Gholamipour, R., Samavatian, V.: Discovery of novel quaternary bulk metallic glasses using a developed correlation-based neural network approach. Comput. Mater. Sci. 186, 110025 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2020.110025
Scapin, M., Manes, A.: Behaviour of Al6061-T6 alloy at different temperatures and strain-rates: experimental characterization and material modelling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 734, 318–328 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.08.011
Song, Y., Durkan, C., Murray, I., Ermon, S.: Maximum likelihood training of score-based diffusion models. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 34, 1415–1428 (2021)
Sun, Y., Jin, L., Gong, Y., Wen, X., Yin, G., Wen, Q., Tang, B.: Experimental evaluation of surface generation and force time-varying characteristics of curvilinear grooved micro end mills fabricated by EDM. J. Manuf. Process. 73, 799–814 (2022)
Unune, D.R., Mali, H.S.: Current status and applications of hybrid micro-machining processes: a review. Proc. Inst Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 229, 1681–1693 (2015)
Vela, B., Khatamsaz, D., Acemi, C., Karaman, I., Arróyave, R.: Data-augmented modeling for yield strength of refractory high entropy alloys: a Bayesian approach. Acta Mater. 261, 119351 (2023)
Venkata Rao, K.: Power consumption optimization strategy in micro ball-end milling of D2 steel via TLBO coupled with 3D FEM simulation. Measurement 132, 68–78 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.09.044
Wang, Z., Cao, Y., Gorbachev, S., Kuzin, V., He, W., Guo, J.: Research on conventional and high-speed machining cutting force of 7075–T6 aluminum alloy based on finite element modeling and simulation. Metals (basel) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081395
Wang, N., Samavatian, M., Samavatian, V., Sun, H.: Bayesian machine learning-aided approach bridges between dynamic elasticity and compressive strength in the cement-based mortars. Mater. Today Commun. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.106283
Wu, Q., Xie, D.-J., Si, Y., Zhang, Y.-D., Li, L., Zhao, Y.-X.: Simulation analysis and experimental study of milling surface residual stress of Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al. J. Manuf. Process. 32, 530–537 (2018)
Yadav, R., Das Chakladar, N., Paul, S.: Effects of tailored residual stress on micro-end milling: numerical modelling and validation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 127, 5449–5470 (2023)
Yasir, M., Danish, M., Mia, M., Gupta, M.K., Sarikaya, M.: Investigation into the surface quality and stress corrosion cracking resistance of AISI 316L stainless steel via precision end-milling operation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 112, 1065–1076 (2021)
Yu, Z., Li, D., Yang, J., Zeng, Z., Yang, X., Li, J.: Fabrication of micro punching mold for micro complex shape part by micro EDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 100, 743–749 (2019)
Zeng, H.H., Yan, R., Peng, F.Y., Zhou, L., Deng, B.: An investigation of residual stresses in micro-end-milling considering sequential cuts effect. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 91, 3619–3634 (2017)
Zhang, Y., Bai, Q., Qing, L., Chen, S.: 3D coupled thermo-mechanical simulation of surface roughness and residual stress in end milling aluminum alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 123, 4489–4504 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-10468-w
Zhang, P., Wang, S., Lin, Z., Yue, X., Gao, Y., Zhang, S., Yang, H.: Investigation on the mechanism of micro-milling CoCrFeNiAlX high entropy alloys with end milling cutters. Vacuum 211, 111939 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2023.111939
Zhou, R., Yang, W.: Analytical modeling of machining-induced residual stresses in milling of complex surface. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 105, 565–577 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04219-7
Zhou, Y., Yang, B.: Uncertainty quantification of predicting stable structures for high-entropy alloys using Bayesian neural networks. J. Energy Chem. 81, 118–124 (2023)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M.K., Alkhazaleh, H.A., Askar, S. et al. FEM-supported machine learning for residual stress and cutting force analysis in micro end milling of aluminum alloys. Int J Mech Mater Des (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-024-09713-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-024-09713-9