Abstract
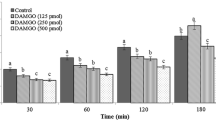
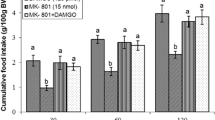
Arginine-phenylalanine-amide (RFamide)-related peptides known as neuropeptide VF (NPVF) have a crucial role in feeding regulation. The present study purposed to determine the effect of intracerebroventricular (ICV) injection of the NPVF on dietary intake and possible interactions of NPVF with glutamate and opioid systems in broiler chicken. In experiment 1, chickens received ICV administration of the control solution, NPVF (16 nmol), 15 nmol of MK-801 (NMDA glutamate receptors antagonist), and injection of the NPVF with MK-801 together. In experiments, 2–8 chickens were injected intracerebroventricularly with 390 nmol of CNQX (antagonist of AMPA glutamate receptors), 2 nmol of AIDA (an antagonist of mGLUR1 glutamate receptors), 150 nmol of LY341495 (an antagonist of mGLUR2 glutamate receptors), 2 nmol of UBP1112 (an antagonist for mGLUR3 glutamate receptors), 5 µg of β-FNA (an antagonist for mu (µ) receptors), 5 µg of NTI (an antagonist for delta (δ) receptors), nor-BNI (kappa (κ) receptors antagonist; 5 µg) instead of MK-801. Following the injection, at 30, 60, and 120 min, the chick's dietary intake was recorded. As a result, NPVF (16 nmol) reduced feed intake in broilers (P < 0.05). NPVF + MK-801 co-injection reduced the hypophagic action of the NPVF (P < 0.05). Injection of NPVF + CNQX together reduced the anorectic action of NPVF (P < 0.05). Co-injection of NPVF + β-FNA reduced the effects of NPVF injection (P < 0.05). Thus, in newborn broilers, NPVF-induced anorexia is probably mediated by NMDA/ AMPA glutamate and µ opioid receptors.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be made available upon request.
References
Adeli A, Zendehdel M, Babapour V, Panahi N (2020) Interaction between leptin and glutamatergic system on food intake regulation in neonatal chicken: role of NMDA and AMPA receptors. Int J Neurosci 130(7):713–721
Ahmadi F, Zendehdel M, Babapour V, Panahi N (2019) CRF1/CRF2 and MC3/MC4 receptors affect glutamate-induced food intake in neonatal meat-type chicken. Braz J Poultry Sci. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9061-2018-0821
Anand BK, Brobeck JR (1951) Hypothalamic control of food intake in rats and cats. Yale J Biol Med 24(2):123
Angelopoulou E, Quignon C, Kriegsfeld LJ, Simonneaux V (2019) Functional implications of RFRP-3 in the central control of daily and seasonal rhythms in reproduction. Front Endocrinol 10(10):183. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00183
Blevins JE, Stanley BG, Reidelberger RD (2002) DMSO as a vehicle for central injections: tests with feeding elicited by norepinephrine injected into the paraventricular nucleus. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71(1–2):277–282
Bonini JA, Jones KA, Adham N, Forray C, Artymyshyn R, Durkin MM, Smith KE, Tamm JA, Boteju LW, Lakhlani PP, Raddatz R (2000) Identification and characterization of two G protein-coupled receptors for neuropeptide FF. J Biol Chem 275(50):39324–39331
Cline MA, Bowden CN, Calchary WA, Layne JE (2008) Short-term anorexigenic effects of central neuropeptide vf are associated with hypothalamic changes in chicks. J Neuroendocrinol 20(8):971–977. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01749.x
Davis JL, Masuoka DT, Gerbrandt LK, Cherkin AA (1979) Autoradiographic distribution of L- proline in chicks after intracerebral injection. Physiol Behav 22:693–695
Elhabazi K, Humbert JP, Bertin I, Quillet R, Utard V, Schneider S, Schmitt M, Bourguignon JJ, Laboureyras E, Boujema MB, Simonnet G (2017) RF313, an orally bioavailable neuropeptide FF receptor antagonist, opposes effects of RF-amide-related peptide-3 and opioid-induced hyperalgesia in rodents. Neuropharmacology 15(118):188–198
Furuse M, Matsumoto M, Saito N, Sugahara K, Hasegava S (1997) The central corticotropin-releasing factor and glucagon-like peptide -1 in food intake of the neonatal chick. Eur J Pharmacol 339:211–214
Hassanpour S, Zendehdel M, Babapour V, Charkhkar S (2015) Endocannabinoid and nitric oxide interaction mediates food intake in neonatal chicken. Br Poult Sci 56(4):443–451. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071668.2015.1059407
Jaefari-Anari M, Zendehdel M, Gilanpour H, Asghari A, Babapour V (2018) Central opioidergic system interplay with histamine on food intake in neonatal chicks: role of µ-opioid and H1/H3 receptors. Braz J Poultry Sci 20:595–604
Kim JS, Brown CH, Anderson GM (2016) Anti-opioid effects of RFRP-3 on magnocellular neuron activity in morphine-naïve and morphine-treated female rats. Endocrinology 157(10):4003–11.2018)
Liu Q, Guan XM, Martin WJ, McDonald TP, Clements MK, Jiang Q, Zeng Z, Jacobson M, Williams DL Jr, Yu H, Bomford D, Figueroa D, Mallee J, Wang R, Evans J, Gould R, Austin CP (2001) Identification and characterization of novel mammalian neuropeptide FF-like peptides that attenuate morphine-induced antinociception. J Biol Chem 276(40):36961–36969. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M105308200
Mobarhan Fard M, Vazir B, Zendehdel M, Asghari A (2021) Interaction of central glutamatergic and histaminergic systems on food intake regulation in layer chickens. Arch Razi Inst 76(3):537–551
Mohapatra SS, Mukherjee J, Banerjee D, Das PK, Ghosh PR, Das K (2021) RFamide peptides, the novel regulators of mammalian HPG axis: a review. Veterinary World 14(7):1867–1873
Moosadoost Y, Zendehdel M, Khodadadi M (2021) The effect of rfamide-related peptide-3 (RFRP-3 or NPVF) on food intake in neonatal chickens: the role of MC3/MC4 and CRF 1/CRF 2 receptors. Int J Pept Res Ther 27:253–262
Mortezaei SS, Zendehdel M, Babapour V, Hasani K (2013) The role of glutamatergic and GABAergic systems on serotonin- induced feeding behavior in chicken. Vet Res Commun 37:303–310
Murakami M, Matsuzaki T, Iwasa T, Yasui T, Irahara M, Osugi T, Tsutsui K (2008) Hypophysiotropic role of RFamide-related peptide-3 in the inhibition of LH secretion in female rats. J Endocrinol 199(1):105–112. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-08-0197
Newmyer BA, Cline MA (2009) Neuropeptide SF is associated with reduced food intake in chicks. Behav Brain Res 205(1):311–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.06.013
Nicklous DM, Simansky KJ (2003) Neuropeptide FF exerts pro-and anti-opioid actions in the parabrachial nucleus to modulate food intake. Am J Physiol-Regul Integrat Comparat Physiol 285(5):1046–1054
Olanrewaju HA, Purswell J, Collier SD, Branton SL (2017) Effects of light ingress through ventilation fan apertures on selected blood variables of male broilers. Int J Poult Sci 16:288–295
Parker KE, Johns HW, Floros TG, Will MJ (2014) Central amygdala opioid transmission is necessary for increased high-fat intake following 24-h food deprivation, but not following intra-accumbens opioid administration. Behav Brain Res 260:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2013.11.014
Qi W, Ding D, Salvi RJ (2008) Cytotoxic effects of dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) on cochlear organotypic cultures. Hearing Res 236:52–60
Rahmani B, Ghashghayi E, Zendehdel M, Khodadadi M, Hamidi B (2021) The crosstalk between brain mediators regulating food intake behavior in birds: a review. Int J Pept Res Ther 27:2349–2370
Raji-Dahmardeh F, Vazir B, Zendehdel M, Asghari A, Panahi N (2020) Interaction between oxytocin and opioidergic system on food intake regulation in neonatal layer type chicken. Int J Pept Res Ther 26:1905–1912
Saito ES, Kaiya H, Tachibana T, Denbow DM, Kangawa K, Furuse M (2005) Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on food intake is mediated by the corticotropin-releasing factor system in neonatal chicks. Regul Pept 125:201–208
Sharkey KA, Darmani NA, Parker LA (2014) Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system. Eur J Pharmacol 722:134–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.09.068
Tachibana T, Sato M, Takahashi H, Ukena K, Tsutsui K, Furuse M (2005) Gonadotrophin-inhibiting hormone stimulates feeding behavior in chicks. Brain Res 1050:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.05.035
Tachibana T, Sato M, Oikawa D, Takahashi H, Boswell T, Furuse M (2007) The anorexic effect of a-melanocyte-stimulating hormone is mediated by corticotrophin releasing factor in chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 147:173–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.12.044
Tsutsui K, Bentley GE, Kriegsfeld LJ, Osugi T, Seong JY, Vaudry H (2010) Discovery and evolutionary history of gonadotrophin-inhibitory hormone and kisspeptin: new key neuropeptides controlling reproduction. J Neuroendocrinol 22(7):716–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.02018.x
Van Tienhoven A, Juhasz LP (1962) The chicken telencephalon, diencephalon and mesencephalon in sterotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol 118:185–197
Wang H, Khoradmehr A, Jalali M, Salehi MS, Tsutsui K, Shirazi MR, Tamadon A (2018) The roles of RFamide-related peptides (RFRPs), mammalian gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) orthologues in female reproduction. Iran J Basic Med Sci 21(12):1210
Zendehdel M, Ghashghayi E, Hassanpour S, Baghbanzadeh A, Jonaidi H (2016) Interaction between opioidergic and dopaminergic systems on food intake in neonatal layer type chicken. Int J Pept Res Ther 22:83–92
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their deepest gratitude to the central laboratory (Dr. Rastegar Lab.) of the Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, the University of Tehran, for cooperation. This study was obtained from a Ph.D. thesis performed by the first author.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BH, MZ, BV, and AA wrote the main manuscript text and prepared Figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8. All authors reviewed the manuscript. The work is original and not previously published. All data are true and accurate to the knowledge of the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of interest
Authors has no potential conflicts of interest.
Informed Consent
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by any authors.
Research Involving Human and/or Animals Rights
All experiments were executed according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the institutional animal ethics committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamidi, B., Zendehdel, M., Vazir, B. et al. The Effect of the Central Administration of the Neuropeptide VF on Feed Intake and Its Possible Interactions with Glutamate and Opioid Systems in Broiler Chicken. Int J Pept Res Ther 28, 101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10407-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10407-z