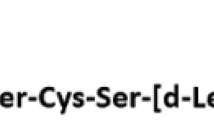Abstract
Diabetic dyslipidemia, a common pattern of lipid abnormalities associated with diabetes, is characterized by hyperglycemia, elevated serum levels of triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol, and reduced serum levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol. These lipid abnormalities make diabetes an independent risk-factor for the development of cardiovascular disease. Two mouse models of diabetes were used in the present study: 1) streptozotocin (STZ)-induced insulin-deficient male Swiss Webster mice (a model of T1DM), and 2) male diet-induced obese (DIO) mice rendered insulin-resistant by maintenance on a high-fat diet for 30 weeks (a model of T2DM). Both models were then treated with MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3 by oral gavage for 14 or 17 days. At the end of the test period, the mice were exsanguinated by cardiac puncture; serum was prepared from the whole blood and analyzed by ELISA for total-, HDL-, LDL/VLDL-cholesterol, and triglyceride content. In mouse models of both T1DM and T2DM, MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3 significantly (P < 0.05) reduced serum levels of triglycerides and LDL/VLDL-cholesterol, and elevated serum HDL-cholesterol to levels approaching or equivalent to those seen in normal non-diabetic mice of the same age and sex. Our results suggest that in addition to its effects on energy balance, glycemic control, and cognitive function, MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3, by modulating serum lipid levels, may also be beneficial in reducing the risk of adverse cardiovascular events associated with both T1DM and T2DM.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abasi A, Corpeleijn E, Gansevoort RT, Gans ROB, Hillege HL, Stolk RP, Navis G, Bakker SJL, Dullaart RPF (2013) Role of HDL cholesterol and estimates of HDL particle composition in future development of type 2 diabetes in the general population: the PREEND study. J Clin endocrinol Metab 98:E1352-1359. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2013-1680
Anagnostoulis S, Karayiannakis AJ, Lambropoulou M, Efthimiadou A, Polychronidis A, lsimkopoulos C, (2008) Human leptin induces angiogenesis in vivo. Cytokine 42:351–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2008.03.009
Anderson BM, Hirschstein Z, Novakovic ZM, Grasso P (2019) MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3, a small molecule synthetic peptide leptin mimetic, improves glycemic control and episodic memory in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s-like cognitive impairment. Inter J Pept Res Ther. https://doi.org/10.1007/s109089-019-09995-0
Anderson BA, Jacobson L, Novakovic ZM, Grasso P (2017) Oral delivery of [D-Leu-4]-OB3 and MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3, synthetic peptide leptin mimetics: immunofluorescent localization in the mouse hypothalamus. Brain Res 1664:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.03.020
Balland E, Cowley MA (2015) New insights in leptin resistance mechanisms in mice. Front Neuroendocinol 19:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yfrne.2015.09.004
Banks WA (2008) The blood-brain barrier as a cause of obesity. Curr Phar Des 14:1606–1614. https://doi.org/10.2174/138181208784705496
Barquera S, Pedroza-Tobias A, Medina C, Hernandez-Barrera L, Bibbins-Domingo K, Lozano R, Moral AE (2015) Global overview of the epidemiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Arch Med Res 46:328–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/jarcmed.2015.06.006
Cojocaru M, Cojocaru IM, Silosi I, Rogoz S (2013) Role of leptin in autoimmune disease. Maedica 8:86–74
Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Grimm RH Jr, Probstfield JL, Simons-Morton DG, Friedewald WT (2008) Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 24:2545–2559. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0802743
Gill JM, Brown JC, Bedford D, Wright DM, Cooney J, Hughes DA, Packard CJ (2004) Caslake MJ (2004) Hepatic production of VLDL1 but not VLDL2 is related to insulin resistance in normoglycaemic middle-aged subjects. Atherosclerosis 176:49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2004.04.022
Haffner SM, Stern MP, Hazuda HP, Mitchell BD, Patterson JK (1990) Cardiovascular risk factors in confirmed prediabetic individuals. Does the clock for coronary heart disease start ticking before the onset of clinical diabetes? JAMA 263:2893–2898. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.263.21.2893
Hirano T (2018) Pathophysiology of diabetic Dyslipidemia. J Atheroscler Thromb 25:771–782. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.RV17023
Hirschstein Z, Novakovic ZM, Grasso P (2019) MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3, a small molecule synthetic peptide leptin mimetic, normalized glucose tolerance and episodic memory in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s Disease-like cognitive impairment. Inter J Pept Res Ther. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-019-09995-0
Hirschstein Z, Reddy Vanga G, Wang G, Novakovic ZM (1864) MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3, a small molecule synthetic peptide leptin mimetic, reduces serum levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha and neurodegeneration in mouse models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Alzheimer’s Disease-like cognitive impairment. BBA Gen Subjects 92020:12969
Ho Y, Wang S-H,Chen Y-R, Li Z-L, Chin Y-T, Yang Y-CSH, Wu-Y-H, Su K-W, Chu H-R, Chiu HJ-C, Crawford DR, Shih, Y-S, Grasso P, Tang H-Y, Lin H-Y, Davis PJ, Shang-Peng J, Wang, K (2019) Leptin-derived peptides block leptin-induced proliferation by reducing expression of pro-inflammatory genes in hepatocellular cells. Food Chem Toxicol 133:110808. https://doi.org/10.12017/j.fct.2019.110808dx.
Howard BV, Robbins DC, Sirvers ML, Lee ET, Rhodes D, Devereux RB, Cowan LD, Gray RS, Welty TK, Go OT, Howard WJ (2000) LDL cholesterol as a strong predictor of coronary heart disease in diabetic Individuals with insulin resistance and low LDL: the Strong Heart Study. Artertioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:830–835. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.atc.20.3.830
Jialal I, Singh G (2019) Management of diabetic dyslipidemia: an update. World J Diabetesd 10:280–290. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v10.15.280
Lorenzo C, Hartnett S, Hanley AJ, Rewers MJ, Wagenknecht LE, Karter AJ, Haffner SM (2013) Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance have distinct lipoprotein and apolipoprotein changes: the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 98:1622–1630. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012.31851614
Modzelewska P, Chludzinska S, Lewko J, Reszek J (2019) The influence of leptin on the process of carcinogenesis. Contemp Oncol 233:63–68. https://doi.org/10.5114/wo.2019.85877
Sawar N, Gao P, Kondapally Seshasai SR, Gobin R, Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio E, Ingelsson E, Lawlor DA, Selvin E, Stampler M, Stehouwer CDA, Lewington S, Pennellis L, Thompson A, Sattar N, White IR, Ray KK, Danesh J (2010) Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 375:2215–2222. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60484-9J
Schofield JD, Liu Y, Rao-Balakrishna P, Malik RA (2016) Diabetes dyslipidemia. Diabetes Ther 7:209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-016-0167-x
Wang A, Anderson BM, Novakovic ZM, Grasso P (2018) [D-Leu-4]-OB3 and MA-[D-Leu-4]-OB3, small molecule synthetic peptide leptin mimetics, improve glycemic control in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice. Peptides. 2018;101:51–59. Subjects 1864 (2020) 12969
West KM, Ahuja MM, Bennett PH, Czyzyk A, De Acosta OM, Fuller JH, Grab V, Grabauskas V, Jarrett RJ, Kosaka K (1983) The role of circulating glucose and triglyceride concentrations and their interactions with other “risk factors” as determinants of arterial disease in nine diabetic population samples from the WHO multinational study. Diabetes Care 6:361–369. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.6.4.361
Wu L, Parhofer KG (2014) Diabetic dyslipidemia. Metabolism 68:1469–1479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.08.010
Yang Y-CSH, Chin U-T, Hsieh M-T, Lai H-Y, Ke C-C, Crawford DR, Lee OK, Mousa SA, Grasso P, Liu LF, Chang H-Y, Tang H-Y, Lin H-Y, Davis PJ (2016) Novel leptin OB3 peptide- induced signaling and progression in thyroid cancers: comparison with leptin. Oncotarget 7:27641–27654. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8505
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the Willard B. Warring Memorial Fund, Albany Medical College, Albany NY, USA (to PG). The Intravail® reagent was graciously provided by Aegis Therapeutics, San Diego, CA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: PG, ZMN. Methodology: ZH, AW, BMA. Formal analysis and investigation: PG, ZMN, ZH; AW, BMA. Writing—original draft preparation: PG. Writing—review and editing: PG, ZMN, ZH, AW, BMA. Funding acquisition: PG. Supervision: PG.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Zall Hirschstein, Anke Wang, Brian M. Anderson, Zachary M. Novakovic, and Patricia Grasso declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirschstein, Z., Wang, A., Anderson, B.M. et al. MA-[D-Leu-4)-OB3, a Small Molecule Synthetic Peptide Leptin Mimetic, Improves Serum Lipid Profiles in Mouse Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Int J Pept Res Ther 27, 1121–1128 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10155-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10155-y