Abstract
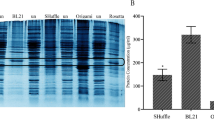
The epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) is a membrane glycoprotein overexpressed in epithelial-derived neoplasms and therefore is a highly interesting target for antibody therapy in a wide range of carcinomas. Single chain variable fragment (ScFv) antibodies, generated by the association of the variable heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins through a short polypeptide linker, retain the binding properties of classical antibodies. Due to its characteristics, Escherichia coli (E. coli) has inspired a great deal of interest for production of antibody fragments with high concentrations. Here, ScFv against EpCAM extracellular domain (EpEX) was expressed in E. coli BL21™(DE3) strain. The effect of different expression conditions on the total protein level was also investigated. Moreover, an attempt was made to overcome the problem of insolubility of the recombinant protein with alterations of expression condition like inducer concentration and temperature as well as addition of the solubility-enhancing agents. Our results showed that the maximum total protein expression was attained 7 h after induction at 37 °C with 0.5 mM IPTG (663.53 ± 7.33 mg/l). Moreover, the expressed antiEpEX-ScFv protein was 39.8% or 29.1% soluble in the presence of 50% glycerol, and Tween20 plus 50% glycerol respectively. Although the solubility of recombinant protein was significantly increased from 39.8% at 37 °C to 43.7% at 16 °C, the maximum level of soluble recombinant protein was attained at 37 °C. Consequently, we report a strategy combining different culture conditions and the solubility-enhancing additives such as glycerol for improving protein solubility.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbari V, Sadeghi HMM, Jafarian-Dehkordi A, Chou CP, Abedi D (2015) Optimization of a single-chain antibody fragment overexpression in Escherichia coli using response surface methodology. Res Pharm Sci 10:75
Brischwein K et al (2006) MT110: a novel bispecific single-chain antibody construct with high efficacy in eradicating established tumors. Mol Immunol 43:1129–1143
Cornelis P (2000) Expressing genes in different Escherichia coli compartments. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:450–454
Farajnia S, Ghorbanzadeh V, Dariushnejad H (2019) effect of molecular chaperone on the soluble expression of recombinant fab fragment in E. coli international. J Pept Res Ther:1–8
Francis DM, Page R (2010) Strategies to optimize protein expression in E. coli. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 61:5–21–25, 29
Kholodenko V et al (2019) Multimerization through Pegylation improves pharmacokinetic properties of scFv fragments of GD2-specific antibodies. Molecules 24:3835
Kim YP et al (2014) Effective therapeutic approach for head and neck cancer by an engineered minibody targeting the EGFR receptor. PLoS ONE 9:e113442
Kirchner E, Gerhards R, Voigtmann R (2002) Sequential immunochemotherapy and edrecolomab in the adjuvant therapy of breast cancer: reduction of 17–1A-positive disseminated tumour cells. Ann Oncol 13:1044–1048
Leibly DJ, Nguyen TN, Kao LT, Hewitt SN, Barrett LK, Van Voorhis WC (2012) Stabilizing additives added during cell lysis aid in the solubilization of recombinant proteins. PLoS ONE 7:e52482
Lim K-P, Li H, Nathan S (2004) Expression and purification of a recombinant scFv towards the exotoxin of the pathogen, Burkholderia pseudomallei. J Microbiol 42:126–132
Malekian R, Jahanian-Najafabadi A, Moazen F, Ghavimi R, Mohammadi E, Akbari V (2019) High-yield production of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in E. coli BL21 (DE3) by an auto-induction strategy. Iran J Pharma Res: IJPR 18:469
Martowicz A, Seeber A, Untergasser G (2016) The role of EpCAM in physiology and pathology of the epithelium. Histol Histopathol 31:349–355
Mohammadgholizad F, Hashemi A (2019) Construction of recombinant Pichia pastoris expressing single-chain antibody fragment against extracellular domain of EpCAM. Koomesh 21:743–750
Patriarca C, Macchi RM, Marschner AK, Mellstedt H (2012) Epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression (CD326) in cancer: a short review. Cancer Treat Rev 38:68–75
Piubelli L et al (2013) Optimizing Escherichia coli as a protein expression platform to produce Mycobacterium tuberculosis immunogenic proteins. Microb Cell Fact 12:115
Rasooli F, Hashemi A (2019) Efficient expression of EpEX in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli using thioredoxin fusion protein. Res Pharm Sci 14:554–565
Simon M, Stefan N, Plückthun A, Zangemeister-Wittke U (2013) Epithelial cell adhesion molecule-targeted drug delivery for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 10:451–468
Sun W, Xie J, Lin H, Mi S, Li Z, Hua F, Hu Z (2012) A combined strategy improves the solubility of aggregation-prone single-chain variable fragment antibodies. Protein Expr Purif 83:21–29
Tsai W-C, Wu T-C, Chiang B-L, Wen H-W (2017) Cloning, expression, and purification of recombinant major mango allergen Man i 1 in Escherichia coli. Protein Exp Purif 130:35–43
Vasina JA, Baneyx F (1997) Expression of aggregation-prone recombinant proteins at low temperatures: a comparative study of the Escherichia coli cspA and tacPromoter systems. Protein Exp Purif 9:211–218
Volontè F, Piubelli L, Pollegioni L (2011) Optimizing HIV-1 protease production in Escherichia coli as fusion protein. Microb Cell Fact 10:53
Wang M, Zhang Y, Li B, Zhu J (2015) Construction of scFv that bind both fibronectin-binding protein A and clumping factor A of Stapylococcus aureus. Res Vet Sci 100:109–114
Willuda J, Honegger A, Waibel R, Schubiger PA, Stahel R, Zangemeister-Wittke U, Plückthun A (1999) High thermal stability is essential for tumor targeting of antibody fragments: engineering of a humanized anti-epithelial glycoprotein-2 (epithelial cell adhesion molecule) single-chain Fv fragment. Cancer Res 59:5758–5767
Zhang J, Wang J, Zhong R, Niu B (2009) Optimization of human anti-HBsAg scFv secretary expression in Escherichia coli Zhonghua shi yan he lin chuang bing du xue za zhi= Zhonghua shiyan he linchuang bingduxue zazhi= Chin J Exp Clin Virol 23:50–52
Zheng P, Sun X, Guo L, Shen J (2015) Cloning, expression, and characterization of an acetolactate synthase (ALS) gene from Anabaena azotica. Process Biochem 50:1349–1356
Funding
This study was funded by the research deputy of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences in Tehran, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Atieh Hashemi and Masoumeh Rajabibazl contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Reyhaneh Najafi Soulari, Majid Basafa and Atieh Hashemi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Atieh Hashemi and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soulari, R.N., Basafa, M., Rajabibazl, M. et al. Effective Strategies to Overcome the Insolubility of Recombinant ScFv Antibody against EpCAM Extracellular Domain in E. coli. Int J Pept Res Ther 26, 2465–2474 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10044-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-020-10044-4