Abstract
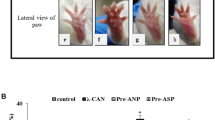
We sought to determine the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) using 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced acute and chronic skin inflammatory mice model. ANP treatment (2 μg/kg body weight/day/i.p. for acute and 0.5 μg/kg body weight/day/i.p. for chronic inflammatory study) was started after 30 min of TPA application. The standard drug, aspirin (ASP) (20 μg/kg body weight/day/i.p.; 10 μg/kg body weight/day/i.p., respectively) was used as a positive control for the both acute and chronic study. TPA alone treated mice exhibited a marked increase in the ear length (7 ± 0.08 vs. 13 ± 0.7 mm, p < 0.001) as well as in ear weight (80 ± 1.3 vs. 130 ± 1.5 mg, p < 0.001) as compared with control mice. Upon treatment with ANP, the increased ear length and weight were reverted back to near normal level. Similarly, ANP treatment markedly suppressed the TPA-induced chronic skin inflammatory lesion (5.7 ± 0.2 vs. 0.95 ± 0.05, p < 0.001) as compared with TPA-induced mouse skin. TPA-induced alterations in the levels of serum C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), total white blood cell (TWBC), serum tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), natriuretic peptide receptor-A (NPR-A), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 (MMP-2/-9) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) (p < 0.01, respectively) were reverted back to near normal levels. The results of the present study clearly show the in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of ANP, which is comparable with that of a standard drug, ASP. Our results suggest that ANP elicits its anti-inflammatory activity by down-regulating the expressions of NPR-A, COX-2, MMPs and NF-κB.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardou M, Barkun AN, Ghosn J, Hudson M, Rahme E (2004) Effect of chronic intake of NSAIDs and cyclooxygenase 2-selective inhibitors on esophageal cancer incidence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:880–887
Bhakdi S, Torzewski M, Klouche M, Hemmes M (1999) Binding of CRP to degraded, nonoxidized LDL enhances complement activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:2348–2354
Chen W, Gassner B, Börner S, Nikolaev VO, Schlegel N, Waschke J, Steinbronn N, Strasser R, Kuhn M (2012) Atrial natriuretic peptide enhances microvascular albumin permeability by the caveolae-mediated transcellular pathway. Cardiovasc Res 93:141–151
Coruzzi G, Pozzoli C, Adami M, Grandi D, Guido N, Smits R, de Esch I, Leurs R (2012) Strain-dependent effects of the histamine H4 receptor antagonist JNJ7777120 in a murine model of acute skin inflammation. Exp Dermatol 21:32–37
Curry F-R (2014) Atrial natriuretic peptide attenuates thrombin-induced inflammation. FASEB J. 4:672
Gopi V, Subramanian V, Manivasagam S, Vellaichamy E (2015) Angiotensin II down-regulates natriuretic peptide receptor-A expression and guanylyl cyclase activity in H9c2 (2-1) cardiac myoblast cells: role of ROS and NF-κB. Mol Cell Biochem 409:67–79
Grimm RH, Neaton JD, Ludwig W (1985) Prognostic importance of the white blood cell count for coronary, cancer, and all-cause mortality. JAMA 254:1932–1937
Hum D, Besnard S, Sanchez R, Devost D, Gossard F, Hamet P et al (2004) Characterization of a cGMP-response element in the guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor A gene promoter. Hypertension 43:1270–1278
Ingelsson E, Arnlov J, Sundstrom J, Lind L (2005) Inflammation, as measured by the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), is an independent predictor for the development of heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 45:1802–1806
Kandasamy R, Park SJ, Boyapalle S, Mohapatra S, Hellermann GR, Lockey RF, Mohapatra SS (2010) Isatin down-regulates expression of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor A and inhibits airway inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Int Immunopharmacol 10:218–225
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663
Kiemer AK, Vollmar AM (1998) Autocrine regulation of inducible nitric-oxide synthase in macrophages by atrial natriuretic peptide. J Biol Chem 273:13444–13451
Kiemer AK, Vollmar AM (2001) The atrial natriuretic peptide regulates the production of inflammatory mediators in macrophages. Ann Rheum Dis 60:68–70
Kiemer AK, Hartung T, Vollmar AM (2000) cGMP-mediated inhibition of TNF-alpha production by the atrial natriuretic peptide in murine macrophages. J Immunol 165:175–181
Kiemer AK, Lehner MD, Hartung T, Vollmar AM (2002) Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 by natriuretic peptides. Endocrinology 143:846–852
Kumar M, Behera AK, Lockey RF, Vesely DL, Mohapatra SS (2002) Atrial natriuretic peptide gene transfer by means of intranasal administration attenuates airway reactivity in a mouse model of allergic sensitization. J Allergy Clin Immunol 110:879–882
Kumar P, Tripathi S, Pandey KN (2014) Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate the transcriptional regulation of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-A gene: interactive roles of modified histones, HATS, p300, and Sp1. J Biol Chem 289:6991–7002
Ladetzki-Baehs K, Keller M, Kiemer AK (2007) Atrial natriuretic peptide, a regulator of nuclear factor-kappaB activation in vivo. Endocrinology 148:332–336
Lee YC, Lee HB, Rhee YK, Song CH (2001) The involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in airway inflammation of patients with acute asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 31:1623–1630
Lee SH, Kim DW, Eom SA, Jun S-Y (2012) Suppression of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced skin inflammation in mice by transduced Tat-Annexin protein. BMB Rep 45:354–359
Li Q, Park PW, Wilson CL (2002) Matrilysin shedding of syndecan-1 regulates chemokine mobilization and transepithelial efflux of neutrophils in acute lung injury. Cell 111:635–646
Mallela J, Ravi S, Jean Louis F, Mulaney B, Cheung M, Sree Garapati U (2013) Natriuretic peptide receptor A signaling regulates stem cell recruitment and angiogenesis: a model to study linkage between inflammation and tumorigenesis. Stem cell. 31:1321–1329
Mani I, Garg R, Tripathi S, Pandey KN (2015) Subcellular trafficking of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-A with concurrent generation of intracellular cGMP. Biosci Rep 35:e00260
Metcalf D, Nicola NA, Gearing DP (1990) Effects of injected leukemia inhibitory factor on hematopoietic and other tissues in mice. Blood 76:50–56
Mezzasoma L, Antognelli C, Talesa VN (2015) Atrial natriuretic peptide down-regulates LPS/ATP-mediated IL-1β release by inhibiting NF-kB, NLRP3 inflammasome and caspase-1 activation in THP-1 cells. Immunol Res 64:303–312
Mohapatra SS, Lockey RF, Vesely DL, Gower WR Jr (2004) Natriuretic peptides and genesis of asthma: an emerging paradigm? J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:520–526
Moore BA, Manthey CL, Johnson DL, Bauer AJ (2011) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 inhibition reduces inflammation and improves motility in murine models of postoperative ileus. Gastroenterology 141:1283–1292
Nathan C, Ding A (2010) Nonresolving inflammation. Cell 140:871–882
Pan MH, Li S, Lai CS, Miyauchi Y, Suzawa M (2012) Inhibition of citrus flavonoids on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced skin inflammation and tumorigenesis in mice. Food Sci Hum Wellness 1:65–73
Pandey KN (2011) Guanylyl cyclase/atrial natriuretic peptide receptor-A: role in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular regulation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 89:557–573
Pandey KN (2014) Guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-A signaling antagonizes phosphoinositide hydrolysis, Ca(2+) release, and activation of protein kinase C. Front Mol Neurosci 7:75
Pandey KN (2015) Endocytosis and trafficking of natriuretic peptide receptor-A: potential role of short sequence motifs. Membranes (Basel) 5:253–287
Pober JS, Sessa WC (2015) Inflammation and the blood microvascular system. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7:016345
Potter LR, Abbey-Hosch S, Dickey DM (2006) Natriuretic peptides, their receptors, and guanosine monophosphate dependent functions. Endocr Rev 27:47–72
Puimège L, Libert C, Van Hauwermeiren F (2014) Regulation and dysregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 25:285–300
Rumzhum NN, Ammit AJ (2016) Cyclooxygenase 2: its regulation, role and impact in airway inflammation. Clin Exp Allergy 46:397–410
Schottelius AJ et al (2002) An aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 stable analog displays a unique topical anti-inflammatory profile. J Immunol 169:7063–7070
Subramanian V, Vellaichamy E (2014) Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) inhibits DMBA/TPA induced skin tumor growth by modulating NF-κB, MMPs, and infiltrating mast cells in swiss albino mice. Eur J Pharmacol 740:388–397
Subramanian V, Venkatesan B, Tumala A, Vellaichamy E (2014) Topical application of Gallic acid suppresses the 7,12-DMBA/TPA induced two-step skin carcinogenesis by modulating anti-oxidants and MMP-2/MMP-9 in Swiss albino mice. Food Chem Toxicol 66:44–55
Tartakoff AM, Jamieson JD (1974) Subcellular fractionation of the pancreas. Methods Enzymol 31:41–59
Thomsen JS, Benfeldt E, Jensen SB, Serup J, Menné T (2002) Topically applied aspirin decreases histamine-induced wheal and flare reactions in normal and SLS-inflamed skin, but does not decrease itch. A randomized, double-blind and placebo-controlled human study. Acta Derm Venereol 82:30–35
Trichopoulos D, Psaltopoulou T, Orfanos P, Trichopoulou A, Boffetta P (2006) Plasma C-reactive protein and risk of cancer: a prospective study from Greece. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 4:15–381
Tsukagoshi H, Shimizu Y, Kawata T, Hisada T, Shimizu Y, Iwamae S (2001) Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by interferon-gamma-activated macrophages via suppression of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappa B activation. Regul Pept 99:21–29
Vellaichamy E, Khurana ML, Fink J, Pandey KN (2005) Involvement of the NF-kappa B/matrix metalloproteinase pathway in cardiac fibrosis of mice lacking guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor A. J Biol Chem 280:19230–19242
Vellaichamy E, Kaur K, Pandey KN (2007) Enhanced activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice lacking natriuretic peptide receptor-A. Peptides 28:893–899
Vellaichamy E, Das S, Subramanian U, Maeda N, Pandey KN (2014) Genetically altered mutant mouse models of guanylyl cyclase/natriuretic peptide receptor-A exhibit the cardiac expression of proinflammatory mediators in a gene-dose dependent manner. Endocrinology 155:1045–1056
Verdu EF, Ahmetaj-Shala B (2016) Systematic study of constitutive cyclooxygenase-2 expression: role of NF-κB and NFAT transcriptional pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:434–439
Vito PD (2014) Atrial natriuretic peptide: an old hormone or a new cytokine? J Pept. 58:108–116
Vollmar AM (2005) The role of atrial natriuretic peptide in the immune system. Peptides 26:1086–1094
Volpe M, Carnovali M, Mastromarino V (2015) The natriuretic peptides system in the pathophysiology of heart failure: from molecular basis to treatment. Clin Sci 130:57–77
Walter L, Harper C, Garg P (2013) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in inflammation/colitis-associated colon cancer. Immunogastroenterology 2:22–28
Weber NC, Blumenthal SB, Hartung T, Vollmar AM, Kiemer AK (2003) ANP inhibits TNF-alpha-induced endothelial MCP-1 expression—involvement of p38 MAPK and MKP-1. J Leukoc Biol 74:932–941
Windgassen EB, Funtowicz L, Lunsford TN (2015) C-reactive protein and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein: an update for clinicians. Postgrad Med 123:114–119
Xing J, Birukova AA (2010) ANP attenuates inflammatory signaling and Rho pathway of lung endothelial permeability induced by LPS and TNFα. Microvasc Res 79:56–62
Xing J, Yakubov B, Poroyko V, Birukova A (2012) Opposite effects of ANP receptors in attenuation of LPS-induced endothelial permeability and lung injury. Microvasc Res 83:194–199
Zhang J, Li M, Yang Y, Yan Y, Li J (2015) NPR-A: a therapeutic target in inflammation and cancer. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 25:41–46
Zhu YB, Zhang YB, Liu DH (2013) Atrial natriuretic peptide attenuates inflammatory responses on oleic acid-induced acute lung injury model in rats. Chin Med J 126:747–750
Acknowledgments
Dr. EV wishes to thank the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), and Department of Biotechnology (DBT), India for the financial support in the form of research project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Lakshmi Priya Kalaiarasu and Vimala Subramanian contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalaiarasu, L.P., Subramanian, V., Sowndharrajan, B. et al. Insight into the Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism of Action of Atrial Natriuretic Peptide, a Heart Derived Peptide Hormone: Involvement of COX-2, MMPs, and NF-kB Pathways. Int J Pept Res Ther 22, 451–463 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-016-9525-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-016-9525-9