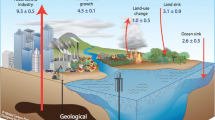
Abstract
Context
Riparian buffers reduce subsurface nutrient losses to streams but there is a clear need to identify and prioritize locations for riparian buffer placement to optimize buffer performance. Scaling relations can be used to extrapolate hydrologic behavior within river networks and across catchments.
Objectives
We combined field and laboratory measurements of soils and groundwater quality collected at five riparian monitoring sites of different stream-order scales with landscape analysis to accomplish the following objectives: (1) evaluate the degree to which riparian zone patterns and processes are scaled in a pre-Wisconsin glacial landscape; and (2) use the scaling information to identify optimal placement of riparian buffers in the landform region for nutrient reduction benefits.
Results
Results indicated that there is proportional scaling of riparian zones within the region in terms of sediment texture, groundwater geochemistry and, to a lesser extent, in groundwater nutrient concentrations.
Conclusions
Placement of riparian buffers should be a priority along low order streams (< 3rd order) to best utilize the scaling characteristics of regional riparian zones, although buffering 2nd and 3rd streams may be the most cost effective locations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman SJ, Parizek RR (1995) Dilution of nonpoint-source nitrate in groundwater. J Environ Qual 24:707–718
Baker RG, Bettis EA III, Denniston RF, Gonzalez LA, Strickland LE, Krieg JR (2002) Holocene paleoenvironments in southeastern Minnesota—chasing the prairie-forest ecotone. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 177:103–122
Bettis EA III, Autin WJ (1997) Complex response of a mid-continent North America drainage system to late Wisconsinan sedimentation. J Sediment Res 67:740–748
Bettis EA III, Baker RG, Green WR, Whelan MK, Benn DW (1992) Late Wisconsinan and Holocene alluvial stratigraphy, paleoecology, and archeological geology of east-central Iowa. Iowa Dept. Natural Resources. Geological Survey Bureau, Iowa City, IA
Bettis EA III, Littke JP (1987) Holocene Alluvial Stratigraphy and Landscape Development In: Soap Creek Watershed. Appanoose, Davis, Monroe, and Wapello Counties, Iowa. Iowa Depart. Natural Resources, Geological Survey Bureau, Iowa City, IA
Bettis EA III (1990) Holocene alluvial stratigraphy and selected aspects of the Quaternary history of western Iowa: guidebook for the 37th field conference of the Midwest Friends of the Pleistocene. Iowa Dept. Natural Resources. Geological Survey Bureau, Iowa City, IA
Bishop K, Buffam I, Erlandsson M, Fölster MJ, Laudon H, Seibert L, Temnerud J (2008) Aqua incognita: the unknown headwaters. Hydrol Process 22:1239–1242
Brooks PD, McKnight DM, Bencala KE (1999) The relationship between soil heterotrophic activity, soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) leachate, and catchment-scale DOC export in headwater catchments. Water Resour Res 35:1895–1902
Burt TP, Matchett LS, Goulding KWT, Webster CP, Haycock NE (1999) Denitrification in riparian buffer zones: the role of floodplain sediments. Hydrol Process 13:1451–1463
Cey EE, Rudolph DL, Aravena R, Parkin G (1999) Role of the riparian zone in controlling the distribution and fate of agricultural nitrogen near a small stream in southern Ontario. J Contam Hydrol 37:45–67
Clement JC, Aquilina L, Bour O, Plaine K, Burt TP, Pinay G, (2003) Hydrological flowpaths and nitrate removal rates within a riparian floodplain along a fourth-order stream in Brittany (France). Hydrol Process 17:1177–1195
Clement J, Pinay G, Marmonier P (2002) Seasonal dynamics of denitrification along tophydrosequences in three different riparian wetlands. J Environ Qual 31:1025–1037
DeVito KJ, Fitzgerald D, Hill AR, Aravena R (2000) Nitrate dynamics in relation to lithology and hydrologic flow path in a river riparian zone. J Environ Qual 29:1075–1084
Dinnes DL, Karlen DL, Jaynes DB, Kaspar TC, Hatfield JL, Colvin TS, Cambardella CA (2002) Nitrogen management strategies to reduce nitrate leaching in tile-drained Midwestern soils. Agron J 94:153–171
Dosskey MG (2001) Toward quantifying water pollution abatement in response to installing buffer on crop land. Environ Manag 28:577–698
Dosskey MG, Helmers MJ, Eisenhauer DE (2006) An approach for using soil surveys to guide the placement of water quality buffers. J Soil Water Conserv 61:344–354
Dunn OJ (1964) Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 6(3):241–252
Dunn WC, Milne BT, Mantilla R, Gupta VK (2011) Scaling relations between riparian vegetation and stream order in the Whitewater River network, Kansas, USA. Landscape Ecol 26:983–997
Duval TP, Hill AR (2007) Influence of base flow stream bank seepage on riparian zone nitrogen biogeochemistry. Biogeochemistry 85:85–199
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis. In: Methods of soil analysis: Part 1—Physical and mineralogical methods. p 383–411
Gold AJ, Groffman PM, Addy K, Kellogg DQ, Stolt M, Rosenblatt AE (2001) Landscape attributes as control on ground water nitrate removal capacity of riparian zones. J Am Water Resour Assoc 37:1457–1464
Grabs T, Bishop K, Laudon H, Lyon SW, Seibert J (2012) Riparian zone hydrology and soil water total organic carbon (TOC): implications for spatial variability and upscaling of lateral riparian TOC exports. Biogeosciences 9:3901–3916
Hallberg GR (1980) Pleistocene stratigraphy in east-central Iowa. Iowa Depart. Natural Resources, Geological Survey Bureau, Iowa City, IA
Hill AR, DeVito KJ, Campagnolo S, Sanmugadas K (2000) Subsurface denitrification in a forest riparian zone: interactions between hydrology and supplies of nitrate and organic carbon. Biogeochemistry 51:193–223
Hill AR, Vidon PGF, Langat J (2004) Denitrification potential in relation to lithology in five headwater riparian zones. J Environ Qual 33:911–919
Horton RE (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins: hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol Soc Am Bull 56:275–370
Hoffmann CC, Kjaergaard C, Uusi-Kämppä J, Hansen HCB, Kronvang B (2009) Phosphorus retention in riparian buffers: review of their efficiency. J Environ Qual 38:1942–1955
Hupp CR (1992) Riparian vegetation recovery patterns following stream channelization: a geomorphic perspective. Ecology 73:1209–1226
Iowa Nutrient Reduction Strategy (INRS) (2013). http://www.nutrientstrategy.iastate.edu/. Accessed 6 March 2013
Jacobs TC, Gilliam JW (1985) Riparian losses of nitrate from agricultural drainage waters. J Environ Qual 14:472–478
Junk WJ, Bayley PB, Sparks RE (1989) The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. Can Spec Publ Fish Aquat Sci 106:110–127
Knox JC (1977) Historical valley sedimentation in the Upper Mississippi valley. Ann Assoc Am Geogr 77:224–244
Laudon H, Sjöblom V, Buffam I, Seibert J, Mörth M (2007) The role of catchment scale and landscape characteristics for runoff generation of boreal streams. J Hydrol 344:198–209
Lee KH, Isenhart TM, Schultz RC, Mickelson SK (2000) Multispecies riparian buffers trap sediment and nutrients during rainfall simulations. J Environ Qual 29:1200–1205
Leopold B, Miller JP (1956) Ephemeral streams-hydraulic factors and their relation to the drainage net. U.S. Geol Professional Papers, 282-A, pp 1–37
Lowrance R (1992) Groundwater nitrate and denitrification in a coastal plain riparian forest. J Environ Qual 21:401–405
Mantilla R, Gupta VK (2005) A GIS numerical framework to study the process basis of scaling statistics in river networks. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 2:404–408
Mayer PM, Reynolds SK, McCutchen MD, Canfield TJ (2006) Riparian buffer width, vegetative cover and nitrogen removal effectiveness: a review of current science and regulations. EPA/600/R-05/118, Cincinnati, OH
McClain ME, Boyer EW, Dent L, Gergel SE, Grimm NB, Groffman PM, Hart SC, Harvey JW, Johnston CA, Mayorga E, McDowell WH, Pinay G (2003) Biogeochemical hot spots and hot moments at the interface of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 6:301–312
McDonnell JJ, Sivapalan M, Vaché K, Dunn S, Grant G, Haggerty R, Hinz C, Hooper R, Kirchner J, Roderick ML, Selker J (2007) Moving beyond heterogeneity and process complexity: a new vision for watershed hydrology. Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006WR005467
McGuire KJ, McDonnell JJ, Weiler M, Kendall C, McGlynn BL, Welker JM, Seibert J (2005) The role of topography on catchment‐scale water residence time. Water Resources Research, 41(5)
Mittelstet AR, Heeren DM, Fox GA, Storm DE, White MJ, Miller RB (2011) Comparison of subsurface and surface runoff phosphorus transport rates in alluvial floodplains. Agric Ecosyst Environ 141:417–425
Newbold JD, Elwood JW, O’Neill RV, Van Winkle W (1981) Measuring nutrient spiraling in streams. Can J Fisher Aquat Sci 38:860–863
Noe GB, Hupp CR, Rybicki NB (2013) Hydrogeomorphology influences soil nitrogen and phosphorus mineralization in floodplain wetlands. Ecosystems 16:75–94
Orellana F, Verma P, Loehide II SP, Daly E (2012) Monitoring and modeling water-vegetation interactions in groundwater-dependent systems. Reviews of Geophysics 50: RG3003
Palmer JA, Schilling KE, Isenhart TM, Schultz RC (2014) Streambank erosion rates and loads with a single watershed: bridging the gap between temporal and spatial scales. Geomorphology 209:66–78
Peterson BJ, Wollheim WM, Mulholland PJ, Webster JR, Meyer JL, Tank JL, Martí E, Bowden WB, Valett HM, Hershey AE, McDowell WH (2001) Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 292:86–90
Pinay G, Black VJ, Planty-Tabacchi AM, Gumiero B, Decamps H (2000) Geomorphic control of denitrification in large river floodplain soils. Biogeochemistry 50:163–182
Prior JC (1991) Landforms of Iowa. University of Iowa Press, Iowa City, IA
Rodriguez-Iturbe I, Rinaldo A (1997) Fractal river basins. Cambridge University Press, New York
Russell MJ, Weller DE, Jordan E, Sigwart KJ, Sullivan KJ (2008) Net anthropogenic phosphorus inputs: spatial and temporal variability in the Chesapeake Bay region. Biogeochemistry 88:285–304
Schilling KE, Drobney P (2014) Restoration of prairie hydrology at the watershed scale: two decades of progress at Neal Smith National Wildlife Refuge. Land 3:206–238
Schilling KE, Jacobson P (2008) Nutrient concentration patterns near an incised stream: effects of floodplain lithology and land management. Biogeochemistry 87:199–216
Schilling KE, Jacobson P (2009) Water uptake and nutrient concentrations under a floodplain oak savanna during a non-flood period, lower Cedar River, Iowa. Hydrol Process 23:3006–3016
Schilling KE, Jacobson P (2011) Spatial relations of topography, lithology and water quality in a large river floodplain. River Res Appl. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.1531
Schilling KE, Jacobson P (2014) Effectiveness of perennial riparian buffers to reduce subsurface nutrient losses to incised streams in southern Iowa. CATENA 114:140–148
Schilling KE, Jacobson P (2016) Water and nutrient discharge to a high-value terrace-floodplain fen: resilience and risk. Ecohydrology. https://doi.org/10.1002/eco.1718
Schilling KE, Li Z, Zhang YK (2006) Groundwater-surface water interaction in the riparian zone of an incised channel, Walnut Creek, Iowa. J Hydrol 327:140–150
Schilling KE, McLellan E, Bettis EA III (2013) Letting wet spots be wet: restoring natural bioreactors in the dissected glacial landscape. Environ Manag 52:1440–1452
Schilling KE, Palmer JA, Bettis EA III, Jacobson P, Schultz RC, Isenhart TM (2009) Vertical distribution of total carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in riparian soils of Walnut Creek, southern Iowa (USA). CATENA 77:266–273
Schilling KE, Tomer MD, Zhang YK, Weisbrod T, Jacobson P, Cambardella CA (2007) Hydrogeologic controls on nitrate transport in a small agricultural catchment, Iowa. J Geophys Res 112:G03007
Schilling KE, Zhang YK, Drobney P (2004) Water table fluctuations near an incised stream, Walnut Creek, Iowa. J Hydrol 286:236–248
Schoonover JE, Williard KWJ (2003) Ground water nitrate reduction in giant cane and forest riparian buffer zones. J Am Water Resour Assoc 39:347–354
Schultz RC, Colletti JP, Isenhart TM, Simpkins WW, Mize CW, Thompson ML (1995) Design and placement of a multi-species riparian buffer strip. Agrofor Syst 29:201–225
Shields FD, Knight SS, Cooper CM (1995) Rehabilitation of watersheds with incising channels. Water Resour Bull 31:971–982
Simon A (1989) A model of channel response in disturbed alluvial channels. Earth Surf Proc Land 14:11–26
Sivapalan M (2003) Process complexity at hillslope scale, process simplicity at the watershed scale: is there a connection? Hydrol Process 17:1037–1041
Soulsby C, Tetzlaff D, Rodgers P, Dunn S, Waldron S (2006) Runoff processes, stream water residence times and controlling landscape characteristics in a mesoscale catchment: an initial evaluation. J Hydrol 325:197–221
Speed M, Tetzlaff D, Soulsby C, Hrachowitz M, Waldron S (2010) Isotopic and geochemical tracers reveal similarities in transit times in contrasting mesoscale catchments. Hydrol Process 24:1211–1224
Spruill TB (2000) Statistical evaluation of effects of riparian buffers on nitrate and ground water quality. J Environ Qual 29:1523–1538
Strahler AN (1952) Dynamic basis of geomorphology. Geol Soc Am Bull 63:923–938
Tetzlaff D, Carey SK, Laudon H, McGuire K (2010) Catchment processes and heterogeneity at multiple scales—Benchmarking observations, conceptualization and prediction. Hydrol Process 24:2203–2208
Tetzlaff D, Seibert J, McGuire KJ, Laudon H, Burns DA, Dunn SM, Soulsby C (2009) How does landscape structure influence catchment transit time across different geomorphic provinces? Hydrol Process 23:945–953
Thorp JH, Thoms MC, DeLong MD (2006) The riverine ecosystem synthesis: biocomplexity in river networks across space and time. River Res Appl 22:123–147
Tomer MD, Dosskey Burkart MR, James DE, Helmers MJ, Eisenhauer DE (2009) Methods to prioritize placement of riparian buffers for improved water quality. Agrofor Syst 75:17–25
Tomer MD, Schilling KE, Cambardella CA, Jacobson P, Drobney P (2010) Groundwater nutrient concentrations during prairie reconstruction on an Iowa landscape. Agric Ecosyst Environ 139:206–213
Troch PA, Carrillo GA, Heidbüchel I, Rajagopal S, Switanek M, Volkmann TH, Yaeger M (2009) Dealing with landscape heterogeneity in watershed hydrology: a review of recent progress toward new hydrological theory. Geogr Compass 3:375–392
Turner RE, Rabalais N, Justic D (2008) Gulf of Mexico hypoxia: altered states and a legacy. Environ Sci Technol 42:2323–2327
Vannote RL, Minshall GW, Cummins KW, Cushing JR (1980) The river continuum concept. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 37:130–137
Vidon PGF, Hill AR (2004) Landscape controls on the hydrology of stream riparian zones. J Hydrol 292:210–228
Vidon PG, Hill AR (2006) A landscape-based approach to estimate riparian hydrological and nitrate removal functions. J Am Water Resour Assoc 42:1099–1112
Wiens JA (1989) Spatial scaling in ecology. Funct Ecol 3:385–397
Withers PJA, Jarvie HP (2008) Delivery and cycling of phosphorus in rivers: a review. Sci Total Environ 400:379–395
Zaimes GN, Schultz RC, Isenhart TM (2008) Streambank Soil and Phosphorus Losses Under Different Riparian Land-Uses in Iowa. J Am Water Resourc Assoc 44:935–947
Zhang X, Liu X, Zhang M, Dahlgren RA, Eitzel M (2010) A review of vegetated buffers and a meta-analysis of their mitigation efficacy in reducing nonpoint source pollution. J Environ Qual 39:76–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schilling, K.E., Jacobson, P.J. & Wolter, C.F. Using riparian Zone scaling to optimize buffer placement and effectiveness. Landscape Ecol 33, 141–156 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-017-0589-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-017-0589-5