Abstract
Context
The relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning (BEF) is a central topic in ecology on local, regional, and global scales. A powerful approach to BEF studies is large-scale field manipulative experimentation.
Objectives
The Inner Mongolian Grassland Removal Experiment (IMGRE) was designed to examine the mechanisms of the BEF relationship in the world’s largest grassland, explicitly considering multiple trophic levels and grazing by grasshoppers and sheep.
Methods
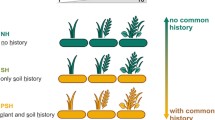
IMGRE followed a randomized block design, with a total of 512 plots (6 m × 6 m each). The project involved massive field campaigns and laboratory analyses, and unprecedentedly employed two removal protocols in parallel: complete removal (eradicating all targeted functional types) and partial removal (an equal-disturbance removal scheme).
Results
We summarize key findings on aboveground and belowground primary production, functional richness, identity, and composition, compensation at the species, PFT, and community levels, soil water and N retention, net N mineralization, microbial biomass, and grazing by grasshoppers and sheep. Comparing and contrasting results from the two removal protocols, we have found that the responses of ecosystem processes depend on plant functional richness and identity, as well as disturbance characteristics.
Conclusions
As part of the special issue on the ecological patterns and processes in the Inner Mongolian Plateau, this article provides an overview of the IMGRE project. The findings of this project shed new light on the BEF relationship in natural grasslands, and have important implications for ecosystem management in the Mongolian Plateau.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Y, Han X, Wu J, Chen Z, Li L (2004) Ecosystem stability and compensatory effects in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Nature 431:181–184
Bai YF, Wu J, Pan QM, Huang JH, Wang QB, Li FS, Buyantuyev A, Han XG (2007) Positive linear relationship between productivity and diversity: evidence from the Eurasian Steppe. J Appl Ecol 44(5):1023–1034
Bai Y, Wu JG, Clark CM, Naeem S, Pan Q, Huang J, Zhang L, Han X (2010) Tradeoffs and thresholds in the effects of nitrogen addition on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: evidence from Inner Mongolia grasslands. Glob Change Biol 16(1):358–372
Cadotte MW (2013) Experimental evidence that evolutionarily diverse assemblages result in higher productivity. PNAS 110:8996–9000
Cardinale BJ, Duffy JE, Gonzalez A, Hooper DU, Perrings C, Venail P, Narwani A, Mace GM, Tilman D, Wardle DA, Kinzig AP, Daily GC, Loreau M, Grace JB, Larigauderie A, Srivastava DS, Naeem S (2012) Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 486:59–67
Cease AJ, Hao SG, Kang L, Elser JJ, Harrison JF (2010) Are color or high rearing density related to migratory polyphenism in the band-winged grasshopper, Oedaleus asiaticus? J Insect Physiol 56(8):926–936
Cease AJ, Elser JJ, Ford CF, Hao SG, Kang L, Harrison JF (2012) Heavy livestock grazing promotes locust outbreaks by lowering plant nitrogen content. Science 335(6067):467–469
Díaz S, Symstad AJ, Chapin FS III, Wardle DA, Huenneke LF (2003) Functional diversity revealed by removal experiments. Trends Ecol Evol 18:140–146
Downing AL, Liebold MA (2002) Ecosystem consequences of species richness and composition in pond food webs. Nature 416:837–841
Duffy JE (2002) Biodiversity and ecosystem function: the consumer connection. Oikos 99:201–219
Duffy JE, McDonald SK, Rhode JM, Parker JD (2001) Grazer diversity, functional redundancy, and productivity in seagrass beds: an experimental test. Ecology 82:2417–2434
Ehleringer JR, Dawson TE (1992) Water-uptake by plants: perspectives from stable isotope composition. Plant Cell Environ 15:1073–1082
Elser JJ, Sterner RW, Gorokhova E, Fagan WF, Markow TA, Cotner JB, Harrison JF, Hobbie SE, Odell GM, Weider LW (2001) Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecol Lett 3:540–550
Flynn DFB, Mirotchnick N, Jain M, Palmer MI, Naeem S (2011) Functional and phylogenetic diversity as predictors of biodiversity–ecosystem-function relationships. Ecology 92:1573–1581
Fridley JD (2003) Diversity effects on production in different light and fertility environments: an experiment with communities of annual plants. J Ecol 91(3):396–406
Heemsbergen DA, Berg MP, Loreau M, van Hal JR, Faber JH, Verhoef HA (2004) Biodiversity effects on soil processes explained by interspecific functional dissimilarity. Science 306(5698):1019–1020
Hooper DU (1998) The role of complementarity and competition in ecosystem responses to variation in plant diversity. Ecology 79(2):704–719
Hooper DU, Vitousek PM (1998) Effects of plant composition and diversity on nutrient cycling. Ecol Monogr 68:121–149
Hooper DU, Chapin FS III, Ewel JJ, Hector A, Inchausti P, Lavorel S, Lawton JH, Lodge DM, Loreau M, Naeem S, Schmid B, Setala H, Symstad AJ, Vandermeer J, Wardle DA (2005) Effects of biodiversity on ecosystem functioning: a consensus of current knowledge. Ecol Monogr 75:3–35
Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ, Byrnes JE, Hungate BA, Matulich KL, Gonzalez A, Duffy JE, Gamfeldt L, O’Connor MI (2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature 486:105–108
Huston MA (1997) Hidden treatments in ecological experiments: re-evaluating the ecosystem function of biodiversity. Oecologia 110(5):449–460
Li A, Wu JG, Huang JH (2012) Distinguishing between human-induced and climate-driven vegetation changes: a critical application of RESTREND in Inner Mongolia. Landscape Ecol 27(7):969–982
Liu W, Wand JM, Wang ZP (2011) Plant functional type effects on methane uptake by soils in typical grasslands of Inner Mongolia. Chin J Plant Ecol 35:275–283
Loreau M (1998) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: A mechanistic model. Proc Natl Acad Sci 95:5632–5636
Loreau M (2000) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: recent theoretical advances. Oikos 91(1):3–17
Loreau M, Hector A (2001) Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature 412:72–76
Loreau M, Naeem S, Inchausti P (eds) (2002) Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning: synthesis and perspectives. Oxford University Press, Oxford
McNaughton SJ (1977) Diversity and stability of ecological communities: a comment on the role of empiricism in ecology. Am Nat 111:515–525
MEA (2005) Ecosystems and human well-being: current state and trends. Island Press, Washington
Mulder CPH, Koricheva J, Huss-Danell K, Högberg P, Joshi J (1999) Insects affect relationships between plant species richness and ecosystem processes. Ecol Lett 2:237–246
Naeem S (2002a) Disentangling the impacts of diversity on ecosystem functioning in combinatorial experiments. Ecology 83:2925–2935
Naeem S (2002b) Ecosystem consequences of biodiversity loss: the evolution of a paradigm. Ecology 83:1537–1552
Naeem S, Li S (1997) Biodiversity enhances ecosystem reliability. Nature 390:507–509
Naeem S, Wright JP (2003) Disentangling biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning: deriving solutions to a seemingly insurmountable problem. Ecol Lett 6:567–579
Naeem S, Thompson LJ, Lawler SP, Lawton JH, Woodfin RM (1994) Declining biodiversity can alter the performance of ecosystems. Nature 368:734–737
Naeem S, Bunker DE, Hector A, Loreau M, Perrings C (eds) (2009) Biodiversity, ecosystem functioning, and human wellbeing: an ecological and economic perspective. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Naeem S, Duffy JE, Zavaleta E (2012) The functions of biological diversity in an age of extinction. Science 336(6087):1401–1406
Norberg J (2000) Resource-niche complementarity and autotrophic compensation determines ecosystem-level responses to increased cladoceran species richness. Oecologia 122:264–272
Pan QM, Bai YF, Wu JG, Han XG (2011) Hierarchical plant responses and diversity loss after nitrogen addition: testing three functionally-based hypotheses in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Plos One 6(5):ARTN e20078. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020078
Petchey OL, Hector A, Gaston KJ (2004) How do different measures of functional diversity perform? Ecology 85:847–857
Pfisterer AB, Schmid B (2002) Diversity-dependent production can decrease the stability of ecosystem functioning. Nature 416:84–86
Pimm SL (1984) The complexity and stability of ecosystems. Nature 307:321–326
Solan M, Cardinale BJ, Downing AL, Engelhardt KAM, Ruesink JL, Srivastava DS (2004) Extinction and ecosystem function in the marine benthos. Science 306:1177–1180
Srivastava DS, Vellend M (2005) Biodiversity-ecosystem function research: is it relevant to conservation? Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 36:267–290
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Su YY, Guo LD, Hyde KD (2010) Response of endophytic fungi of Stipa grandis to experimental plant function group removal in Inner Mongolia steppe, China. Fungal Divers 43(1):93–101
Sun XF, Huang JH, Wang M, Han XG (2009) Responses of litter decomposition to biodiversity manipulation in the Inner Mongolia grassland of China. Biodivers Sci 17:397–405
Symstad A, Tilman D (2001) Diversity loss, recruitment limitation, and ecosystem functioning: lessons learned from a removal experiment. Oikos 92:424–435
Symstad AJ, Chapin FS, Wall DH et al (2003) Long-term and large-scale perspectives on the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Bioscience 53(1):89–98
Tilman D (1997) Distinguishing the effects of species diversity and species composition. Oikos 80:185
Tilman D (1999) The ecological consequences of changes in biodiversity: a search for general principles. Ecology 80(5):1455–1474
Tilman D, Wedin D, Knops J (1996) Productivity and sustainability influenced by biodiversity in grassland ecosystems. Nature 379:718–720
Wardle DA (2002) Communities and ecosystems: linking the aboveground and belowground components. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Wardle DA, Grime JP (2003) Biodiversity and stability of grassland ecosystem functioning. Oikos 100(3):622–623
Wardle DA, Bonner KI, Barker GM et al (1999) Plant removals in perennial grassland: Vegetation dynamics, decomposers, soil biodiversity, and ecosystem properties. Ecol Monogr 69:535–568
Wardle DA, Bardgett RD, Klironomos JN, Setala H, van der Putten WH, Wall DH (2004a) Ecological linkages between aboveground and belowground biota. Science 304(5677):1629–1633
Wardle DA, Walker LR, Bardgett RD (2004b) Ecosystem properties and forest decline in contrasting long-term chronosequences. Science 305(5683):509–513
Wu J (2013) Landscape sustainability science: ecosystem services and human well-being in changing landscapes. Landscape Ecol 28(6):999–1023
Wu J, Loucks OL (1992) Xilingole grassland. In: US National Research Council (ed) Grasslands and grassland sciences in Northern China. National Academy Press, Washington, pp 67–84
Wu J, Loucks OL (1995) From balance of nature to hierarchical patch dynamics: a paradigm shift in ecology. Q Rev Biol 70(4):439–466
Wu J, Bai Y, Han X, Li L, Chen Z (2005) Ecosystem stability in Inner Mongolia. Nature 435:E6–E7. doi:10.1038/nature03584
Yu Q, Chen Q, Elser JJ, He N, Wu H, Zhang G, Wu J, Bai Y, Han X (2010) Linking stoichiometric homeostasis with ecosystem structure, functioning, and stability. Ecol Lett 13:1390–1399
Yuan F, Wu J, Li A, Rowe H, Bai Y, Huang J, Han X (2015) Spatiotemporal patterns of soil nutrients, plant diversity, and aboveground biomass during a biodiversity removal experiment in Inner Mongolia. Landscape Ecol 30. doi:10.1007/s10980-015-0154-z
Zhang GM, Han XG, Elser JJ (2011) Rapid top-down regulation of plant C:N:P stoichiometry by grasshoppers in an Inner Mongolia grassland ecosystem. Oecologia 166(1):253–264
Acknowledgments
The IMGRE research was supported by National Science Foundation (NSF, DEB-0618193) as well as grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), and Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this publication are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of NSF, NSFC, or CAS. We thank all our collaborators and graduate students from both the Chinese and American institutions for their participation in the IMGRE project. Also, comments from two anonymous reviewers are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, J., Naeem, S., Elser, J. et al. Testing biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relationship in the world’s largest grassland: overview of the IMGRE project. Landscape Ecol 30, 1723–1736 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0155-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0155-y