Abstract
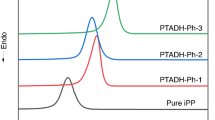
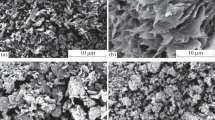
In this work, the applicability of a series of bisamide compounds (DCDC-R-n/R) with different structures as nucleating agents for isotactic polypropylene (iPP) was investigated. The effect of these nucleating agents on crystallization and melting behavior of iPP was analyzed using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), results revealing a clear impact on the nucleus density in iPP. It is shown that the nucleation effect is better when the carbon number of the methylene chain in the intermediate structure is even rather than odd. In addition, the effect is stronger when the side substitution is a cyclic group rather than a branched group, while bisamide nucleating agents containing a cyclic intermediate group tends to form more β-crystals in iPP. The crystallization peak temperature (\({T}_{\mathrm{c}})\) of iPP can be increased by more than 10 °C when the addition amount of DCDA-Cy-4, DCDA-Cy-6 and DCDA-Cp-6 is 0.3 mass%. The analysis of the iPP mechanical properties shows that DCDA-Cy-4 and DCDA-Cy-6 greatly improve its stiffness, while DCDA-Cy-Cy and DCDA-Cy-pPh have an excellent toughening effect on iPP as a result of β-phase. The structure-nucleation effect relationship of bisamide compounds was confirmed by further tests using wide-angle X-ray diffractometer (WAXD) and Materials Studio, showing good agreement with DSC data. Furthermore, the nucleation mechanism of these nucleating agents in iPP was investigated by using the lattice matching theory. The unit cell parameters of nucleating agents and iPP match well, indicating that these nucleating agents can induce epitaxial growth of iPP on their surface.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lotz B, Wittmann JC, Lovinger AJ. Structure and morphology of poly(propylenes): a molecular analysis. Polymer. 1996;37:4979–92.
Varga J. β-modification of isotactic polypropylene: preparation, structure, processing, properties, and application. J Macromol Sci, Part B. 2007;41:1121–71.
Menyhárd A, Bredács M, Simon G, Horváth Z. Determination of nucleus density in semicrystalline polymers from nonisothermal crystallization curves. Macromolecules. 2015;48:2561–9.
Kawaia T, Iijimaa R, Yamamotob Y, Kimura T. Crystal orientation of b-phase isotactic polypropylene induced by magnetic orientation of N, N’-dicyclohexyl-2,6-naphthalenedicarboxamide. Polymer. 2002;43:7301–6.
An YJ, Zhang ZJ, Bi WG, Wang YH, Tang T. Characterization of high melt strength polypropylene synthesized via silane grafting initiated byin situheat induction reaction. J Appl Polym Sci. 2008;110:3727–32.
Xie L, Zhong JR, Li Y, Zhang YF. In-situ synthesis of calcium pimelate as a highly dispersed β-nucleating agent for improving the crystallization behavior and mechanical properties of isotactic polypropylene. Polym Advan Technol. 2023;34:377–385.
Liu ZZ, Zheng GQ, Shi HH, Liu CT, Mi LW, Li Q, Liu XH. Simultaneous enhancement of toughness and strength of stretched ipp film via tiny amount of β-nucleating agent under “shear-free” mel-extrusion. Chin J Polym Sci. 2021;39:1481–8.
Zhao SC, Qin W, Xin Z, Zhou S, Gong HZ, Ni YM, Zhang K. In situ generation of a self-dispersed β-nucleating agent with increased nucleation efficiency in isotactic polypropylene. Polymer. 2018;151:84–91.
Kotek J, Kelnar I, Baldrian J, Raab M. Tensile behaviour of isotactic polypropylene modified by specific nucleation and active fillers. Eur Polym J. 2004;40:679–84.
Bai HW, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Liu L, Zhou ZW. A comparative study of polypropylene nucleated by individual and compounding nucleating agents I melting and isothermal crystallization. J Appl Polym Sci. 2009;111:1624–37.
Deshmukh YS, Wilsens CHRM, Leoné N, Portale G, Harings JAW, Rastogi S. Melt-miscible oxalamide based nucleating agents and their nucleation efficiency in isotactic polypropylene. Ind EngChemRes. 2016;55:11756–66.
Yue Y, Wang XX, Feng JC. Concentration effect of a bis-amide nucleating agent on the shear-induced crystallization behavior of isotactic polypropylene. ACS Appl Energy Mater. 2021;3:1145–56.
Yang R, Ding L, Chen WL, Chen L, Zhang X, Li JC. Chain folding in main-chain liquid crystalline polyester with strong π-π interaction: an efficient β-nucleating agent for isotactic polypropylene. Macromolecules. 2017;50:1610–7.
Wang B, Utzeri R, Castellano M, Stagnaro P, Müller AJ, Cavallo D. Heterogeneous nucleation and self-nucleation of isotactic polypropylene microdroplets in immiscible blends: from nucleation to growth-dominated crystallization. Macromolecules. 2020;53:5980–91.
Zhou H, Zhang YF. Effect of aromatic dihydrazide compounds on crystallization behavior and mechanical properties of isotactic polypropylene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;147:6239–47.
Horváth F, Bihari L, Menyhárd A. Effect of N, N’-dicyclohexyl terephthalic dihydrazide on the crystallization and properties of isotactic polypropylene. Period Polytech Chem Eng. 2022;66(2):182–91.
Chang BB, Schneider K, Vogel R, Heinrich G. Influence of nucleating agent self-assembly on structural evolution of isotactic polypropylene during uniaxial stretching. Polymer. 2018;138:329–42.
Niu H, Wang N, Li Y. Influence of β-nucleating agent dispersion on the crystallization behavior of isotactic polypropylene. Polymer. 2018;150:371–9.
Wang Y, Zhao J, Qu MJ, Guo J, Yang SG, Lei J, Xu JZ, Chen YH, Li ZM, Hsiao BS. An unusual promotion of γ-crystals in metallocene-made isotactic polypropylene from orientational relaxation and favorable temperature window induced by shear. Polymer. 2018;134:196–203.
Wilsens CHRM, Hawke LGD, Kort GWd, Saidi S, Roy M, Leone N, Hermida-Merino D, Peters GWM, Rastogi S. Effect of thermal history and shear on the viscoelastic response of iPP containing an oxalamide-based organic compound. Macromolecules. 2019;52:2789–802.
Ding C, Wu GG, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Yin B, Yang MB. Effect of surfactant assisted β-nucleating agent self-assembly on the crystallization of polypropylene. Polymer. 2019;184:121895.
Wang BH, Wang G, He SS, Sun TC, Chen JB, Shen CY, Zhang B. Self-nucleation of β-form isotactic polypropylene lamellar crystals in thin films. Macromolecules. 2021;54:11404–11.
Rhoades AM, Gohn AM, Seo J, Androsch R, Colby RH. Sensitivity of polymer crystallization to shear at low and high supercooling of the melt. Macromolecules. 2018;51:2785–95.
Sowinski P, Piorkowska E, Boyer SAE, Haudin JM. On the structure and nucleation mechanism in nucleated isotactic polypropylene crystallized under high pressure. Polymer. 2018;151:179–86.
Mohmeyer N, Schmidt HW, Kristiansen PM, Altstädt V. Influence of chemical structure and solubility of bisamide additives on the nucleation of isotactic polypropylene and the improvement of its charge storage properties. Macromolecules. 2006;39:5760–7.
Horvath F, Bihari L, Bodrogi D, Gombar T, Hilt B, Keszei B, Krain T, Simon A, Menyhard A. Effect of N, N’-dicyclohexyldicarboxamide homologues on the crystallization and properties of isotactic polypropylene. ACS Omega. 2021;6:9053–65.
Xia MQ, Zhang YF. The relation between chemical structure of branched amide nucleating agents and nucleation effect in isotactic polypropylene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;145:3053–66.
Zhang X, Zhao SC, Kuo SW, Chen WC, Mohamed MG, Xin Z. An effective nucleating agent for isotactic polypropylene (iPP): zinc bis- (nadic anhydride) double-decker silsesquioxanes. Polymer. 2021;220:123574.
Zhang YF, Mao JJ, Zhou PZ. The relation between chemical structure of dicarboxylic dihydrazide compounds and nucleation effect in isotactic polypropylene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2021;145:2379–87.
Horváth F, Bodrogi D, Hilt B, Pregi E, Menyhárd A. Organogelators with dual β- and α-nucleating ability in isotactic polypropylene. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2022;147:9451–68.
Phulkerd P, Yamazaki A, Iwasaki S, Yamaguchi M. Effect of molecular weight on molecular orientation and morphology of polypropylene sheets containing a β-nucleating agent. Polym Eng Sci. 2020;61:367–78.
Ma YJ, Xin ML, Xu K, Chen MC. A novel β-nucleating agent for isotactic polypropylene. Polym Int. 2013;62:744–50.
Kotek J, Raab M, Baldrian J, Grellmann W. The effect of specific β-nucleation on morphology and mechanical behavior of isotactic polypropylene. J Appl Polym Sci. 2002;85:1174–84.
Raab M, Ščudla J, Kolařı́K J. The effect of specific nucleation on tensile mechanical behaviour of isotactic polypropylene. Eur Polym J. 2004;40:1317–23.
Song B, Wang Y, Bai HW, Liu L, Li YL, Zhang JH, Zhou ZW. Crystallization and melting behaviors of maleic anhydride grafted poly(propylene) nucleated by an aryl amide derivative. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;99:563–70.
Kang J, Wang B, Peng H, Li J, Chen J, Gai J, Cao Y, Li HL, Yang F, Xiang M. Investigation on the dynamic crystallization and melting behavior of β-nucleated isotactic polypropylene with different stereo-defect distribution-the role of dual-selective β-nucleation agent. Polym Adv Technol. 2014;25:97–107.
Shentu BQ, Li JP, Weng ZX. Additive effects of N, N, N′, N′-tetraalkyl terephthalamide on crystalline morphology and mechanical properties of polypropylene. J ZheJiang Univ-Sci A. 2006;7:330–4.
Zhang ZS, Chen CY, Wang CG, Guo JQ, Mai KC. Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of isotactic polypropylene nucleated with a novel supported β-nucleating agent. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;103:311–8.
Varga J, Stoll K, Menyhárd A, Horváth Z. Crystallization of isotactic polypropylene in the presence of a β-nucleating agent based on a trisamide of trimesic acid. J Appl Polym Sci. 2011;121:1469–80.
Zhang YF, Chen H. Effects of nucleating agent 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid tris(cyclohexylamide) on properties and crystallization behaviors of isotactic polypropylene. Colloid Polym Sci. 2013;292:493–8.
Zhang YF, Chen H, Liu BB, Gu YH, Li XX. Isothermal and non-isothermal crystallization of isotactic polypropylene nucleated with 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid tris(cyclohexylamide). Thermochim Acta. 2014;590:226–31.
Zhang YF, Zhou PZ, Guo LH, Hou HH. The relationship between crystal structure and nucleation effect of 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid tris(phenylamide) in isotactic polypropylene. Colloid Polym Sci. 2017;295:619–26.
Zhang YF, Zhou PZ, Jiang YZ, Yang X. The relationship between side chain isomerism of aliphatic C4 substituted 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylamides and nucleation effects in isotactic polypropylene. Thermochim Acta. 2017;655:219–25.
Yue Y, Feng JC. Structure evolution upon heating and cooling and its effects on nucleation performance: a review on aromatic amide β-nucleating agents for isotactic polypropylene. Polym Cryst. 2019;2:e10049.
Menyhárd A, Molnár J, Horváth Z, Horváth F, Cavallo D, Polyák P. Self-organization of micro reinforcements and the rules of crystal formation in polypropylene nucleated by non-selective nucleating agents with dual nucleating ability. Polym Cryst. 2020;3:e10136.
Yue Y, Yi JJ, Wang L, Feng JC. Toward a more comprehensive understanding on the structure evolution and assembly formation of a bisamide nucleating agent in polypropylene melt. Macromolecules. 2020;53:4381–94.
Liu LY, Zhao Y, Zhang CB, Dong ZY, Wang KZ, Wang DJ. Morphological characteristics of β-nucleating agents governing the formation of the crystalline structure of isotactic polypropylene. Macromolecules. 2021;54:6824–34.
Ding C, Yang Y, Liu L, Wu GG, Yin B, Yang MB. Surfactant-assisted β-NA supramolecular self-assembly in mini injection molding PP composite. Polymer. 2020;204:122816.
Schmidt HW, Smith P, Blomenhofer M. Polypropylene resin compositions.: U.S. Pat., US7235191.
Jones AT, Aizlewood JM, Beckett DR. Crystalline forms of isotactic polypropylene. MacromolChem Phys. 1964;75:134–58.
Qin W, Zhang XX, Shao LS, Xin Z, Ling H, Zhao SC. Failure mechanism of zinc adipate as a β-nucleating agent for polypropylene in the presence of calcium stearate. Polymer. 2021;215:123374.
Bhatia A, Jayaratne VN, Simon GP, Edward GH, Turney TW. Nucleation of isotactic polypropylene with metal monoglycerolates. Polymer. 2015;59:110–6.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of Changsha (No. kq2202184), Postgraduate Scientific Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province (No. CX20210815), Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Materials Protection for Electric Power and Transportation (No. 2021CL03) and Hunan Provincial Science & Technology Department (No. 2021GK5007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, J., Li, Y., Zhong, JR. et al. Influence of chemical structures of bisamide nucleating agents on the crystallization behavior and properties of isotactic polypropylene. J Therm Anal Calorim 148, 2417–2428 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11874-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-022-11874-8