Abstract
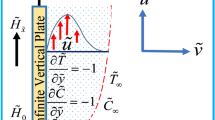
In the current article, an effort has been made to model the forced convection flow phenomenon of magnetized viscoelastic fluid near a stagnation point. Moreover, Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model and the impact of uniform heat rise/fall are employed to examine the aspects of thermal energy transport. Additionally, the scrutiny of the fluid concentration feature by utilizing homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions is also an important effort of the present investigation. Ordinary differential equations (ODEs) are achieved by adopting the method of similarity transformations. The characteristics of physical parameters are assessed by employing numerical technique BVP Midrich scheme. Pertained outcomes are depicted in the form of graphs. The thermal distribution of Burgers’ fluid exhibits a diminishing trend for escalation in the extent of thermal relaxation heat flux parameter. Moreover, the concentration rate of the fluid deteriorates for higher strength of homogenous response, whereas it augments for greater magnitude of heterogeneous response. The validation of the present investigation is ensured by comparing with already published studies. The numerical values for the coefficient of heat transfer rate of Burgers’ fluid are also computed and depicted in graph.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fourier JBJ. Théorie Analytique De La Chaleur, Paris; 1822.
Cattaneo C. Sulla conduzione del calore, Atti Semin. Mat Fis Univ Modena Reggio Emilia. 1948;3:83–101.
Christov CI. On frame indifferent formulation of the Maxwell–Cattaneo model of finite-speed heat conduction. Mech Res Commun. 2009;36:481–6.
Straughan B. Thermal convection with the Cattaneo–Christov model. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2010;53:95–8.
Ciarletta M, Straughan B. Uniqueness and structural stability for the Cattaneo–Christov equations. Mech Res Commun. 2010;37:445–7.
Haddad SAM. Thermal instability in Brinkman porous media with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;68:659–68.
Tibullo V, Zampoli V. A uniqueness result for the Cattaneo–Christov heat conduction model applied to incompressible fluids. Mech Res Commun. 2011;38:77–9.
Han S, Zheng L, Li C, Zhang X. Coupled flow and heat transfer in viscoelastic fluid with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Appl Math Lett. 2014;38:87–93.
Hayat T, Khan MI, Farooq M, Alsaedi A, Waqas M, Yasmeen T. Impact of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model in flow of variable thermal conductivity fluid over a variable thicked surface. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;99:702–10.
Waqas M, Hayat T, Farooq M, Shehzad SA, Alsaedi A. Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model for flow of variable thermal conductivity generalized Burgers fluid. J Mol Liq. 2016;220:642–8.
Malik R, Khan M, Mushtaq M. Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model for Sisko fluid flow past a permeable non-linearly stretching cylinder. J Mol Liq. 2016;222:430–4.
Khan M, Ahmad L, Khan WA, Alshomrani AS, Alzahrani AK, Alghamdi MS. A 3D Sisko fluid flow with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model and heterogeneous-homogeneous reactions: a numerical study. J Mol Liq. 2017;238:19–26.
Hsiao KL. Combined electrical MHD heat transfer thermal extrusion system using Maxwell fluid with radiative and viscous Dissipation effects. Appl Therm Eng. 2017;112:1281–8.
Hsiao KL. Stagnation electrical MHD nanofluid mixed convection with slip boundary on a stretching sheet. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;98:850–61.
Hsiao KL. To promote radiation electrical MHD activation energy thermal extrusion manufacturing system efficiency by using Carreau-nanofluid with parameters control method. Energy. 2017;130:486–99.
Hsiao KL. Micropolar nanofluid flow with MHD and viscous dissipation effects towards a stretching sheet with multimedia feature. Int J Heat and Mass Transf. 2017;112:983–90.
Irfan M, Khan M, Khan WA. On model for three-dimensional Carreau fluid flow with Cattaneo–Christov double diffusion and variable conductivity: a numerical approach. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. 2018;40:577.
Alamri SZ, Khan AA, Azeez M, Ellahi R. Effects of mass transfer on MHD second grade fluid towards stretching cylinder: a novel perspective of Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model. Phy Lett A. 2019;383:276–81.
Iqbal Z, Khan M, Ahmed A, Ahmed J, Hafeez A. Thermal energy transport in Burgers nanofluid flow featuring the Cattaneo–Christov double diffusion theory. Appl Nanosci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01386-y.
Ahmed S, Nadeem S, Muhammad N, Khan MN. Cattaneo–Christov heat flux model for stagnation point flow of micropolar nanofluid toward a nonlinear stretching surface with slip effects. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09504-2.
Rahman UJ, Khan U, Ahmad S, Ramzan M, Suleman M, Lu D, Inam S. Numerical simulation of Darcy–Forchheimer 3D unsteady nanofluid flow comprising carbon nanotubes with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux and velocity and thermal slip conditions. Processes. 2019;7(10):687.
Ahmad S, Nadeem S. Cattaneo–Christov-based study of SWCNT–MWCNT/EG Casson hybrid nanofluid flow past a lubricated surface with entropy generation. Appl Nanosci. 2020;10:10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01367-1.
Nadeem S, Ahmad S, Muhammad N. Analysis of ferrite nanoparticles in liquid. Pramana J Phys. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-019-1913-1.
Chaudhary MA, Merkin JH. A simple isothermal model for homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary-layer flow. I equal diffusivities. Fluid Dyn Res. 1995;16:311–33.
Merkin JH. A model for isothermal homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in boundary layer flow. Math Comput Model. 1996;24:125–36.
Hayat T, Khan MI, Farooq M, Yasmeen T, Alsaedi A. Stagnation point flow with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux and homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. J Mol Liq. 2016;220:49–55.
Xu H. A homogeneous-heterogeneous reaction model for heat fluid flow in the stagnation region of a plane surface. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2017;87:112–7.
Hayat T, Haider F, Muhammad T, Ahmad B. Darcy-Forchheimer flow of carbon nanotubes due to a convectively heated rotating disk with homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;137:1939–49.
Hayat T, Aziz A, Muhammad T, Alsaedi A. Significance of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in Darcy–Forchheimer three-dimensional rotating flow of carbon nanotubes. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139:183–95.
Ahmed J, Khan M, Ahmed L. Effectiveness of homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions in Maxwell fluid flow between two spiraling disks with improved heat conduction features. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020;139:3185–95.
Khan M, Ahmed J, Ali W. An improved heat conduction analysis in swirling viscoelastic fluid with homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09342-2.
Khan M, Ahmed A, Ahmed J. Analysis of Cattaneo–Christov theory for unsteady flow of Maxwell fluid over stretching cylinder. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09343-1.
Hafeez A, Khan M, Ahmed J. Thermal aspects of chemically reactive Oldroyd-B fuid flow over a rotating disk with Cattaneo–Christov heat flux theory. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09421-4.
Hafeez A, Khan M, Ahmed J, Ahmed A, Iqbal Z. Flow of Oldroyd-B fluid over a rotating disk through porous medium with Soret–Dufour effects. Arab J Sci Eng. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04575-7.
Hayat T, Khan SA, Khan MI, Momani S, Alsaedi A. Cattaneo–Christov (CC) heat flux model for nanomaterial stagnation point flow of Oldroyd-B fluid. Comput Methods Prog Biomed. 2020;187:105247.
Khan M, Iqbal Z, Ahmed A. Stagnation point flow of magnetized Burgers’ nanofluid subject to thermal radiation. Appl Nanosci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01360-8.
Fathizadeh M, Madani M, Khan Y, Faraz N, Yildirim A, Tutkun S. An effective modification of the homotopy perturbation method for MHD viscous flow over a stretching sheet. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2013;25:107–13.
Ahmed A, Khan M, Irfan M, Ahmed J. Transient MHD flow of Maxwell nanofluid subject to non linear thermal radiation and convective heat transport. Appl Nanosci. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01375-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iqbal, Z., Khan, M. & Ahmed, A. On modified Fourier heat flux in stagnation point flow of magnetized Burgers' fluid subject to homogeneous–heterogeneous reactions. J Therm Anal Calorim 147, 815–826 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10308-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-10308-7