Abstract
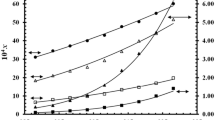
The solubility and solution thermodynamic properties of a “bioactive nutraceutical” sinapic acid (SA) in different “2-(2-ethoxyethoxy)ethanol (Carbitol®) + water” mixtures were investigated. The “mole fraction solubilities (xe)” of SA in various “Carbitol + water” systems were determined at “T = 298.15–318.15 K” and “p = 0.1 MPa.” The measured xe values of SA were found well regressed by “Apelblat, van’t Hoff, Yalkowsky, Jouyban–Acree and Jouyban–Acree–van’t Hoff” models with mean percent deviations of < 4.0%. The maximum xe value of SA was recorded in pure Carbitol (4.15 × 10−2 at T = 318.15 K), and the minimum one was estimated in neat water (6.28 × 10−5 at T = 298.15 K). The regressed results were found to be in accordance with experimental results of SA. Using activity coefficients, mixing thermodynamic parameters of SA were determined. The results showed spontaneous dissolution of SA in most of the cosolvent mixtures.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T :
-
Absolute temperature (K)
- p :
-
Atmospheric pressure (MPa)
- m :
-
Mass fraction of Carbitol in “Carbitol + water” mixtures
- m 1 :
-
Mass of sinapic acid (g)
- m 2 :
-
Mass of neat Carbitol (g)
- m 3 :
-
Mass of neat water (g)
- x e :
-
Experimental mole fraction solubility of sinapic acid
- x idl :
-
Ideal solubility of sinapic acid in mole fraction
- x van’t :
-
van’t Hoff model solubility of sinapic acid in mole fraction
- x Apl :
-
Apelblat model solubility of sinapic acid in mole fraction
- x Yal :
-
Yalkowsky model solubility of sinapic acid in mole fraction
- x m,T :
-
Jouyban–Acree model solubility of sinapic acid in mole fraction
- x 1 :
-
Mole fraction of sinapic acid in neat Carbitol
- x 2 :
-
Mole fraction of neat Carbitol
- x 3 :
-
Mole fraction of neat water
- δ d :
-
Dispersion Hansen solubility parameter (MPa1/2)
- δ p :
-
Polar Hansen solubility parameter (MPa1/2)
- δ h :
-
Hydrogen-bonded Hansen solubility parameter (MPa1/2)
- δ mix :
-
Hansen solubility parameter for “Carbitol + water” mixtures (MPa1/2)
- α :
-
Volume fraction of Carbitol in “Carbitol + water” mixtures
- δ 1 :
-
Hansen solubility parameter of neat Carbitol (MPa1/2)
- δ 2 :
-
Hansen solubility parameter of neat water (MPa1/2)
- γ i :
-
Activity coefficient of sinapic acid
- R 2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- MPD:
-
Mean percent deviations (%)
- a and b :
-
Parameters of van’t Hoff model
- A, B and C :
-
Parameters of Apelblat model
- J i :
-
Parameter of Jouyban–Acree model
- A1, B1, A2 and B2 :
-
Parameter of Jouyban–Acree–van’t Hoff model
- ΔmixGid :
-
Mixing Gibbs free energy for ideal solution (J mol−1)
- ΔmixHid :
-
Mixing enthalpy for ideal solution (J mol−1)
- ΔmixSid :
-
Mixing entropy for ideal solution (J mol−1 K−1)
- ΔmixG :
-
Mixing Gibbs free energy for non-ideal solution (J mol−1)
- ΔmixH :
-
Mixing enthalpy for non-ideal solution (J mol−1)
- ΔmixS :
-
Mixing entropy for non-ideal solution (J mol−1 K−1)
- G E :
-
Excess Gibbs free energy (J mol−1)
- H E :
-
Excess enthalpy (J mol−1)
- T fus :
-
Fusion temperature (K)
- R :
-
Universal gas constant (J mol−1 K−1)
- ΔHfus :
-
Molar fusion enthalpy (kJ mol−1)
- ΔCp :
-
Difference in molar heat capacity (J mol−1 K−1)
References
Niciforovic N, Abramovic H. Sinapic acid and its derivatives: natural sources and bioactivity. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2014;13:34–51.
Shakeel F, Haq N, Raish M, Anwer MK, Al-Shdefat R. Solubility and thermodynamic analysis of sinapic acid in various neat solvents at different temperatures. J Mol Liq. 2016;222:167–71.
Silambarasan T, Manivannan J, Priya MK, Suganya N, Chatterjee S, Raja B. Sinapic acid protects heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury and H9c2 cardiomyoblast cells against oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;456:853–9.
Natella F, Nardini M, Di Felice M, Scaccini C. Benzoic and cinnamic acid derivatives as antioxidants: structure–activity relation. J Agric Food Chem. 1999;47:1453–9.
Nenadis N, Lazaridou O, Tsimidou MZ. Use of reference compounds in antioxidant activity assessment. J Agric Food Chem. 2007;55:5452–60.
Robbins RJ. Phenolic acids in foods: an overview of analytical methodology. J Agric Food Chem. 2003;51:2866–87.
Cuvelier ME, Richard H, Berset C. Comparison of the antioxidative activity of some acid-phenols: structure–activity relationship. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1992;56:324–5.
Firuzi O, Giansanti L, Vento R, Seibert C, Petrucci R, Marrosu G, Agostino R, Saso L. Hypochlorite scavenging activity of hydroxycinnamic acids evaluated by a rapid microplate method based on the measurement of chloramines. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2003;55:1021–7.
Shakeel F, Raish M, Anwer MK, Al-Shdefat R. Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system of sinapic acid: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Mol Liq. 2016;224:351–8.
Andreasen MF, Landbo AK, Christensen LP, Hansen A, Meyer AS. Antioxidant effects of phenolic rye (Secale cereale L.) extracts, monomeric hydroxycinnamates, and ferulic acid dehydrodimers on human low-density lipoproteins. J Agric Food Chem. 2001;49:4090–6.
Lu C, Yao S, Lin N. Studies on reactions of oxidizing sulfur–sulfur three-electron-bond complexes and reducing alpha-amino radicals derived from OH reaction with methionine in aqueous solution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;16:89–96.
Yun KJ, Koh DJ, Kim SH, Park SJ, Ryu JH, Kim DG, Lee JY, Lee KT. Anti-inflammatory effects of sinapic acid through the suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygase-2, and proinflammatory cytokines expressions via nuclear factor-κB inactivation. J Agric Food Chem. 2008;56:10265–1072.
Nowak H, Kujava R, Zadernowski R, Roczniak B, Kozlowska H. Antioxidative and bactericidal properties of phenolic compounds in rapeseeds. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol. 1992;94:149–52.
Teixeira J, Gaspar A, Garrido EM, Garrido J, Borges F. Hydroxycinnamic acid antioxidants: an electrochemical overview. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:E251754.
Engels C, Schieber A, Ganzle MG. Sinapic acid derivatives in defatted oriental mustard (Brassica juncea L.) seed meal extracts using UHPLC-DADESI-MSn and identification of compounds with antibacterial activity. Eur Food Res Technol. 2012;234:535–42.
Maddox CE, Laur LM, Tian L. Antibacterial activity of phenolic compounds against the phytopathogen Xylella fastidiosa. Curr Microbiol. 2010;60:53–8.
Tesaki S, Tanabe S, Ono H, Fukushi E, Kawabata J, Watanabe M. 4-Hydroxy-3-nitrophenyllactic and sinapic acids as antibacterial compounds from mustard seeds. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998;62:998–1000.
Barber MS, McConnell VS, DeCaux BS. Antimicrobial intermediates of the general phenylpropanoid and lignin specific pathways. Phytochemistry. 2000;54:53–6.
Johnson ML, Dahiya JP, Olkowski AA, Classen HL. The effect of dietary sinapic acid (4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxy-cinnamic acid) on gastrointestinal tract microbial fermentation, nutrient utilization, and egg quality in laying hens. Poult Sci. 2008;87:958–63.
Yoon BH, Jung JW, Lee JJ, Cho YW, Jang CG, Jin C, Oh TH, Ryu JH. Anxiolytic-like effects of sinapic acid in mice. Life Sci. 2007;81:234–40.
Roy SJ, Prince PSM. Protective effects of sinapic acid on cardiac hypertrophy, dyslipidaemia and altered electrocardiogram in isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarcted rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;699:213–8.
Silambarasan T, Manivannan J, Priya MK, Suganya N, Chatterjee S, Raja B. Sinapic acid prevents hypertension and cardiovascular remodeling in pharmacological model of nitric oxide inhibited rats. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:E115682.
Hudson EA, Dinh PA, Kokubun T, Simmonds MSJ, Gescher A. Characterization of potentially chemopreventive phenols in extracts of brown rice that inhibit the growth of human breast and colon cancer cells. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2000;9:1163–70.
Ansari MA, Raish M, Ahmad A, Ahmad SF, Mudassar S, Mohsin K, Shakeel F. Sinapic acid mitigates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and associated oxidative/nitrosative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation in rats. Life Sci. 2016;165:1–8.
Sinha AS, Khandavilli UBR, Connor ELO, Deadman BJ, Maguire AR, Lawrence SE. Novel co-crystals of the nutraceutical sinapic acid. CrystEngComm. 2015;17:4832–41.
Shakeel F, Haq N, Salem-Bekhit MM. Thermodynamics of solubility of isatin in Carbitol + water mixed solvent systems at different temperatures. J Mol Liq. 2015;207:274–8.
Shakeel F, Haq N, Siddiqui NA, Alanazi FK, Alsarra IA. Solubility and thermodynamics of vanillin in Carbitol-water mixtures at different temperatures. LWT Food Sci Technol. 2015;64:1278–82.
Shakeel F, Haq N, Siddiqui NA, Alanazi FK, Alsarra IA. Thermodynamics of the solubility of reserpine in {2-(2-ethoxyethoxy)ethanol + water} mixed solvent systems at different temperatures. J Chem Thermodyn. 2015;82:57–60.
Shakeel F, Haq N, Salem-Bekhit MM, Raish M. Solubility and dissolution thermodynamics of sinapic acid in (DMSO + water) binary solvent mixtures at different temperatures. J Mol Liq. 2017;225:833–9.
Higuchi T, Connors KA. Phase-solubility techniques. Adv Anal Chem Inst. 1965;4:117–22.
El-Badry M, Haq N, Fetih G, Shakeel F. Measurement and correlation of tadalafil in five pure solvents at (298.15 to 333.15) K. J Chem Eng Data. 2014;59:839–43.
Shakeel F, Anwer MK. Dissolution thermodynamics and solubility of silymarin in PEG 400-water mixtures at different temperatures. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2015;41:1819–23.
Zhu QN, Wang Q, Hu YB, Abliz X. Practical determination of the solubility parameters of 1-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide ([CnC1im]Br, n = 5, 6, 7, 8) ionic liquids by inverse gas chromatography and the Hansen solubility parameter. Molecules. 2019;24:E1346.
Alanazi A, Alshehri S, Altamimi M, Shakeel F. Solubility determination and three dimensional Hansen solubility parameters of gefitinib in different organic solvents: experimental and computational approaches. J Mol Liq. 2020;299:E112211.
Kalam MA, Alshamsan A, Alkholief M, Alsarra IA, Ali R, Haq N, Anwer MK, Shakeel F. Solubility measurement and various solubility parameters of glipizide in different neat solvents. ACS Omega. 2020;5:1708–16.
Wan Y, He H, Huang Z, Zhang P, Sha J, Li T, Ren B. Solubility, thermodynamic modeling and Hansen solubility parameter of 5-norbornene-2,3-dicarboximide in three binary solvents (methanol, ethanol, ethyl acetate + DMF) from 278.15 K to 323.15 K. J Mol Liq. 2020;300:E112097.
Apelblat A, Manzurola E. Solubilities of o-acetylsalicylic, 4-aminosalicylic, 3,5-dinitrosalicylic and p-toluic acid and magnesium-DL-aspartate in water from T = (278–348) K. J Chem Thermodyn. 1999;31:85–91.
Manzurola E, Apelblat A. Solubilities of l-glutamic acid, 3-nitrobenzoic acid, acetylsalicylic, p-toluic acid, calcium-l-lactate, calcium gluconate, magnesium-dl-aspartate, and magnesium-l-lactate in water. J Chem Thermodyn. 2002;34:1127–36.
Yalkowsky SH, Roseman TJ. Solubilization of drugs by cosolvents. In: Yalkowsky SH, editor. Techniques of solubilization of drugs. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc; 1981. p. 91–134.
Sotomayor RG, Holguín AR, Romdhani A, Martínez F, Jouyban A. Solution thermodynamics of piroxicam in some ethanol + water mixtures and correlation with the Jouyban–Acree model. J Sol Chem. 2013;42:358–71.
Jouyban A. Review of the cosolvency models for predicting solubility of drugs in water-cosolvent mixtures. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2008;11:32–58.
Babaei M, Shayanfar A, Rahimpour E, Barzegar-Jalali M, Martínez F, Jouyban A. Solubility of bosentan in propylene glycol + water mixtures at various temperatures: experimental data and mathematical modeling. Phys Chem Liq. 2019;57:338–48.
Jouyban A, Chan HK, Chew NY, Khoubnasabiafari N, Acree WE Jr. Solubility prediction of paracetamol in binary and ternary solvent mixtures using Jouyban–Acree model. Chem Pharm Bull. 2006;54:428–31.
Jouyban A, Acree WE Jr. In silico prediction of drug solubility in water–ethanol mixtures using Jouyban–Acree model. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2006;9:262–9.
Khoubnasabjafari M, Shayanfar A, Martínez F, Acree WE Jr, Jouyban A. Generally trained models to predict solubility of drugs in carbitol + water mixtures at various temperatures. J Mol Liq. 2016;219:435–8.
Jouyban A, Fakhree MAA, Acree WE Jr. Comment on “Measurement and correlation of solubilities of (Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetic acid in different pure solvents and binary mixtures of water + (ethanol, methanol, or glycol)”. J Chem Eng Data. 2012;57:1344–6.
Jouyban-Gharamaleki A, Hanaee J. A novel method for improvement of predictability of the CNIBS/R-K equation. Int J Pharm. 1997;154:245–7.
Shakeel F, Haq N, Siddiqui NA. Thermodynamic solubility and solvation behavior of ferulic acid in different (PEG-400 + water) binary solvent mixtures. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019;45:1468–76.
Smith JM, Ness HCV, Abbott MM. Introduction to chemical engineering thermodynamics. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2001.
Li X, Cong Y, Du C, Zhao H. Solubility and solution thermodynamics of 2-methyl-4-nitroaniline in eleven organic solvents at elevated temperatures. J Chem Thermodyn. 2017;105:276–88.
Zhao K, Yang P, Du S, Li K, Li X, Li Z, Liu Y, Lin L, Hou B, Gong J. Determination and correlation of solubility and thermodynamics of mixing of 4-aminobutyric acid in mono-solvents and binary solvent mixtures. J Chem Thermodyn. 2016;102:276–86.
Vanderbilt BM, Clayton RE. Bonding of fibrous glass to elastomers. Ind Eng Chem Prod Res Dev. 1965;4:18–22.
Ruidiaz MA, Delgado DR, Martínez F, Marcus Y. Solubility and preferential solvation of indomethacin in 1,4-dioxane + water solvent mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2010;299:259–65.
Manrique YJ, Pacheco DP, Martínez F. Thermodynamics of mixing and solvation of ibuprofen and naproxen in propylene glycol + water cosolvent mixtures. J Sol Chem. 2008;37:165–81.
Kalam MA, Alshehri S, Alshamsan A, Alkholief M, Ali R, Shakeel F. Solubility measurement, Hansen solubility parameters and solution thermodynamics of gemfibrozil in different pharmaceutically used solvents. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019;45:1258–64.
Hildebrand JH, Prausnitz JM, Scott RL. Regular and related solutions. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold; 1970.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for funding this work through the research group project number RG-1435-005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflict of interest associated with this manuscript.
Data availability
All the data associated with this manuscript have been included in supplementary materials which can be found online.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shakeel, F., Haq, N., Alanazi, F.K. et al. Solubility of sinapic acid in various (Carbitol + water) systems: computational modeling and solution thermodynamics. J Therm Anal Calorim 142, 1437–1446 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09451-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09451-y