Abstract
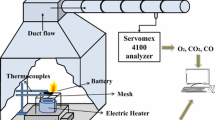
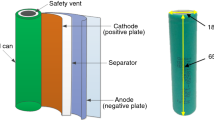
The lithium ion battery has been widely used, but it has high fire risk due to its flammable materials. In this study, a series of combustion tests are conducted on the 18650-type lithium ion batteries using the modified cone calorimeter. The temperature and voltage variation of the battery, heat release rate and gas generation during combustion are measured in this study. The battery is heated evenly by the self-made heater, and the reliable trigger temperatures of thermal runaway are obtained for different states of charge (SOCs) batteries in this study. The fire behavior of the 100% SOC batteries is shown in this paper. The net heat absorption by the battery before thermal runaway is calculated based on the heat transfer theory. It ranges from 56.81 to 64.05 kJ for 0 to 100% SOC batteries, which shows a decreasing trend as SOC increases. The peak combustion heat release rate of 100% SOC batteries is 3.747 ± 0.858 kW. CH4 and CO gases are detected before and after thermal runaway. The generation of CO shows an increasing trend as SOC increases. Some suggestions on the early warning system of battery thermal runaway are proposed based on this study.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen M, Yuen R, Wang J. An experimental study about the effect of arrangement on the fire behaviors of lithium-ion batteries. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;129(1):181–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6158-y.
Chen M, Zhou D, Chen X, Zhang W, Liu J, Yuen R, et al. Investigation on the thermal hazards of 18650 lithium ion batteries by fire calorimeter. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;122(2):755–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4751-5.
Liu X, Wu Z, Stoliarov SI, Denlinger M, Masias A, Snyder K. Heat release during thermally-induced failure of a lithium ion battery: impact of cathode composition. Fire Saf J. 2016;85:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.firesaf.2016.08.001.
Feng X, Sun J, Ouyang M, Wang F, He X, Lu L, et al. Characterization of penetration induced thermal runaway propagation process within a large format lithium ion battery module. J Power Sources. 2015;275:261–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.11.017.
Ramadass P, Fang W, Zhang Z. Study of internal short in a Li-ion cell I. Test method development using infra-red imaging technique. J Power Sources. 2014;248:769–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.09.145.
Ye J, Chen H, Wang Q, Huang P, Sun J, Lo S. Thermal behavior and failure mechanism of lithium ion cells during overcharge under adiabatic conditions. Appl Energy. 2016;182:464–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.124.
Wang Q, Huang P, Ping P, Du Y, Li K, Sun J. Combustion behavior of lithium iron phosphate battery induced by external heat radiation. J Loss Prev Process Ind. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2016.12.002.
Fu Y, Lu S, Li K, Liu C, Cheng X, Zhang H. An experimental study on burning behaviors of 18650 lithium ion batteries using a cone calorimeter. J Power Sources. 2015;273:216–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.09.039.
Huang P, Ping P, Li K, Chen H, Wang Q, Wen J, et al. Experimental and modeling analysis of thermal runaway propagation over the large format energy storage battery module with Li4Ti5O12 anode. Appl Energy. 2016;183:659–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.160.
Huang PF, Wang QS, Li K, Ping P, Sun JH. The combustion behavior of large scale lithium titanate battery. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07788.
Ping P, Wang Q, Huang P, Li K, Sun J, Kong D, et al. Study of the fire behavior of high-energy lithium-ion batteries with full-scale burning test. J Power Sources. 2015;285:80–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.03.035.
Ribière P, Grugeon S, Morcrette M, Boyanov S, Laruelle S, Marlair G. Investigation on the fire-induced hazards of Li-ion battery cells by fire calorimetry. Energy Environ Sci. 2012;5(1):5271–80. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ee02218k.
Feng X, Fang M, He X, Ouyang M, Lu L, Wang H, et al. Thermal runaway features of large format prismatic lithium ion battery using extended volume accelerating rate calorimetry. J Power Sources. 2014;255:294–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.01.005.
Liu X, Stoliarov SI, Denlinger M, Masias A, Snyder K. Comprehensive calorimetry of the thermally-induced failure of a lithium ion battery. J Power Sources. 2015;280:516–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.125.
Babrauskas V. Development of the cone calorimeter—a bench-scale heat release rate apparatus based on oxygen-consumption. Fire Mater. 1984;8(2):81–95. https://doi.org/10.1002/fam.810080206.
Spotnitz R, Franklin J. Abuse behavior of high-power, lithium-ion cells. J Power Sources. 2003;113(1):81–100.
Fouchard D, Xie L, Ebner W, Megahed S. Rechargeable lithium and lithium ion (RCT) batteries. In: Megahed SA, editor. Electrochemical society PV 94-28. Florida: Miami Beach; 1994.
Wang Q, Sun J, Yao X, Chen C. Thermal behavior of lithiated graphite with electrolyte in lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2006;153(2):A329. https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2139955.
Maleki H, Deng G, Kerzhner-Haller I, Anani A, Howard JN. Thermal stability studies of binder materials in anodes for lithium-ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2000;147(12):4470–5.
Zhang Z, Fouchard D, Rea J. Differential scanning calorimetry material studies: implications for the safety of lithium-ion cells. J Power Sources. 1998;70(1):16–20.
Biensan P, Simon B, Peres J, De Guibert A, Broussely M, Bodet J, et al. On safety of lithium-ion cells. J Power Sources. 1999;81:906–12.
Fu Y, Lu S, Shi L, Cheng X, Zhang H. Combustion characteristics of electrolyte pool fires for lithium ion batteries. J Electrochem Soc. 2016;163(9):A2022–8. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0721609jes.
Wang Q, Ping P, Zhao X, Chu G, Sun J, Chen C. Thermal runaway caused fire and explosion of lithium ion battery. J Power Sources. 2012;208:210–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.02.038.
Incropera F, DeWitt D, Bergman T, Lavine A. Fundamentals of heat and mass transfer. 6th ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press; 2007 (in Chinese).
Jiang L, He J-J, Sun J-H. Sample width and thickness effects on upward flame spread over PMMA surface. J Hazard Mater. 2018;342:114–20.
Röder P, Baba N, Wiemhöfer HD. A detailed thermal study of a Li[Ni0.33Co0.33Mn0.33]O2/LiMn2O4-based lithium ion cell by accelerating rate and differential scanning calorimetry. J Power Sources. 2014;248:978–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.09.146.
Eshetu GG, Grugeon S, Laruelle S, Boyanov S, Lecocq A, Bertrand JP, et al. In-depth safety-focused analysis of solvents used in electrolytes for large scale lithium ion batteries. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2013;15(23):9145–55. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cp51315g.
Huggett C. Estimation of rate of heat release by means of oxygen consumption measurements. Fire Mater. 1980;4(2):61–5.
Roth EP, Orendorff CJ. How electrolytes influence battery safety. Electrochem Soc Interface. 2012;21(2):45–9.
Sun J, Li J, Zhou T, Yang K, Wei S, Tang N, et al. Toxicity, a serious concern of thermal runaway from commercial Li-ion battery. Nano Energy. 2016;27:313–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.06.031.
Golubkov AW, Fuchs D, Wagner J, Wiltsche H, Stangl C, Fauler G, et al. Thermal-runaway experiments on consumer Li-ion batteries with metal-oxide and olivin-type cathodes. RSC Adv. 2014;4(7):3633–42. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra45748f.
Abraham DP, Roth EP, Kostecki R, McCarthy K, MacLaren S, Doughty DH. Diagnostic examination of thermally abused high-power lithium-ion cells. J Power Sources. 2006;161(1):648–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.04.088.
Somandepalli V, Marr K, Horn Q. Quantification of combustion hazards of thermal runaway failures in lithium-ion batteries. SAE Int J Altern Powertrains. 2014;3(1):98–104. https://doi.org/10.4271/2014-01-1857.
Larsson F, Bertilsson S, Furlani M, Albinsson I, Mellander B-E. Gas explosions and thermal runaways during external heating abuse of commercial lithium-ion graphite-LiCoO2 cells at different levels of ageing. J Power Sources. 2018;373:220–31.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the Science and Technology Project from China Southern Power Grid (No. GDKJQQ20152008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, G., Mao, B., Wang, C. et al. Thermal runaway and fire behavior investigation of lithium ion batteries using modified cone calorimeter. J Therm Anal Calorim 135, 2879–2889 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7599-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-018-7599-7