Abstract
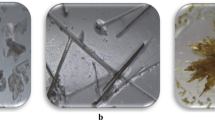
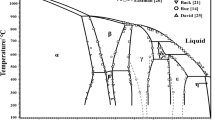
A new non-mesogenic Schiff-based carboxylic acid, viz. 4-((hexylimino)methyl)benzoic acid (HIMB), is synthesized and is used to prepare the binary mixtures with mesogenic 4-n-alkyloxybenzoic acids (nOBAs, where n = 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9 and 12) in 1:1 molar ratio. The mesomorphism in HIMB and nOBA mixtures is studied by polarizing optical microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. The mesomorphic thermal stabilities of these mixtures are found to vary with those of the nOBAs. The results are discussed with the reported mixtures of nOBAs with other Schiff-based pyridyl moieties, which are found to exhibit new phase variants and mesomorphic thermal stabilities. The phase transition temperatures and the enthalpy changes at the phase transitions are discussed in comparison with the other similar binary mixtures. The effects of intermolecular interactions on mesomorphism are discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reinitzer F. Contributions to the knowledge of cholesterol. Monatsch Chem. 1888;9(1):421–441 ibid (English Trans.) Liq Cryst 1989;5:7–18.
Lehmann O. On flowing crystals. Z Phys Chem. 1889;4:462–72.
Friedel G. The mesomorphic states of matter. Ann Phys. 1922;18:273–473.
Grey GW. Molecular structure and properties of liquid crystals. New York: Academic Press; 1962.
Chandrasekhar S. Liquid crystals. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1992.
Fréedericksz V, Repiewa AZ. Phys Soc. 1927;42:532–46. doi:10.1007/BF01397711.
Goodby JW. The nanoscale engineering of nematic liquid crystals for displays. Liq Cryst. 2011;38:1363–87.
Baughman RH, Zakhidov AA, de Heer WA. Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science. 2002;297:787–92.
Tans SJ, Verschueren ARM, Dekker C. Room-temperature transistor based on a single carbon nanotube. Nature. 1998;393:49–52.
Collins PG, Avouris P. Nanotubes for electronics. Sci Am. 2000;283:62–9.
de Heer WA, Chátelian A, Ugarte D. A carbon nanotube field-emission electron source. Science. 1995;270:1179–80.
Kumar S. Functional discotic liquid crystals. Isr J Chem. 2012;52:820–9.
Malthéte J, Nguyen HT, Destrade C. Phasmids and polycatenar liquid crystals. Liq Cryst. 1993;13:171–87.
Niori T, Sekine T, Watanabe J. Distinct ferroelectric smectic liquid crystals consisting of banana shaped achiral molecules. J Mater Chem. 1996;6:1231–3.
Kato T, Mizoshita N, Kishimoto K. Functional liquid-crystalline assemblies: self-organized soft materials. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2006;45:38–68.
Kato T, Fréchet JMJ. A new approach to mesophase stabilization through hydrogen bonding molecular interactions in binary mixtures. J Am Chem Soc. 1989;111:8533–4.
Paleos CM, Tsiourvas D. Supramolecular hydrogen-bonded liquid crystals. Liq Cryst. 2001;28:1127–61.
Kato T, Mizoshita N, Kanie K. Hydrogen-bonded liquid crystalline materials: supramolecular polymeric assembly and the induction of dynamic function. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2001;22:797–814.
Srinivasulu M, Satyanarayana PVV, Kumar PA, Pisipati VGKM. Induced smectic-G phase through intermolecular hydrogen bonding part VIII: phase and crystallization behaviours of 2-(p-n-heptyloxybenzyIidene imino)-5-chIoro-pyridine: p-n-alkoxybenzoic acid (HICP:n ABA) complexes. Z Naturforsch. 2001;56a:685–91.
Barmatov EB, Barmatova MV. Induction of the chiral nematic phase in hydrogen-bonded blends of smectic copolymers and low molar mass dopant. Liq Cryst. 2003;30:1075–8.
Wei Q, Shi L, Yuan X, Zhang L, Cao H, Yang H. Synthesis and phase behaviour of hydrogen-bonded liquid crystalline complexes of allyloxybenzoic acid compounds with 4,4′-bipyridine. Liq Cryst. 2007;34:855–60.
Kohmoto S, Someya Y, Kishikawa K. Liquid crystalline molecules with hydrogen-bonding networks in the direction of molecular short axes. Liq Cryst. 2010;37:209–16.
Vijayakumar VN, Madhu Mohan MLN. Study of optical shutter in cholesteric phase of a double hydrogen bonded ferroelectric liquid crystal with two chiral carbons. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2010;528:163–7.
Kato T, Adachi H, Fujishima A, Fréchet JMJ. Self-assembly of liquid crystalline complexes having angular structures through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Chem Lett. 1992;21:265–8.
Kato T, Fujishima A, Fréchet JMJ. Self-assembly of a twin liquid crystalline complex through intermolecular hydrogen bondings. Chem Lett. 1990;19:919–22.
Vorländer D. About transparently clear, crystalline liquids. Verh Dtsch Chem Ges. 1908;41:2033–52.
Mallia VA, Antharjanam PKS, Das S. Synthesis and studies of some 4-substituted phenyl-4′-azopyridine-containing hydrogen-bonded supramolecular mesogens. Liq Cryst. 2003;30:135–41.
Parra M, Hidalgo P, Barbera J, Alderete J. Properties of thermotropic liquid crystals induced by hydrogen bonding between pyridyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole derivatives and benzoic acid, 4-chlorobenzoic acid or 4-methylbenzoic acid. Liq Cryst. 2005;32:573–7.
Naoum MM, Fahmi AA, Alaasar MA. Supramolecular hydrogen-bonded liquid crystals formed from 4-(4′-pyridylazophenyl)-4″-substituted benzoates and 4-alkoxybenzoic acids. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2008;482:57–70.
Naoum MM, Fahmi AA, Alaasar MA. Supramolecular hydrogen-bonded liquid crystals formed from 4-(4′-pyridylazophenyl)-4″-alkoxy benzoates and 4-substituted benzoic acids. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2008;487:74–91.
Naoum MM, Fahmi AA, Alaasar MA. Supramolecular liquid crystals induced by hydrogen-bonding interactions between non-mesomorphic compounds. I. 4-(4′-Pyridylazophenyl)-4″-substituted benzoates and 4-substituted benzoic acids. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2009;506:22–33.
Bhagavath P, Bhat SG, Mahabaleshwara S, Girish SR, Potukuchi DM, Srinivasulu M. Induced Smectic-A phase at low temperatures through self-assembly. J Mol Struct. 2013;1039:94–100.
Bhagavath P, Mahabaleshwara S, Bhat SG, Potukuchi DM, Pallavajhula VC, Srinivasulu M. Thermal stabilities in supramolecular liquid crystals: Influence of the size and position of a substituent. J Mol Liq. 2013;186C:56–62.
Kumar PA, Srinivasulu M, Pisipati VGKM. Induced smectic G phase through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Liq Cryst. 1999;26:1339–43.
Alshahateet SF. Synthesis and supramolecularity of hydrogen-bonded cocrystals of pharmaceutical model rac-ibuprofen with pyridine derivatives. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2010;533(1):152–161 and the references therein.
Naoum MM, Saad G, Nessim R, Seliger H. Effect of molecular structure on the phase behavior of some liquid crystalline compounds and their binary mixtures II. 4-Hexadecyloxyphenyl arylates and aryl 4-hexadecyloxy benzoates. Liq Cryst. 1997;23:789–95.
Bhat SG, Srinivasulu M, Girish SR, Padmalatha, Bhagavath P, Mahabaleshwara S, Potukuchi DM, Muniprasad M. Influence of moieties and chain length on the abundance of orthogonal and tilted phases of linear hydrogen-bonded liquid crystals, Py16BA:nOBAs. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2012;552(1):83–96.
Acknowledgements
I acknowledge the management of Manipal University, Manipal, for providing the laboratory facilities. I extend my sincere thanks to Dr. M. Srinivasulu, for his guidance in accomplishing this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhagavath, P., Mahabaleshwara, S. Mesomorphism in binary mixtures of 4-((hexylimino)methyl)benzoic acid and 4-alkyloxybenzoic acids. J Therm Anal Calorim 129, 339–345 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6105-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6105-y