Abstract
In this work, new dilute magnetic semiconductor compositions and broad spectrum photocatalysts based on Gd doped and (Gd, Mn) codoped CuO were synthesized by adapted sol gel method. The analyzed XRD peaks were completely indexed to the crystallographic planes of monoclinic copper oxide (CuO) structure. The effectual substitution of Cu2+-sites by Gd and (Gd, Mn) ions was verified from the expansion of the unit cell and shift of the XRD peaks. The inclusion of Gd and (Gd, Mn) ions move the band gap energy of pure CuO (1.41 eV, λ = 879 nm) to low energy region with measured values of 1.3 eV (λ = 953 nm) and 1.26 eV (λ = 984 nm), respectively. The morphological analysis illustrates that the existence of Gd and Mn ions enhances the reduction of the grains size of CuO with more distribution of fine particles. The room temperature ferromagnetic order was impressively improved after incorporation of (Gd, Mn) ions into the lattice of CuO. Herein, Cu0.96Gd0.02Mn0.02O composition exhibits a high saturation magnetization of 1.21 emu/g while the coercivity and remanence values were 156 Oe and 0.15 emu/g, respectively. On the other hand, Cu0.96Gd0.02Mn0.02O as a photocatalyst has large efficiencies for removal of brilliant green and Congo red under normal solar energy and Xenon photoreactor radiation. The measured photodegradation efficiency of Cu0.96Gd0.02Mn0.02O catalyst was 96% and 91% during 70 min with strong stability for 4 series and high mineralization of both dyes to CO2 and H2O. The obtained results highlight that Cu0.96Gd0.02Mn0.02O composition possesses dual-functions operation linked to spin-electronic devices and photocatalysis applications.

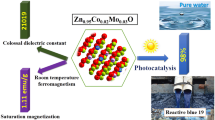
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
New compositions composed of Gd-doped and (Gd, Mn) codoped CuO.
-
Cu0.96Gd0.02Mn0.02O composition exhibits high room temperature ferromagnetism.
-
Cu0.96Gd0.02Mn0.02O has a remarkable photodegradation for brilliant green and Congo red.
-
Spin-electronic devices and photocatalysis applications.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are existing in the main paper.
References
Si R, Li Y, Tian J, Tan C, Chen S, Lei M, Guo X, Zhang S (2023) The stability of SnO2 and In2O3 gas sensors to water under temperature modulation mode. Sens Actuators B Chem 393:134222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2023.134222
Deka S (2023) Nanostructured mixed transition metal oxide spinels for supercapacitor applications. Dalton Trans 52:839–856. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2DT02733J
Lei Z, Lee JM, Singh G, Sathish CI, Chu X, Al-Muhtaseb AH, Vinu A, Yi J (2021) Recent advances of layered-transition metal oxides for energy-related applications. Energy Stor Mater 36:514–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.01.004
Saha S, Ali MR, Khaleque MA, Bacchu MS, Aly MAS, Khan MZH (2023) Metal oxide nanocarrier for targeted drug delivery towards the treatment of global infectious diseases: a review. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 86:104728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2023.104728
Yakout SM (2020) Spintronics: Future technology for new data storage and communication devices. J Supercond Nov Magn 33:2557–2580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05545-8
Geldasa FT, Kebede MA, Shura MW, Hone FG (2023) Experimental and computational study of metal oxide nanoparticles for the photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants: a review. RSC Adv 13:18404–18442. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3RA01505J
Ayodhya D, Veerabhadram G (2018) A review on recent advances in photodegradation of dyes using doped and heterojunction based semiconductor metal sulfide nanostructures for environmental protection. Mater Today Energy 9:83–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtener.2018.05.007
Nazri MKHM, Sapawe N (2020) A short review on photocatalytic toward dye degradation. Mater Today Proc 31(2020):A42–A47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.967
Basavaraj N, Sekar A, Yadav R (2021) Review on green carbon dot-based materials for the photocatalytic degradation of dyes: fundamentals and future perspective. Mater Adv 2:7559–7582. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1MA00773D
Darabdhara J, Roy S, Ahmaruzzaman MD (2023) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of an organic dye by the fabrication of a novel ternary composite based on zeolitic imidazolate framework via a facile in-situ synthetic approach. Inorg Chem Commun 152:110694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110694
Ullah R, Naeemullah, Tuzen M (2023) Photocatalytic removal of organic dyes by titanium doped alumina nanocomposites: Using multivariate factorial and kinetics models. J Mol Struct 1285:135509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.135509
Gade R, Ahemed J, Yanapu KL, Abate SY, Tao Y-T, Pola S (2018) Photodegradation of organic dyes and industrial wastewater in the presence of layer-type perovskite materials under visible light irradiation. J Environ Chem Eng 6:4504–4513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.06.057
Lan J, Wang Y, Huang B, Xiao Z, Wu P (2021) Application of polyoxometalates in photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. Nanoscale Adv 3:4646–4658. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NA00408E
Pérez-Álvarez DT, Brown J, Elgohary EA, Mohamed YMA, El Nazer HA, Davies P, Stafford J (2022) Challenges surrounding nanosheets and their application to solar-driven photocatalytic water treatment. Mater Adv 3:4103–4131. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2MA00276K
Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh A, Salimi Z (2011) Solar photocatalytic degradation of o-phenylenediamine by heterogeneous CuO/X zeolite catalyst. Desalination 280:281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2011.07.021
Zhu C, Yao H, Le S, Yin Y, Chen C, Xu H, Wang S, Duan X (2022) S-scheme photocatalysis induced by ultrathin TiO2(B) nanosheets-anchored hierarchical In2S3 spheres for boosted photocatalytic activity. Compos B Eng 242:110082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.110082
Moriomoto T, Oka R, Minagawa K, Masui T (2022) Novel near-infrared reflective black inorganic pigment based on cerium vanadate. RSC Adv 12:16570–16575. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA02483G
Xu J, Shen J, Jiang H, Yu X, Qureshi WA, Maouche C, Gao J, Yang J, Liu Q (2023) Progress and challenges in full spectrum photocatalysts: Mechanism and photocatalytic applications. J Ind Eng Chem 119:112–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2022.11.057
Ullah S, Ferreira-Neto EP, Hazra C, Parveen R, Rojas-Mantilla HD, Calegaro ML, Serge-Correales YE, Rodrigues-Filho UP, Ribeiro SJL (2019) Broad spectrum photocatalytic system based on BiVO4 and NaYbF4:Tm3+ upconversion particles for environmental remediation under UV-vis-NIR illumination. Appl Catal B 243:121–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.091
Motora KG, Wu C-M (2020) Magnetically separable highly efficient full-spectrum light-driven WO2.72/Fe3O4 nanocomposites for photocatalytic reduction of carcinogenic chromium (VI) and organic dye degradation. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 117:123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2020.12.006
Shen J-H, Tang Y-H, Jiang Z-W, Liao D-Q, Horng J-J (2021) Optimized preparation and characterization of Co-N codoped TiO2 with enhanced visible light activity: An insight into effect of dopants on surface redox reactions of photogenerated charge carriers for hydroxyl radical formation. J Alloy Compd 862:158697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158697
Yu F, Wang W, Li Y, Du M, Liu F, Liang D (2023) Ultralow Fe doping induced high photocatalytic activity toward ciprofloxacin degradation and CO2 reduction. J Mol Struct 1273:134344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.134344
Hou L, Zhang C, Li L, Du C, Li X, Kang X-F, Chen W (2018) CO gas sensors based on p-type CuO nanotubes and CuO nanocubes: Morphology and surface structure effects on the sensing performance. Talanta 188:41–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.05.059
Chauhan M, Sharma B, Kumar R, Chaudhary GR, Hassan AA, Kumar S (2019) Green synthesis of CuO nanomaterials and their proficient use for organic waste removal and antimicrobial application. Environ Res 168:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.09.024
Kaur M, Tovstolytkin A, Lotey GS (2018) Magnetoelectric coupling in CuO nanoparticles for spintronics applications. Electron Mater Lett 14:370–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-018-0026-1
Dubal DP, Gund GS, Lokhande CD, Holze R (2013) CuO cauliflowers for supercapacitor application: Novel potentiodynamic deposition. Mater Res Bull 48:923–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.11.081
Baste Y, Jadhav V, Roy A, Alghamdi S, Abbas M, Algethami JS, Almehmadi M, Allahyani M, Verma D, Yadav KK, Jeon BH, Park HK (2023) Polyol synthesis of Ag-doped copper oxide nanoparticles as a methylene blue-degrading agent. Catalysts 13:1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071143
Uma HB, Kumar MSV, Ananda S (2022) Semiconductor-assisted photodegradation of textile dye, photo-voltaic and antibacterial property of electrochemically synthesized Sr-doped CuO nano photocatalysts. J Mol Struct 1264:133110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.133110
Jaihindh DP, Anand P, Chen RS, Yu WY, Wong MS, Fu YP (2023) Cl-doped CuO for electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction and tetracycline photocatalytic degradation. J Environ Chem Eng 11:109852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.109852
Iqbal M, Thebo AA, Shah AH, Iqbal A, Thebo KH, Phulpoto S, Mohsin MA (2017) Influence of Mn-doping on the photocatalytic and solar cell efficiency of CuO nanowires. Inorg Chem Commun 76:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2016.11.023
Phutanon N, Pisitsak P, Manuspiya H, Ummartyotin S (2018) Synthesis of three-dimensional hierarchical CuO flower-like architecture and its photocatalytic activity for rhodamine b degradation. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 3:310–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsamd.2018.05.001
Jamal M, Nishat SS, Sharif A (2021) Effects of transition metal (Fe, Co & Ni) doping on structural, electronic and optical properties of CuO: DFT + U study. Chem Phys 545:111160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2021.111160
Ayed RB, Ajili M, Piñeiro Y, Rivas J, Kamoun NT (2020) First investigation on (Ni, Co) co-doping effects on the physical properties of Fe2O3 thin films for optoelectronic applications. Optik 213:164645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164645
Siriwong C, Wetchakun N, Inceesungvorn B, Channei D, Samerjai T, Phanichphant S (2012) Doped-metal oxide nanoparticles for use as photocatalysts. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 58:145–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2012.02.004
Asl HZ, Rozati SM (2017) Effects of HCl and methanol in the precursor on physical properties of spray-deposited nanostructured CuO thin films for solar applications. J Electron Mater 46:5020–5027. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-017-5510-0
Jana S, Das S, Das NS, Chattopadhyay KK (2010) CuO nanostructures on copper foil by a simple wet chemical route at room temperature. Mater Res Bull 45:693–698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2010.02.014
Singh SJ, Chinnamuthu P (2021) Highly efficient natural-sunlight-driven photodegradation of organic dyes with combustion derived Ce-doped CuO nanoparticles. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng 625:126864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126864
Siddiqui H, Shrivastava M, Parra MR, Pandey P, Ayaz S, Qureshi MS (2018) The effect of La3+ ion doping on the crystallographic, optical and electronic properties of CuO nanorods. Mater Lett 229:225–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.07.029
Gao D, Yang G, Li J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Xue D (2010) Room-temperature ferromagnetism of flowerlike CuO nanostructures. J Phys Chem C 114:18347–18351. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp106015t
Chandrasekar M, Subash M, Logambal S, Udhayakumar G, Uthrakumar R, Inmozhi C, Al-Onazi WA, Al-Mohaimeed AMA, Chen T, Kanimozhi K (2022) Synthesis and characterization studies of pure and Ni doped CuO nanoparticles by hydrothermal method. J King Saud Univ Sci 34:101831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101831
Lu P, Wu P, Wang J, Ma X (2019) Effect of structure distortion and copper vacancy on ferromagnetism in hydrothermally synthesized CuO with aliovalent Cr3+ doping. Chem Phys Lett 730(2019):297–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2019.06.029
Sellaiyan S, Devi LV, Sako K, Uedono A, Sivaji K (2019) Effect of dopant concentration and annealing of Yttrium doped CuO nanocrystallites studied by positron annihilation spectroscopy. J Alloy Compd 788(2019):549–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.247
Basith M, Vijaya JJ, Kennedy LJ, Bououdina M (2013) Structural, optical and room-temperature ferromagnetic properties of Fe-doped CuO nanostructures. Phys E Low Dimens Syst Nanostruct 53:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2013.05.009
Chuai M, Zhao Q, Yang T, Luo Y, Zhang M (2015) Synthesis and ferromagnetism study of Ce doped CuO dilute magnetic semiconductor. Mater Lett 161:205–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.08.075
Park YR, Kim KJ, Choi S, Lee JH, Lee HJ, Kim CS, Park JY (2007) Ferromagnetism in 57Fe-doped cupric oxide. Phys Stat Sol b 244:4578–4581. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.200777116
Belghiti M, Tanji K, El Mersly L, Lamsayety I, Ouzaouit K, Faqir H, Benzakour I, Rafqah S, Outzourhit A (2022) Fast and non-selective photodegradation of basic yellow 28, malachite green, tetracycline, and sulfamethazine using a nanosized ZnO synthesized from zinc ore. React Kinet Mech Catal 135:2265–2278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-022-02232-8
Jiang G, Wei Z, Chen H, Du X, Li L, Liu Y, Huang Q, Chen W (2015) Preparation of novel carbon nanofibers with BiOBr and AgBr decoration for the photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B. RSC Adv 5:30433–30437. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA17290F
Koysuren O, Koysuren HN (2023) Application of CuO and its composite with polyaniline on the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and the Cr(VI) photoreduction under visible light. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 106:131–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06049-2
Degefu DM, Liao Z (2021) Photocatalytic degradation of volatile organic compounds using nanocomposite of P-type and N-type transition metal semiconductors. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 98:605–614. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05532-y
Demir B, Tüter M, Özkara-Aydınoğlu Ş (2022) Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes under visible light on sol-gel derived M/ZnO (M=Cr, Mn, Sn, Fe, Ni, Cu, Co, Ba) catalysts. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 103:214–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-022-05827-8
Author contributions
All work was done by NJ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Janene, N. Strong spin-ferromagnetic order and active dyes-depollution performance of CuO semiconductor: Gd and Gd/Mn dopants. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 109, 543–554 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06302-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06302-8