Abstract
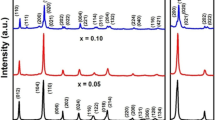
In this work, we report on the synthesis of Gd3+ substituted BiFeO3 nanoparticles and their structural, chemical, and magnetic characterizations. Single rhombohedral phase is obtained till x = 0.06 in Bi1-xGdxFeO3 nanoparticles, as confirmed by the Rietveld refinement of powder X-ray diffraction profiles. Beyond x = 0.06, a mixed phase consisting of both rhombohedral and orthorhombic structures is established. This kind of atom substitution-driven structural change is also confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. Core-level X-ray photoemission spectroscopy reveals the dominance of the Fe3+ oxidation state and also provides an estimation of oxygen vacancies which are found to be ~ 28% and 17% for x = 0.06 and 0.15 samples, respectively. The width of the hysteresis loop increases with the increase in Gd3+ concentration, suggesting an enhancement in magnetic character in contrast with pure BiFeO3 nanoparticles, and ferromagnetic contribution to the magnetization is estimated to a maximum value of 0.50 emu/g for x = 0.12.
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
-
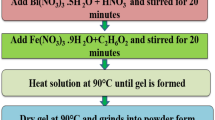
BixGd1-xFeO3 nanoparticles with x = 0.0, 0.03, 0.06, 0.10, 0.12 and 0.15 were synthesized by sol-gel method.
-
Substitutional driven structural phase transformation from rhombohedral (R3c) to orthorhombic (Pnma) has been observed.
-
Reduction in oxygen vacancies along with dominance of Fe3+ oxidation state has been observed.
-
Partial suppression of spiral spin structure, surface effect in nanoparticles and DM interactions all together contributed for the observed weak ferromagnetic nature.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang Q, Gong SJ (2005) The investigation of the magnetodielectric effect in multiferroic ferroelectromagnets. Eur Phys J B 43(3):333–340
Fiebig M, Lottermoser T, Fröhlich D, Goltsev AV, Pisarev RV (2002) Observation of coupled magnetic and electric domains. Nature 419(6909):818–820
Eerenstein W, Mathur ND, Scott JF (2006) Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442(7104):759–765
Setter N, Damjanovic D, Eng L, Fox G, Gevorgian S, Hong S et al. (2006) Ferroelectric thin films: Review of materials, properties, and applications. J Appl Phys 100(5):051606
Pan H, Ma J, Ma J, Zhang Q, Liu X, Guan B et al. (2018) Giant energy density and high efficiency achieved in bismuth ferrite-based film capacitors via domain engineering. Nat Commun 9:1813
Saxena P, Kumar A, Sharma P, Varshney D (2016) Improved dielectric and ferroelectric properties of dual-site substituted rhombohedral structured BiFeO3 multiferroics. J Alloy Compd 682:418–23
Fei L, Hu Y, Li X, Song R, Sun L, Huang H et al. (2015) Electrospun Bismuth Ferrite Nanofibers for Potential Applications in Ferroelectric Photovoltaic Devices. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(6):3665–3670
Li Q, Bao S, Liu Y, Li Y, Jing Y, Li J (2016) Influence of lightly Sm-substitution on crystal structure, magnetic and dielectric properties of BiFeO3 ceramics. J Alloy Compd 682:672–678
You T, Du N, Slesazeck S, Mikolajick T, Li G, Bürger D et al. (2014) Bipolar Electric-Field Enhanced Trapping and Detrapping of Mobile Donors in BiFeO3 Memristors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(22):19758–19765
Zheng H, Wang J, Lofland SE, Ma Z, Mohaddes-Ardabili L, Zhao T et al. (2004) Multiferroic BaTiO3-CoFe2O4 Nanostructures. Science 303(5658):661–663
Hur N, Park S, Sharma PA, Guha S, Cheong SW (2004) Colossal Magnetodielectric Effects in DyMn2O5. Phys Rev Lett 93:107207–107210
Kuang D, Tang P, Ding X, Yang S, Zhang Y (2015) Effects of Y doping on multiferroic properties of sol–gel deposited BiFeO3 thin films. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 26(5):3001–3007
Dubey A, Salamon S, Attanayake SB, Ibrahim S, Landers J, Castillo ME et al. (2022) Rare-earth doped BiFe0.95Mn0.05O3 nanoparticles for potential hyperthermia applications. Front Bioeng Biotechno 10:01–12
Banerjee P, Franco A (2016) Rare earth and transition metal doped BiFeO3 ceramics: structural, magnetic and dielectric characterization. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27(6):6053–6059
Ilić NI, Bobić JD, Stojadinović BS, Džunuzović AS, Petrović MMV, Dohčević-Mitrović ZD et al. (2016) Improving of the electrical and magnetic properties of BiFeO3 by doping with yttrium. Mater Res Bull 77:60–69
Sun W, Li JF, Zhu FY, Yu Q, Cheng LQ, Zhou Z (2015) Thickness-dependent phase boundary in Sm-doped BiFeO3 piezoelectric thin films on Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si substrates. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(30):19759–19765
Kumar P, Kar M (2014) Effect of structural transition on magnetic and optical properties of Ca and Ti co-substituted BiFeO3 ceramics. J Alloy Compd 584:566–572
Kazhugasalamoorthy S, Jegatheesan P, Mohandoss R, Giridharan NV, Karthikeyan B, Joseyphus RJ et al. (2010) Investigations on the properties of pure and rare earth modified bismuth ferrite ceramics. J Alloy Compd 493(1-2):569–572
Nair SG, Satapathy J, Kumar NP (2020) Influence of synthesis, dopants, and structure on electrical properties of bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3). Appl Phys A 126(11):836
Pradhan SK, Roul BK (2012) Electrical behavior of high resistivity Ce-doped BiFeO3 multiferroic. Phys B (Amst, Neth) 407(13):2527–2532
Zhang XQ, Sui Y, Wang XJ, Wang Y, Wang Z (2010) Effect of Eu substitution on the crystal structure and multiferroic properties of BiFeO3. J Alloy Compd 507(1):157–161
Pradhan AK, Zhang K, Hunter D, Dadson JB, Loiutts GB, Bhattacharya P et al. (2005) Magnetic and electrical properties of single-phase multiferroic BiFeO3. J Appl Phys 97(9):093903
Kumar M, Pandey H (2023) Structural Phase Transformation, Magnetic and Optical Properties of Ho3+ Substituted BiFeO3 Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 36(4):1269–1276
Bhushan B, Wang ZX, Tol J, Dalal NS, Basumallick A, Vasanthacharya NY et al. (2012) Tailoring the Magnetic and Optical Characteristics of Nanocrystalline BiFeO3 by Ce Doping. J Am Ceram Soc 95(6):1985–1992
Yan W, Hou ZL, Bi S, Cui RB, Tang M (2018) Enhanced magnetization and bias voltage-dependent dielectric properties of Sm-doped BiFeO3 multiferroic nanofibers. J Mater Sci 53(14):10249–10260
Wang J, Neaton JB, Zheng H, Nagarajan V, Ogale SB, Liu B et al. (2003) Epitaxial BiFeO3 multiferroic thin film heterostructures. Science 299(5613):1719–1722
Patel SKS, Lee JH, Kim MK, Bhoi B, Kim SK (2018) Single-crystalline Gd-doped BiFeO3 nanowires: R3c-to-Pn2(1)a phase transition and enhancement in high-coercivity ferromagnetism. J Mater Chem C 6(3):526–534
Sharma AD, Sharma HB (2021) Influence of Gd doping and thickness variation on structural, morphological and optical properties of nanocrystalline bismuth ferrite thin films via sol-gel technology. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32(15):20612–20624
Lotey GS, Verma NK (2012) Structural, magnetic, and electrical properties of Gd-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles with reduced particle size. J Nanopart Res 14(3):742
Reddy BP, Cui H, Sekhar MC, Vattikuti SVP, Suh Y, Park SH (2019) Influence of Gd doping on the visible-light photocatalytic activity and magnetic properties of BiFeO3 particles. Mater Res Express 6(11):115044
Vashisth BK, Bangruwa JS, Gairola SP, Verma V (2018) Structural, dielectric, ferroelectric and magnetic properties of Gd doped BiFeO3. Integr Ferroelectr 194(1):21–27
Philip GG, Senthamizhan A, Natarajan TS, Chandrasekaran G, Therese HA (2015) The effect of gadolinium doping on the structural, magnetic and photoluminescence properties of electrospun bismuth ferrite nanofibers. Ceram Int 41(10):13361–13365
Dai HY, Ye FJ, Chen ZP, Li T, Liu DW (2018) The effect of ion doping at different sites on the structure, defects and multiferroic properties of BiFeO3 ceramics. J Alloy Compd 734:60–65
Kumar P, Panda C, Kar M (2015) Effect of rhombohedral to orthorhombic transition on magnetic and dielectric properties of La and Ti co-substituted BiFeO3. Smart Mater Struct 24(4):045028
Anthoniappen J, Chang WS, Soh AK, Tu CS, Vashan P, Lim FS (2017) Electric field induced nanoscale polarization switching and piezoresponse in Sm and Mn co-doped BiFeO3 multiferroic ceramics by using piezoresponse force microscopy. Acta Mater 132:174–181
Ionic radii of different ions has been taken from http://abulafia.mt.ic.ac.uk/shannon/radius.php website.
Golic DL, Radojkovic A, Dapcevic A, Pajic D, Dragovic J, Toric F et al. (2019) Change in structural, ferroelectric, and magnetic properties of bismuth ferrite induced by doping with gadolinium. Ceram Int 45(15):19158–19165
Spaldin NA, Ramesh R (2019) Advances in magnetoelectric multiferroics. Nat Mater 18(3):203–212
Kothari D, Reddy VR, Sathe VG, Gupta A, Banerjee A, Awasthi AM (2008) Raman scattering study of polycrystalline magnetoelectric BiFeO3. J Magn Magn Mater 320(3-4):548–552
Fukumura H, Harima H, Kisoda K, Tamada M, Noguchi Y, Miyayama M (2007) Raman scattering study of multiferroic BiFeO3 single crystal. J Magn Magn Mater 310(2):e367–e369
Porporati AA, Tsuji K, Valant M, Axelsson AK, Pezzotti G (2010) Raman tensor elements for multiferroic BiFeO3 with rhombohedral R3c symmetry. J Raman Spectrosc 41(1):84–87
Chen P, Xu XS, Koenigsmann C, Santulli AC, Wong SS, Musfeldt JL (2010) Size-Dependent Infrared Phonon Modes and Ferroelectric Phase Transition in BiFeO3 Nanoparticles. Nano Lett 10(11):4526–4532
Hermet P, Goffinet M, Kreisel J, Ghosez P (2007) Raman and infrared spectra of multiferroic bismuth ferrite from first principles. Phys Rev B 75(22):220102(R)
Ederer C, Spaldin NA (2005) Influence of strain and oxygen vacancies on the magnetoelectric properties of multiferroic bismuth ferrite. Phys Rev B 71(22):224103
Sosnowska I, Peterlinneumaier T, Steichele E (1982) Spiral Magnetic-Ordering in Bismuth Ferrite. J Phys C Solid State 15(23):4835–4846
Huang FZ, Wang ZJ, Lu XM, Zhang JT, Min KL, Lin WW et al. (2013) Peculiar magnetism of BiFeO3 nanoparticles with size approaching the period of the spiral spin structure. Sci Rep. 3:2907
Sakar M, Balakumar S, Saravanan P, Bharathkumar S (2015) Compliments of confinements: substitution and dimension induced magnetic origin and band-bending mediated hotocatalytic enhancements in Bi1−xDyxFeO3 particulate and fiber nanostructures. Nanoscale 7:10667–10679
Chauhan S, Kumar M, Chhoker S, Katyal SC, Singh M (2016) Substitution driven structural and magnetic transformation in Ca-doped BiFeO3 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6:43080–43090
Zhan X, Sui Y, Wang X, Wang Y, Wang Z (2010) Effect of Eu substitution on the crystal structure and multiferroic properties of BiFeO3. J Alloy Compd 507(1):157–161
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the CeNSE facility at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, India, for RAMAN, TEM, and XPS measurements. HP acknowledges the SVNIT Institute seed money grant 2021-22/DOP/04.
Author contributions
MK conceptualized the idea supervised the work and edited the manuscript. SC performed experimental work and analysed the results. HP analysed the results and prepared the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Chauhan, S. & Pandey, H. Effect of Gd3+ substitution on structural, morphological, and magnetic properties of BiFeO3 nanoparticles. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 109, 272–282 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06269-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-023-06269-6