Abstract
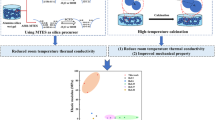
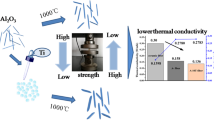
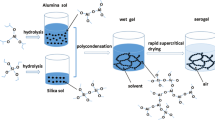
Highly thermally stable alumina-based aerogels are synthesized by the acetone–aniline in situ water formation method and modified by partially hydrolyzed aluminum tri-sec-butoxide at different temperatures (25, 45, and 60 °C). The effects of modification, especially modification temperature, on microstructure and thermal stability of alumina-based aerogels are investigated. After the modification, the morphologies of alumina-based aerogels change from the network structures with interconnected needle-like particles to those with stacked sheet-like particles, resulting in a better heat resistance. The thermal stability of alumina-based aerogels enhances with the increasing modification temperature, whereas the high temperature (more than 60 °C) would lead to the dissolution of wet gels during the modification process due to the high solubility. After annealing at 1200 °C for 2 h, the 45 °C-modified alumina-based aerogel exhibits the best thermal stability with the lowest linear shrinkage of ~7% and the highest specific surface area of 154 m2/g. In addition, the modified aerogels remain in the θ-Al2O3 phase while the unmodified one transforms into α-Al2O3 phase after 1300 °C annealing. The alumina-based aerogels are further reinforced by incorporating with mullite fiber felt and TiO2. The obtained composites show ultralow thermal conductivities of 0.065, 0.086, and 0.118 W/mK at 800, 1000, and 1200 °C, respectively.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ASB:
-
aluminum tri-sec-butoxide
- TMEO:
-
trimethylethoxysilane
- EtOH:
-
ethanol
References
Yoldas BE (1975) Am Ceram Soc Bull 54(3):289–290
Yoldas BE (1975) Am Ceram Soc Bull 54(3):286–288
Hirashima H, Kojima C, Imai H (1997) J Solgel Sci Technol 8(1-3):843–846
Kim J-H, Suh DJ, Park T-J, Kim K-L (2000) Appl Catal A Gen 197(2):191–200
Suh DJ, Park T-J, Lee S-H, Kim K-L (2001) J Non Cryst Solids 285(1):309–316
Pierre AC, Pajonk GM (2002) Chem Rev 102(11):4243–4266
Al-Yassir N, Le Van Mao R (2007) Appl Catal A Gen 317(2):275–283
Aegerter MA, Leventis N, Koebel MM (2011) Aerogels handbook. Springer, New York
Bang Y, Han SJ, Yoo J, Park S, Choi JH, Lee YJ, Song JH, Song IK (2014) Int J Hydrogen Energy 39(10):4909–4916
Wang W, Zhang Z, Zu G, Shen J, Zou L, Lian Y, Liu B, Zhang F (2014) RSC Adv 4(97):54864–54871
Horiuchi T, Osaki T, Sugiyama T, Suzuki K, Mori T (2001) J Non Cryst Solids 291(3):187–198
Horiuchi T, Chen L, Osaki T, Sugiyama T, Suzuki K, Mori T (1999) Catal Lett 58(2-3):89–92
Miller JB, Ko EI (1998) Catal Today 43(1):51–67
Poco JF, Satcher JH, Hrubesh LW (2001) J Non Cryst Solids 285(1):57–63
Baumann TF, Gash AE, Chinn SC, Sawvel AM, Maxwell RS, Satcher JH (2005) Chem Mater 17(2):395–401
Osaki T, Nagashima K, Watari K, Tajiri K (2007) J Non Cryst Solids 353(24):2436–2442
Osaki T, Mori T (2009) J Non Cryst Solids 355(31):1590–1596
Osaki T, Yamada K, Watari K, Tajiri K, Shima S, Miki T, Tai Y (2012) J Solgel Sci Technol 61(1):268–274
Aravind PR, Mukundan P, Pillai PK, Warrier K (2006) Microporous Mesoporous Mater 96(1):14–20
Padmaja P, Warrier K, Padmanabhan M, Wunderlich W, Berry FJ, Mortimer M, Creamer NJ (2006) Mater Chem Phys 95(1):56–61
Mardkhe MK, Huang B, Bartholomew CH, Alam TM, Woodfield BF (2016) J Porous Mater 23(2):475–487
Wu X, Shao G, Cui S, Wang L, Shen X (2016) Ceram Int 42(1):874–882
Mizushima Y, Hori M (1993) J Mater Res 8(11):2993–2999
Yang J, Wang Q, Wang T, Liang Y (2016) RSC Adv 6(31):26271–26279
Zu G, Shen J, Wang W, Zou L, Lian Y, Zhang Z, Liu B, Zhang F (2014) Chem Mater 26(19):5761–5772
Zu G, Shen J, Zou L, Wang W, Lian Y, Zhang Z, Du A (2013) Chem Mater 25(23):4757–4764
Brinker CJ, Scherer GW (2013) Sol-gel science: the physics and chemistry of sol-gel processing. Academic, New York, NY
Leventis N (2007) Acc Chem Res 40(9):874–884
Zu G, Shen J, Wei X, Ni X, Zhang Z, Wang J, Liu G (2011) J Non Cryst Solids 357(15):2903–2906
Sing KS (1985) Pure Appl Chem 57(4):603–619
Boumaza A, Favaro L, Lédion J, Sattonnay G, Brubach J, Berthet P, Huntz A, Roy P, Tétot R (2009) J Solid State Chem 182(5):1171–1176
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Major Science and Technology Projects of Zhejiang Province (2014C01030), “Chen Guang” project supported by Shanghai Municipal Education Commission and Shanghai Education Development Foundation (Grant No. 14CG19) and National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (2013BAJ01B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, W., Wang, X., Wu, Y. et al. Highly thermally stable alumina-based aerogels modified by partially hydrolyzed aluminum tri-sec-butoxide. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 84, 507–514 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4380-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-017-4380-5