Abstract
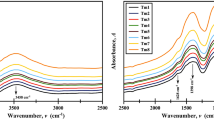
A series of Yb-doped glass films has been prepared by sol–gel processing within the SiO2–Al2O3–P2O5–Yb2O3 system with doping levels up to 30 mol% Yb on a cation basis, with a thickness up to ~36 μm. The refractive indices at 633 nm, measured by spectroscopic ellipsometry, varied between 1.457 and 1.577, depending on the composition. Infrared (IR) and Raman spectroscopies were used to establish the main structural features of the different compositions, which included the presence of mixed Si–O–Al bonds evidenced by a IR peak at 940 cm−1, as well as P=O bonds revealed by a Raman peak at 1326 cm−1. The photoluminescence spectrum of Yb3+ ions was dominated by peaks at 987 and 1020 nm, with a lifetime between ~0.5–1.0 ms.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Francini R, Giovenale F, Grassano UM, Laporta P, Taccheo S (2000) Spectroscopy of Er and Er-Yb-doped phosphate glasses. Opt Mater 13(4):417–425. doi:10.1016/S0925-3467(99)00095-6
Hönninger C, Paschotta R, Graf M, Morier-Genoud F, Zhang G, Moser M, Biswal S, Nees J, Braun A, Mouroun GA, Johannsen I, Giesen A, Seeber W, Keller U (1999) Ultrafast ytterbium-doped bulk lasers and laser amplifiers. Appl Phys B Lasers Opt 69(1):3–17. doi:10.1007/s003400050762
Etzel HW, Gandy HW, Ginther RJ (1962) Stimulated emission of infrared radiation from ytterbium-activated silicate glass. Appl Opt 1(4):534–536. doi:10.1364/AO.1.000534
Lacovara P, Choi HK, Wang CA, Aggarwal RL, Fan TY (1991) Room-temperature diode-pumped Yb:YAG laser. Opt Lett 16(14):1089–1091. doi:10.1364/OL.16.001089
Lu K, Dutta NK (2002) Spectroscopic properties of Yb-doped silica glass. J Appl Phys 91(2):576–581. doi:10.1063/1.1425445
Koch R, Clarkson WA, Hanna DC, Jiang S, Myers MJ, Rhonehouse D, Hamlin SJ, Griebner U, Schönnagel H (1997) Efficient room temperature cw Yb:glass laser pumped by a 946 nm Nd:YAG laser. Opt Commun 134:175–178. doi:10.1016/S0030-4018(96)00537-8
Hönninger C, Morier-Genoud F, Moser M, Keller U, Brovelli LR, Harder C (1998) Efficient and tunable diode-pumped femtosecond Yb:glass lasers. Opt Lett 23(2):126–128. doi:10.1364/OL.23.000126
Danger T, Mix E, Heumann E, Huber G, Ehrt D, Seeber W (1996), Diode pumped continuous-wave Yb laser in fluoride phosphate glasses, advanced solid-state lasers topical meeting, San Francisco, USA. In: Proceedings of the trends in optics and photonics/TOP’s, vol 1, p 23
Zhang L, Leng Y, Zhang J, Hu L (2010) Yb3+-doped fluorophosphate glass with high cross section and lifetime. J Mater Sci Technol 26(10):921–924. doi:10.1016/S1005-0302(10)60148-X
Li Y, Fortes LM, Chiappini A, Ferrari M, Almeida RM (2009) High quality factor Er-doped Fabry–Perot microcavities by sol–gel processing. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:205104. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/42/20/205104
Arai K, Namikawa H, Kumata K, Honda T, Ishii Y, Handa T (1986) Aluminum or phosphorus co-doping effects and structural properties of neodymium-doped silica glass. J Appl Phys 59(10):3430–3436. doi:10.1063/1.336810
Almeida RM, Du XM, Orignac X, Barbier D (1999) Er3+-doped multicomponent silicate glass planar waveguides prepared by sol–gel processing. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 14:209–216. doi:10.1023/A:1008794202103
Orignac X, Barbier D, Du XM, Almeida RM (1996) Fabrication and characterization of sol–gel planar waveguides doped with rare-earth ions. Appl Phys Lett 69(7):895–897. doi:10.1063/1.117980
Barbier D, Orignac X, Du XM, Almeida RM (1997) Improved composition for sol–gel rare-earth doped planar waveguides. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 8(1):1013–1016. doi:10.1007/BF02436976
Almeida RM (1999) Sol–gel planar waveguides for integrated optics. J Non-Cryst Solids 259:176–181. doi:10.1016/S0022-3093(99)00527-X
Almeida RM (1988) Vibrational spectroscopy of glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 106:347–358. doi:10.1016/0022-3093(88)90288-8
Almeida RM (1992) Phys Rev B 45(1):161–170. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.45.161
Almeida RM, Marques AC (2005) Characterization of sol–gel materials by infrared spectroscopy. In: Sakka S (ed) Handbook of sol–gel science and technology: processing, characterization and applications, vol II: Characterization and properties of sol–gel materials and products. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston, MA, pp 65–90
Paluszkiewicz C, Blazewicz M, Podporska J, Gumuła T (2008) Nucleation of hydroxyapatite layer on wollastonite material surface: FTIR studies. Vib Spectrosc. doi:10.1016/j.vibspec.2008.02.020
Harrick NJ (1971) Determination of refractive index and film thickness from interference fringes. Appl Opt 10(10):2344–2349. doi:10.1364/AO.10.002344
Santos LF, Almeida RM (2009) Vibrational spectra and alkali ion motions in binary silicate glasses. Phys Chem Glasses: Eur J Glass Sci Technol, Part B 50(1):41–44
Tamrakar RK, Tiwari N, Dubey V, Upadhyay K (2015) Infrared spectroscopy and luminescence spectra of Yb3+ doped ZrO2 nanophosphor. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 8(3):399–403. doi:10.1016/j.jrras.2015.02.010
Acknowledgments
The present work was funded by ANI (COMPETE program, FEDER, Portugal) through the Multilaser Project (No. 30179).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ribeiro, T.V., Santos, L.F., Gonçalves, M.C. et al. Heavily Yb-doped silicate glass thick films. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 81, 105–113 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4071-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4071-7