Abstract
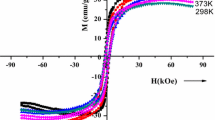
Substitution of NdZn in Ca0.5Ba0.5−x Nd x Zn y Fe12−y O19, (x = 0.00–0.10; y = 0.00–1.00) hexaferrites prepared by sol–gel method is investigated, and their effect on the microwave, structural, and magnetic properties is reported. The XRD patterns reveal single-phase M-type hexaferrite structure. The lattice parameters were found to increase by the substitution of NdZn. The increase in lattice parameters is due to the difference in ionic sizes of the cations involved. The average grain size was found between 16 and 29 nm by Scherer formula and was also confirmed by SEM and TEM. Magnetic behavior of selected sample was observed up to a magnetic field of 8T taken at temperature ranges from 4.2 to 373 K. The coercivity of the sample decreased from 2300 to 1210 Oe with increasing temperatures in a linear fashion up to 373 K. The grain boundaries, and the associated pinning fields, seem to have a resolute role in the magnetic behavior of these hexaferrites. Microwave measurements of the ferrite sample have been measured in the frequency range 0.5–12 GHz. The frequency dispersion of ferrites is credited to the phenomenon of natural magnetic resonance and domain wall pinning.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albnese G, Dariu A, Licci F, Rinaldi S (1978) IEEE Trans Magn MAG-14:710
Kown HJ, Shin JY, Oh JH (1994) J Appl Phys 75:6109
Naiden E, Maltsen V, Ryabtsen G (1990) Phys Status Solidi (a) 120:209
Yoon K, Lee D, Jung H, Yoon S (1992) J Mater Sci 27:2941
Ding J, Maurice D, Miao WF, McCormick PG, Street R (1995) J Magn Magn Mater 150:417
Mendoza-Suarez G, Matutes-Aquino JA, Escalante-Garcıa JI, Mancha-Molinar H, Rıos-Jara D, Johal KK (2001) J Magn Magn Mater 223:55
Abbas SM, Dixit AK, Chatterjee R, Goel TC (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 309:20
Kulikowski J (1984) J Magn Magn Mater 41:56
Ruan S, Xu B, Suo H, Wu F, Xiang S, Zhao M (2000) J Magn Magn Mater 212:175
Stergiou CA, Manolakis I, Yioultsis TV, Litsardakis G (2010) J Magn Magn Mater 322:1532
Ramasamy DSR (1997) International conference electromagnetic interference and compatibility INCEMIC-97. New Jersey 7B-7, 459
Iqbal MJ, Ashiq MN, Gul IH (2010) J Magn Magn Mater 322:1720
Hussain Shahid, Maqsood A (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 316:73–80
Valanzuela R (2009) Magnetic ceramics. In: Chemistry of solid state materials, vol 4. Cambridge University Press, p 44
Iqbal MJ, Ashiq MN (2008) Chem Eng J 136:383
ASTM International, Standard test method for measuring the electromagnetic shielding effectiveness of planar materials, standard number D4935-10, 1 May 2010. doi:10.1520/D4935-10
Rezlescu N, Doroftei C, Rezlescu E, Popa PD (2006) Phys Status Solidi 15:3844
Iqbal MJ, Farooq S (2011) Mater Res Bull 46:662
Popa PD, Rezlescu E, Doroftei C, Rezlescu N (2005) J Optoelectron Adv Mater 7:1553
Lechevallier L, Le Breton JM, Wang JF, Harris IR (2004) J Magn Magn Mater 269:192
Che S, Wang J, Chen Q (2003) J Phys Condens Matter 15:L335
Wagner TR (1998) J Solid State Chem 136:120
Chang Sun, Kangning Sun, Pengfei Chui (2012) J Magn Magn Mater 324:802
Costa ACFM, Tortella E, Morelli MR, Kiminami RHGA (2003) J Magn Magn Mater 256:174
Khan HM, Islam MU, Ali I, Rana MA (2011) Mater Sci Appl 2:1083–1089
Smit J, Wijn HPJ (1959) Ferrites. Wiley, New York
Vasambekar PN, Kolekar CB, Vaigankar AS (1999) Mater Res Bull 34:863
Lee SW, An SY, Shim I, Kim CS (2005) J Magn Magn Mater 290–291:231
Rashad MM, Radwan M, Hessien MM (2008) J Alloys Compd 453:304
Mu C, Chen N, Pan X, Shen X, Gu X (2008) Mater Lett 62:840
Khan HM, Islam MU, Xu Y, Ashiq MN, Ali I, Iqbal MA, Ishaque M (2014) Ceram Int 40:6487–6493
Khan HM, Islam MU, Xu Y, Iqbal MA, Ali I (2014) J Alloys Compd 589:258–262
Iqbal MJ, Ashiq MN, Gul IH (2010) J Magn Magn Mater, 1720–1726
Zhang HJ, Liu ZC, Yao X (2003) Mater Sci Eng B 97:160
Haijun Z, Jia XL, Yao X et al (2004) J Rare Earth 22(3):338
Kim YJ, Kim SS (2002) IEEE Trans Magn 38(5):3108
Gao B, Qiao L, Wang JB, Liu QF, Li FS, Feng J, Xue DS (2008) J Phys D Appl Phys 41:35005
Tsutaoka T, Ueshima M, Tokunaga T (1995) J Appl Phys 78:3983
Zhang XF, Guan PF, Dong XL (2010) Appl Phys Lett 96:102505
Singh P, Babbar VK, Razdan A, Srivastava SL, Goel TC (2000) Mater Sci Eng B 78:70
Wu MZ, Zhang YD, Hui S, Xiao TD, Ge SH, Hines WA, Budnick JI, Taylor GW (2002) Appl Phys Lett 23:4404
Naito Y, Suetake K (1971) IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 19:65–72
Michielssen E, Sajer J, Ranjithan S, Mittra R (1993) IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 41:1024
Wessling B (1991) Polym Eng Sci 16:1200–1206
Oikonomou A, Giannakopoulou T, Litsardakis G (2007) J Magn Magn Mater 316:e827–e830
Feng Y, Qiu T (2012) J Alloys Compd 513:455–459
Meena RS, Bhattachrya S, Chatterjee R (2010) Mater Des 31:3220–3226
Qing Y, Zhou W, Luo F, Zhu D (2011) J Magn Magn Mater 323:600
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, H.M., Islam, M.U., Xu, Y. et al. Structural, magnetic, and microwave properties of NdZn-substituted Ca0.5Ba0.5Fe12O19 hexaferrites. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 75, 305–312 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3700-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3700-x