Abstract
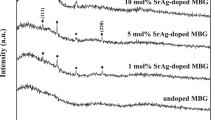
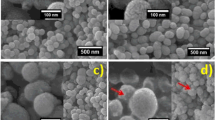
In this study, the antibacterial property of silver-incorporated mesoporous bioactive glass microspheres (Ag-MBGMs) was investigated. The samples belonging to the 80SiO2·(15 − x)CaO·5P2O5·xAg2O system where 0 ≤ x ≤ 5 mol% were successfully prepared for bone regeneration and drug carrier applications. The obtained samples were evaluated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), scanning electron microscope, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and N2 adsorption/desorption measurements. All Ag-MBGMs had spherical particles with particle size 6–10 µm. TEM images showed mesopore structure. The textural properties showed a decrease in surface area and pore volume with an increase in silver content. XRD patterns exhibited the presence of pseudowollastonite and hydroxyapatite phase for silver-incorporating MBGMs, which might increase its bioactivity and bone bonding ability. Finally, all Ag-MBMGs had an antibacterial effect against both Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Therefore, Ag-MBGMs may provide more potential for use as injectable, anticancer and drug-loading biomaterials for bone tissue engineering applications.
Graphical Abstract
In this study, the mesoporous bioactive glass microspheres (MBGMs) belonging to the system 80SiO2·(15 − x)CaO·5P2O5·xAg2O (x = 1, 3, and 5) were successfully prepared by the sol–gel process with surfactant-assisted mesoporous template. Effects of silver addition in MBGMs system were investigated for the first time such as particle shape and size, textural analysis, phase composition, in vitro bioactivity, and antibacterial effect. All prepared MBGMs have uniform microspherical particle (2–5 µm) with hierarchically structure. The textural analysis revealed that all prepared MBGMs had high porosity and relatively high surface area. The incorporation of apatite, pseudowollastonite, and metallic silver crystals were found for adding silver content more than 1 mol%. All prepared MBGMs can induce the crystalline hydroxyl carbonate apatite layer on the surface after soaking in simulated body fluid solution for 7 days. All silver-containing MBGMs had a very good antibacterial effect against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. In addition, silver-incorporated MBGMs exhibited anticancer property against HepG2 cells.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xia W, Chang J (2006) Well-ordered mesoporous bioactive glasses (MBG): a promising bioactive drug delivery system. J Control Release 110(3):522–530. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2005.11.002
Zhu Y, Wu C, Ramaswamy Y, Kockrick E, Simon P, Kaskel S, Zreiqat H (2008) Preparation, characterization and in vitro bioactivity of mesoporous bioactive glasses (MBGs) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 112(1–3):494–503. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.10.029
Hu Q, Chen X, Zhao N, Li Y (2013) Facile synthesis and in vitro bioactivity of monodispersed mesoporous bioactive glass sub-micron spheres. Mater Lett 106:452–455. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2013.04.075
Lei B, Chen X, Wang Y, Zhao N (2009) Synthesis and in vitro bioactivity of novel mesoporous hollow bioactive glass microspheres. Mater Lett 63(20):1719–1721. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2009.04.041
Miao G, Chen X, Dong H, Fang L, Mao C, Li Y, Li Z, Hu Q (2013) Investigation of emulsified, acid and acid-alkali catalyzed mesoporous bioactive glass microspheres for bone regeneration and drug delivery. Mater Sci Eng C 33(7):4236–4243. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2013.06.022
Zhao S, Li Y, Li D (2010) Synthesis and in vitro bioactivity of CaO–SiO2–P2O5 mesoporous microspheres. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 135(1–3):67–73. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2010.06.012
Gristina AG (1987) Biomaterial-centered infection: microbial adhesion versus tissue integration. Science 237(4822):1588–1595
El-Kady AM, Ali AF, Rizk RA, Ahmed MM (2012) Synthesis, characterization and microbiological response of silver doped bioactive glass nanoparticles. Ceram Int 38(1):177–188. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.05.158
Kamitakahara M, Ohtsuki C, Inada H, Tanihara M, Miyazaki T (2006) Effect of ZnO addition on bioactive CaO–SiO2–P2O5–CaF2 glass–ceramics containing apatite and wollastonite. Acta Biomaterialia 2(4):467–471. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2006.03.001
Palza H, Escobar B, Bejarano J, Bravo D, Diaz-Dosque M, Perez J (2013) Designing antimicrobial bioactive glass materials with embedded metal ions synthesized by the sol–gel method. Mater Sci Eng C 33(7):3795–3801. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2013.05.012
Wu C, Zhou Y, Xu M, Han P, Chen L, Chang J, Xiao Y (2013) Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with multifunctional properties of angiogenesis capacity, osteostimulation and antibacterial activity. Biomaterials 34(2):422–433. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.09.066
Diba M, Boccaccini AR (2014) 9—Silver-containing bioactive glasses for tissue engineering applications. In: Baltzer N, Copponnex T (eds) Precious metals for biomedical applications. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, p 177–211. doi:10.1533/9780857099051.2.177
Vernè E, Nunzio SD, Bosetti M, Appendino P, Vitale Brovarone C, Maina G, Cannas M (2005) Surface characterization of silver-doped bioactive glass. Biomaterials 26(25):5111–5119. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.01.038
Lankoff A, Sandberg WJ, Wegierek-Ciuk A, Lisowska H, Refsnes M, Sartowska B, Schwarze PE, Meczynska-Wielgosz S, Wojewodzka M, Kruszewski M (2012) The effect of agglomeration state of silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cellular response of HepG2, A549 and THP-1 cells. Toxicol Lett 208(3):197–213. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.11.006
Prasad RY, McGee JK, Killius MG, Suarez DA, Blackman CF, DeMarini DM, Simmons SO (2013) Investigating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses elicited by silver nanoparticles using high-throughput reporter genes in HepG2 cells: effect of size, surface coating, and intracellular uptake. Toxicol In Vitro 27(6):2013–2021. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2013.07.005
Thati B, Noble A, Creaven BS, Walsh M, McCann M, Devereux M, Kavanagh K, Egan DA (2009) Role of cell cycle events and apoptosis in mediating the anti-cancer activity of a silver(I) complex of 4-hydroxy-3-nitro-coumarin-bis(phenanthroline) in human malignant cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol 602(2–3):203–214
Kawashita M, Toda S, Kim HM, Kokubo T, Masuda N (2003) Preparation of antibacterial silver-doped silica glass microspheres. J Biomed Mater Res A. 66(2):266–274
Kokubo T, Takadama H (2006) How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 27(15):2907–2915. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.017
Ma J, Chen CZ, Wang DG, Meng XG, Shi JZ (2010) Influence of the sintering temperature on the structural feature and bioactivity of sol–gel derived SiO2–CaO–P2O5 bioglass. Ceram Int 36(6):1911–1916. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2010.03.017
Sautier JM, Kokubo T, Ohtsuki T, Nefussi JR, Boulekbache H, Oboeuf M, Loty S, Loty C, Forest N (1994) Bioactive glass-ceramic containing crystalline apatite and wollastonite initiates biomineralization in bone cell cultures. Calcif Tissue Int 55(6):458–466. doi:10.1007/bf00298560
Simon V, Albon C, Simon S (2008) Silver release from hydroxyapatite self-assembling calcium–phosphate glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids 354(15–16):1751–1755. doi:10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.08.063
Zhu M, Zhang J, Tao C, He X, Zhu Y (2014) Design of mesoporous bioactive glass/hydroxyapatite composites for controllable co-delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and proteins. Mater Lett 115:194–197. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2013.10.058
Zhu Y, Kaskel S (2009) Comparison of the in vitro bioactivity and drug release property of mesoporous bioactive glasses (MBGs) and bioactive glasses (BGs) scaffolds. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 118(1–3):176–182. doi:10.1016/j.micromeso.2008.08.046
Vulpoi A, Baia L, Simon S, Simon V (2012) Silver effect on the structure of SiO2–CaO–P2O5 ternary system. Mater Sci Eng C 32(2):178–183. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2011.10.015
Saravanapavan P, Patel MH, Hench LL (2003) Effect of composition and texture on controlled rate of release of an antibacterial agent from bioactive gel-glasses. Bioceramics 15(240–242):233–236. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.240-242.233
Gargiulo N, Cusano AM, Causa F, Caputo D, Netti PA (2013) Silver-containing mesoporous bioactive glass with improved antibacterial properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med 24(9):2129–2135
Nezafati N, Moztarzadeh F, Hesaraki S (2012) Surface reactivity and in vitro biological evaluation of sol gel derived silver/calcium silicophosphate bioactive glass. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 17(4):746–754. doi:10.1007/s12257-012-0046-x
Anjaneyulu U, Sasikumar S (2014) Bioactive nanocrystalline wollastonite synthesized by sol–gel combustion method by using eggshell waste as calcium source. Bull Mater Sci 37(2):207–212. doi:10.1007/s12034-014-0646-5
Bellantone M, Williams HD, Hench LL (2002) Broad-spectrum bactericidal activity of Ag2O-doped bioactive glass. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46(6):1940–1945. doi:10.1128/aac.46.6.1940-1945.2002
Valappil SP, Pickup DM, Carroll DL, Hope CK, Pratten J, Newport RJ, Smith ME, Wilson M, Knowles JC (2007) Effect of silver content on the structure and antibacterial activity of silver-doped phosphate-based glasses. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51(12):4453–4461
Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, Hotze M, Sempf J, Oberley T, Sioutas C, Yeh JI, Wiesner MR, Nel AE (2006) Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett 6(8):1794–1807
Bellantone M, Coleman NJ, Hench LL (2000) Bacteriostatic action of a novel four-component bioactive glass. J Biomed Mater Res 51(3):484–490. doi:10.1002/1097-4636(20000905)51:3<484:aid-jbm24>3.0.co;2-4
Zhang S, Du C, Wang Z, Han X, Zhang K, Liu L (2013) Reduced cytotoxicity of silver ions to mammalian cells at high concentration due to the formation of silver chloride. Toxicol In Vitro 27(2):739–744. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2012.12.003
Acknowledgments
This work has been financed by The Royal Golden Jubilee Ph.D. program supported from Thailand Research Fund and Suranaree University of Technology. The authors would like to thank Dr. Ratchadaporn Oonsivilai and Miss Thasaneewan Srisan for their helps in MTT assay test.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phetnin, R., Rattanachan, S.T. Preparation and antibacterial property on silver incorporated mesoporous bioactive glass microspheres. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 75, 279–290 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3697-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3697-1