Abstract
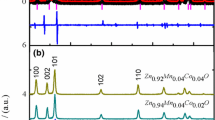
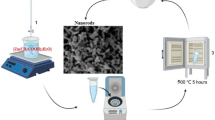
Herein, pure and 3 % transition metals (TM; Cr2+ and Fe2+ ions)-doped ZnO nanostructures with high aspect ratios were prepared by microwave–hydrothermal method. X-ray diffraction, selected area electron diffraction and high resolution transmission electron microscopy analyses revealed that all the TM (Cr2+ and Fe2+ ions)-doped ZnO nanostructures have wurtzite structure and no secondary phase was detected. Field emission scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy results confirmed a higher aspect ratio and highly crystalline nature of nanostructures. Raman spectra reveled that no defect related mode was observed which indicated that the nanostructures have high quality and negligible defects. The value of bandgap was found to be close to the standard value of ZnO, and increased with the increase in atomic number of TM dopants, which indicated that the Cr2+ and Fe2+ ions were uniformly substituted in ZnO. Room temperature ferromagnetism was observed in all the TM (Cr2+ and Fe2+ ions)-doped ZnO nanostructures and the value of saturation magnetization (Ms) and remanent magnetization (Mr) were increased with TM (Cr2+ and Fe2+ ions) dopants. The modification in the magnetization and Hc by microwave hydrothermal might be due to the high aspect ratio of nanostructures. Hence, these nanostructures pave the way for development of multifunctional spintronics and optoelectronic devices that integrate structural, morphological, optical, and magnetic properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dietl T, Ohno H, Matsukura F, Cibert J, Ferrant D (2000) Science 287:1019
Jung SW, An SJ, Yi GC, Jung CU, Lee SI, Cho S (2002) Appl Phys Lett 80:4561
Venkatesan M, Fitzgerald CB, Lunney JG, Coey JMD (2004) Phys Rev Lett 93:177206
Neal JR, Behan AJ, Ibrahim RM, Blythe HJ, Ziese M, Fox AM, Gehring GA (2006) Phys Rev Lett 96:197208
Liu JJ, Yu MH, Zhou WL (2005) Appl Phys Lett 87:172505
Ahmed F, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Lee SH, Byon ES, Lyu NJ, Koo BH (2012) Curr Appl Phys 12:S174
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH, Lee CG (2012) Microelectron Eng 89:129
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH, Lee CG (2012) J Nanosci Nanotechnol 12:1386
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Heo SN, Kim GW, Koo BH (2012) J Korean Phys Soc 60:1644
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH (2012) Cryst Eng Comm 14:4016
Theodoropoulou N, Hebard A, Norton D, Budai J, Boatner L, Lee J (2003) Solid State Electron 47:2231
Gupta A, Cao H, Parekh K, Rao K, Raju A, Waghmare U (2007) J Appl Phys 101:09N513
Venkatesan M, Fitzgerald CB, Lunney JG, Coey JMD (2004) Phys Rev Lett 93:177206
Kim JH, Kim H, Kim D, Ihm YE, Choo WK (2002) J Appl Phys 92:6066
Park JH, Kim MG, Jang HM, Ryu S (2004) Appl Phys Lett 84:1338
Sundaresan A, Bhargavi R, Rangrajan N, Siddesh U, Rao CNR (2006) Phys Rev B 74:161306
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH, Lee CG (2011) Funct Mater Lett 4:1
Garcia MA, Merino JM, Pinel EF, Quesada A, Venta J, Gonzlez MLR (2007) Nano Lett 7:1489
Ahmed F, Kumar S, Arshi N, Anwar MS, Koo BH, Lee CG (2011) Thin Solid Films 519:8199
Kumar S, Kim YJ, Koo BH, Gautam S, Chae KH, Kumar R (2009) Mater Lett 63:194
Breviglieri ST, Cavalherio ETG, Chierice GO (2000) Thermochim Acta 356:79
Roberts BK, Pakhomov AB, Shutthanandan VS, Krishnan KM (2005) J Appl Phys 97:10D310
Xu HY, Liu YC, Xu CS, Liu YX, Shao CL, Mu R (2006) J Chem Phys 124:074707
Anghel J, Thurber A, Tenne DA, Hanna CB, Punnoose A (2010) J Appl Phys 107:09E314
Shannon RD (1976) Acta Crystallogr Sect A 32:751
Senthilkumaar S, Rajendran K, Banerjee S, Chini TK, Sengodan V (2008) Mater Sci Semicond Process 11:6
Dinesha ML, Jayanna HS, Mohanty S, Ravi S (2008) J Alloys Compd 480:618
Wang Iqbal J, Shan X, Huang G, Fu H, Yu R (2009) Mater Chem Phys 113:103
Damen TC, Porto SPS, Tell B (1966) Phys Rev 142:570
Bundesmann C, Ashkenov N, Schubert M, Spemann D, Butz T, Kaidashev EM (2003) Appl Phys Lett 83:1074
Parayanthal P, Pollak FH (1984) Phys Rev Lett 52:1822
Xu HY, Liu YC, Xu CS, Liu YX, Shao CL, Mu R (2006) J Chem Phys 124:074707
Thakur JS, Auner GW, Naik VM, Sudakar C, Kharel P, Lawes G (2007) J Appl Phys 102:093904
Pankove JI (1971) Optical processes in semiconductors. Prentice-Hall Inc., Englewoord Cliffs
Qiu X, Li L, Li G (2006) Appl Phys Lett 88:114103
Radovanovic P, Gamelin DR (2003) Phys Rev Lett 91:157202
Fukumura T, Yamada Y, Toyosaki H, Hasegawa T, Koinuma H, Kawasaki M (2004) Appl Surf Sci 223:62
Zener C (1951) Phys Rev 81:440
Punnoose A, Hays J, Thurber A, Engelhard MH, Kukkadapu RK, Wang C (2005) Phys Rev B 72:054402
Thurber A, Reddy KM, Shutthanandan V, Engelhard MH, Wang C, Hays J (2007) Phys Rev B 76:165206
Komen CV, Punnoose A, Seehra MS (2009) Solid State Commun 149:2257
Xing GZ, Yi JB, Tao JG, Liu T, Wong LM, Zhang Z, Li GP, Wang SJ, Ding J, Sum TC, Huan CHA, Wu T (2008) Adv Mater 20:3521
Stoner EC, Wohlfarth EP (1984) Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A 240:559
Choi J, Oh SJ, Ju H, Cheon J (2005) Nano Lett 5:2179
Girgisa E, Schelten J (2000) Appl Phys Lett 76:3780
Hays J, Punnoose A, Baldner R, Engelhard MH, Peloquin J, Reddy KM (2005) Phys Rev B 72:075203
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST) and National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Human Resource Training Project for Regional Innovation (2012H1B8A2026212). This work was also supported by the MSIP (Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning), Korea. Under the ITRC (Information Technology Research Centre) support program supervised by the NIPA (National IT Industry Promotion Agency) (NIPA-2014-H0301-14-1016). This research was also supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2012-R1A1B3000784).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, F., Arshi, N., Anwar, M.S. et al. Improving functional properties of ZnO nanostructures by transition-metal doping: role of aspect ratio. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 72, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3412-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-014-3412-7