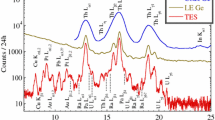
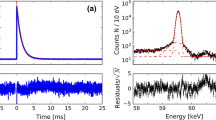
Abstract
PGAA was performed on three 239Pu foils: (1) 1810 kBq electrodeposited on nickel, (2) 17.8 kBq sample, and (3) a 13.9 kBq sample (2 and 3 electrodeposited on SS304). The activities of samples (2) and (3) were determined based on the 2015 and 6102 keV prompt gamma ray net counts from each sample relative to sample (1) counts. Results showed good agreement between measured and certified activities [within 4% for sample (2) and 11% for sample (3)]. Using PGAA, it may be possible to enhance current safeguards techniques to enable 239Pu detection through attenuating nuclear material storage containers.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nguyen C (2006) Verification of the 239Pu content, isotopic composition and age of plutonium in Pu–Be neutron sources by gamma-spectrometry. Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res B 251:227–236
Helmer RG, Reich CW, Gehrke RJ, Baker JD (1982) Emission probabilities and energies of γ-ray transitions from the 239Pu decay. Int J App Radiat Isotop 33:23–26
Egozi C, Charlton W, Landsberger S (2022) Characterization of 239Pu with PGAA for materials accountability. In: IAEA symposium on international safeguards: reflecting on the past and anticipating the future, Vienna, https://www.iaea.org/events/sg-2022
Lindstrom RM (1993) Prompt-gamma activation analysis. J Res Natl Inst Stand Technol 98:127–133
IAEA, 2014. Prompt gamma-ray neutron activation analysis, https://www-nds.iaea.org/pgaa/pgaa7/index.html.
Gladney ES, Curtis DB, Jurney ET (1978) Multielement analysis of major and minor elements by thermal neutron induced capture gamma-ray spectrometry. J Radioanal Chem 46:299–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02519896
Robinson JA, Hartman MR, Reese SR (2010) Design, construction and characterization of a prompt gamma activation analysis facility at the Oregon state university TRIGA® reactor. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 283:359–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0358-2
Zhao L, Robinson L (2009) A comparison between cold and thermal neutron prompt gamma activation analysis in the determination of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in cattail. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 282:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-009-0309-y
Lindstrom RM, Révay Z (2017) Prompt gamma neutron activation analysis (PGAA): recent developments and applications. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314:843–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-017-5483-8
Newton Nathaniel T, Sudarshan K, Goswami A et al (2009) Non-destructive assay technique for the determination of 238U/232Th ratio in the mixed oxides of uranium and thorium using prompt gamma-ray neutron activation. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 279:481–485. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-007-7314-4.(OLD6)
Paul RL, Lindstrom RM (2000) Prompt gamma-ray activation analysis: fundamentals and applications. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 243:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006796003933.(OLD7)
Oliveira C, Salgado J (1993) Elemental composition of coal by using prompt gamma-neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 167:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02035475
Manescu A et al (2008) J Phys: Condens Matter 20:104250
Kasztovszky Z, Panczyk E, Fedorowicz W et al (2005) Comparative archaeometrical study of Roman silver coins by prompt gamma activation analysis and SEM-EDX. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 265:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-005-0809-3
Zeisler R, Lamaze GP, Chen-Mayer HH (2001) Coincidence and anti-coincidence measurements in prompt gamma neutron activation analysis with pulsed cold neutron beams. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 248:35–38. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010609604827
Osawa T (2015) Development of an automatic prompt gamma-ray activation analysis system. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303:1141–1146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3436-z
Prompt Gamma-Ray Activation Analysis (PGAA). NIST, 15 Nov 2019, www.nist.gov/laboratories/tools-instruments/prompt-gamma-ray-activation-analysis-pgaa.
Révay Z, Firestone RB, Belgya T, Molnár GL (2004) Prompt gamma-ray spectrum catalog. In: Molnár GL (ed) Handbook of prompt gamma activation analysis. Springer, Boston, MA
Révay Z (2008) Prompt gamma activation analysis of samples in thick containers. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 276:825
Révay Zs, Harrison RK, Alvarez E, Biegalski SR, Landsberger S (2007) Construction and characterization of the redesigned PGAA facility at the university of 241 Texas at Austin. Nucl Instrum Meth Phys Res A 577(3):611–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2007.04.119
Charlton WS, Lohmeier D, Andrews M, Wermer JR, Cooley JC (2022) Hydrogen measurements in U alloys using prompt gamma-ray activation analysis. Trans Am Nucl Soc 126:245–247
Sonzogni AA (2004) Nucl Data Sheets 103:1
Turhan S (2007) Efficiency calibration of an HPGe detector in the 0.1–2.5 MeV energy range 244 for Am-Be neutron source-based PGAA applications. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 273:443–245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-007-6877-9
Currie LA (1968) Limits for qualitative detection and quantitative determination. Appl radiochem Anal Chem 40:586–593. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60259a007
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) for providing the funding for this work. This paper is approved for release by LANL LA-UR-23-28777.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Egozi, C., Charlton, W.S. & Landsberger, S. Prompt gamma activation analysis for 239Pu characterization. J Radioanal Nucl Chem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-024-09498-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-024-09498-3