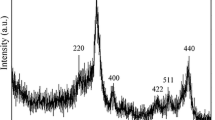
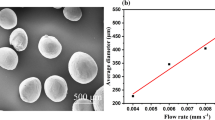
Abstract
New microsphere sorbents are reported, which could find application in demanding radiation environments and especially as targets for the production of nuclear medicines by neutron irradiation. An easily-synthesized Zr anionic complex was introduced into quaternary amine-functionalised polystyrene-divinylbenzene-based anion-exchange resins by batch adsorption. Upon carbothermal reduction, the precursors were converted to porous carbon matrices containing particles of ZrC and ZrO2 polymorphs. The most phase-pure material, ZrAX-1, possessed high surface area, multi-scale porosity and high mechanical strength. Adsorption of Re and W was investigated and its possible deployment as a reusable host for the production of 188W/188Re is discussed.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dash A, Knapp FFRJ (2015) An overview of radioisotope separation technologies for development of 188W/188Re radionuclide generators providing 188Re to meet future research and clinical demands. RSC Adv. 5:39012–39036
Yttrium-90 and Rhenium-188 radiopharmaceuticals for radionuclide therapy (2015). IAEA radioisotopes and radiopharmaceuticals series no. 5. International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna
Argyrou M, Valassi A, Andreou M, Lyra M (2013) Rhenium-188 production in hospitals, by W-188/Re-188 generator, for easy use in radionuclide therapy. Int J Mol Imaging. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/290750
Storms EK (1967) The refractory carbides. Refractory materials, vol 2. Academic Press, New York
Katoh Y, Vasudevamurthy G, Nozawa T, Snead LL (2013) Properties of zirconium carbide for nuclear fuel applications. J Nucl Mater 441:718–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2013.05.037
Gosset D, Dolle M, Simeone D, Baldinozzi G, Thome L (2008) Structural evolution of zirconium carbide under ion irradiation. J Nucl Mater 373(1–3):123–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2007.05.034
Snead LL, Katoh Y, Kondo S (2010) Effects of fast neutron irradiation on zirconium carbide. J Nucl Mater 399:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnucmat.2010.01.020
Scales N, Chen J, Hanley TL, Riley DP, Lumpkin GR, Luca V (2015) Hierarchically porous carbon-zirconium carbide spheres as potentially reusable transmutation targets. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 212:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2015.03.025
Blurton KF (1972) Preparation of highly dispersed platinum on carbon. Carbon 10(3):305–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6223(72)90329-6
Miura K, Nakagawa H (2003) Preparation of metal-loaded porous carbons and their use as a highly active catalyst for reduction of nitric oxide (NO). In: Yasuda M, Inagaki M, Kaneko K, Endo M, Oya A, Tanabe Y (eds) Carbon alloys: novel concepts to develop carbon science and technology. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-008044163-4/50031-0
Trens P, Caps V, Peckett JW (2003) Catalytic oxidation of trans-stilbene using pyrolysed manganese-loaded cation exchange resin. Appl Catal A 251(1):19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(03)00311-9
Trens P, Peckett JW, Stathopoulos VN, Hudson MJ, Pomonis PJ (2003) Phosphotungstate anions supported on spherical beads of carbon as highly efficient catalysts for the dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene. Appl Catal A 241(1–2):217–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-860X(02)00498-2
Li B, Ren Y, Fan Q, Feng A, Dong W (2004) Preparation and characterization of spherical nickel-doped carbonaceous resin as hydrogenation catalysts. I. Carbonization procedures. Carbon 42(12–13):2669–2676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2004.06.010
Yu W, Zheng J, He X, Zhao Y (2008) Synthesis of spherical activated carbon loaded with metal particles and its performance of thiophene adsorption. Huagong Xuebao (Chin Ed) 59(11):2824–2829
Kudo S, Maki T, Miura K, Mae K (2010) High porous carbon with Cu/ZnO nanoparticles made by the pyrolysis of carbon material as a catalyst for steam reforming of methanol and dimethyl ether. Carbon 48(4):1186–1195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2009.11.042
Wilson MS, Delariva A, Garzon FH (2011) Synthesis of sub-2 nm ceria crystallites in carbon matrixes by simple pyrolysis of ion-exchange resins. J Mater Chem 21:7418–7424. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1jm10529a
Kotai L, Pasinszki T, Czegeny Z, Balint S, Sajo I, May Z, Nemeth P, Karoly Z, Sharma PK, Sharma V, Banerji KK (2012) Metal and metal-sulfide containing carbons from sulfonated styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer based ion-exchangers. Eur Chem Bull 1(10):398–400
Li W, Zhang Z, Cui A, Fan J, Sun X (2013) A gasoline desulfurization adsorbent and preparation method thereof, CN103143321A.
Fan J, Lan H, Zhang Z, Li W (2014) Study on gasoline adsorptive desulfurization of resin-based modified spherical activated carbon. Shiyou Lianzhi Yu Huagong 45(9):10–15
Beatty RL (1976) Microspheres containing metal carbide from metal-charged resin beads, DE2527093A1
Tosheva L, Parmentier J, Saadallah S, Vix-Guterl C, Valtchev V, Patarin J (2004) Carbon and SiC macroscopic beads from ion-exchange resin templates. J Am Chem Soc 126(42):13624–13625. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0461217
Scales N, Chen J, Aughterson RD, Karatchevtseva I, Stopic A, Lumpkin GR, Luca V (2018) Porous Zr2SC-carbon microspheres: Possible radiation tolerant sorbents and transmutation hosts for technetium-99. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 259:67–78
Bochkarev GS, Zaitsev LM, Kozhenkova VN (1963) Complexes of zirconium oxalates. Zh Neorg Khim 8:2248–2253
Simonits A, De Corte F, Hoste J (1975) Single-comparator methods in reactor neutron activation analysis. J Radioanal Chem 24(1):31–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02514380
Pimenta MA, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus MS, Cancado LG, Jorio A, Saito R (2007) Studying disorder in graphite-based systems by Raman spectroscopy. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9(11):1276–1291. https://doi.org/10.1039/b613962k
Sing KSW, Everett DH, Haul RAW, Moscou L, Pierotti RA, Rouquerol J, Siemieniewska T (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems. Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
Ferrari AC (2007) Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: disorder, electron-phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun 143(1–2):47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2007.03.052
Baes CF, Mesmer RE (1976) The hydrolysis of cations. Wiley, New York
Sacks MD, Wang C-A, Yang Z, Jain A (2004) Carbothermal reduction synthesis of nanocrystalline zirconium carbide and hafnium carbide powders using solution-derived precursors. J Mater Sci 39:6057–6066. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000041702.76858.a7
Rejasse F, Repaud O, Trolliard G, Masson O, Maitre A (2016) Experimental investigation and thermodynamic evaluation of the C-O-Zr ternary system. RSC Adv 6:100122–100135
Gendre M, Maitre A, Trolliard G (2011) Synthesis of zirconium oxycarbide (ZrCxOy) powders: influence of stoichiometry on densification kinetics during spark plasma sintering and on mechanical properties. J Eur Ceram Soc 31:2377–2385
Acknowledgements
Materials and equipment access were provided and/or funded by Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO). The authors gratefully acknowledge the following ANSTO staff for their contributions: Mr Kerry Cruikshank and Dr Ken Short for ongoing technical support for our tube furnace; Mr Karl Toppler for assistance with mechanical testing equipment; and Mr Joel Davis for SEM data. Mercury Porosimetry data were acquired by Particle & Surface Sciences Pty Ltd, NSW, Australia and O, N microanalysis was conducted by CSIRO Mineral Resources, VIC, Australia; both on a pay-per-sample basis. This research has been conducted with the support of the Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship. Professor Chen acknowledges continuing support from Australian National Fabrication Facility (ANFF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scales, N., Chen, J., Aughterson, R.D. et al. Porous ZrC-carbon microspheres as potential insoluble target matrices for production of 188W/188Re. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 318, 835–847 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6059-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-018-6059-y