Abstract
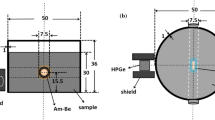
MCNP5 has been used to optimize the design of a Prompt gamma ray neutron activation analysis (PGNAA) facility, which was subsequently constructed for quantification of total chlorine in water to simulate neutron transport from an 241AmBe source into a PGNAA set-up. Modeling calculations were performed to optimize the experimental set-up for Cl measurements in water. The optimization with MCNP5 was focused on maximizing the thermal neutrons flux which leads to improving the gamma prompt production after neutron capture in a water sample. The influence of dimensions and materials for the neutron collimation as well as the dimensions of the sample together were studied. A PGNAA facility with an 241AmBe neutron source was built based on the optimized configuration and used to determine chlorine concentration. Measured values of the chlorine count rate were plotted versus the NaCl in water. The count rate versus amount of chlorine show a good coefficient of correlation of the linear fit. The result permits PGNAA to be a valuable diagnostic tool for getting an indication of the salinity contamination of water.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howell SL, Sigg RA, Moore FS, DeVol TA (2000) Calibration and validation of a Monte Carlo model for PGNAA of chlorine in soil. J. Radioanal. And Nucl. Chem. 244:1173–1178
Borsaru M, Smith C, Merrit J, Aizawa T, Rojc A (2005) In situ determination of salinity by PGNAA. Appl Radiat Isot 64:630–637
Boman B, Sover EW (2015) Managing salinity in florida citrus. http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/AE171
Zhang Z et al (2008) J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:241–245
Zhifang C (2004) Analytical applications of nuclear techniques, IAEA PUB 1181, IAEA, Vienna, pp 62–64
MCNP5 (2003) A General Monte-Carlo N-particle Transport Code, Version 5, X-5 Monte Carlo Team, Report LA-UR-03-1987, Alamos National Laboratory
Sudarshan R, Tripathi R, Nair AGC, Acharya R, Reddy AVR, Goswami A (2005) A simple method for correcting the neutron self-shielding effect of matrix and improving the analytical response in prompt gamma-ray neutron activation analysis. Anal Chem Acta 549:205–211
Khelifi R, Bode P, Amokrane A (2007) Flux calculation in LSNAA using an 241AmBe source. J Radioannal Nucl Chem 274:639–642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khelifi, R., Bode, P. Monte Carlo study of a flexible device for in situ PGNAA using 241Am–Be source: application to total chlorine determination. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 309, 189–193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-4844-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-4844-z