Abstract
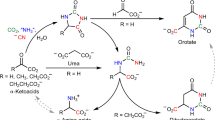
Studies on the contribution to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetic acid from the pyruvic acid transformation from l-alanine in Arthrobacter hyalinus were conducted by means of feeding experiments with l-[1-13C]alanine and l-[3-13C]alanine, followed by an analysis of the labeling patterns of coproporphyrinogen III using 13C NMR spectroscopy. The results demonstrated that l-alanine was transformed via pyruvic acid to both acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetic acid. Additionally, the quantitative analysis indicated that pyruvic acid was transformed to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetic acid in the ratio of 1:0.8.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima I, Maruhashi K, Sato H, Fujiwara Y (1993) A highly active producer of coproporphyrin III and uroporphyrin III. J Ferment Bioeng 76:527–529
Kajiwara M, Mizutani M, Matsuda R, Hara K, Kojima I (1994) A new biosynthetic pathway of porphyrins from isopropanol. J Ferment Bioeng 77:626–629
Iida K (2013) Quantitative evaluation of the biosynthetic pathways leading to δ-aminolevulinic acid from the Shemin precursor glycine via the C5 pathway in Arthrobacter hyalinus by analysis of 13C-labeled coproporphyrinogen III biosynthesized from [2-13C]glycine, [1-13C]acetate, and [2-13C]acetate using 13C NMR spectroscopy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 295:1819–1827
Iida K, Aoki T, Uegaki R, Kajiwara M (1997) Biosynthesis of corrinoids and porphyrinoids. XI. Source of oxaloacetic acid for uroporphyrinogen III biosynthesis in Arthrobacter hyalinus. Chem Pharm Bull 45:397–398
Kojima I, Maruhashi K, Fujiwara Y, Saito T, Kajiwara M, Mizutani M (1993) Identification of porphyrins produced from isopropanol Arthrobacter hyalinus. J Ferment Bioeng 75:353–358
Iida K, Kajiwara M (2000) Evaluation of biosynthetic pathways to δ-aminolevulinic acid in Propionibacterium shermanii based on biosynthesis of vitamin B12 from d-[1-13C]glucose. Biochemistry 39:3666–3670
Iida K, Mimura I, Kajiwara M (2002) Evaluation of two biosynthetic pathways to δ-aminolevulinic acid in Euglena gracilis. Eur J Biochem 269:291–297
Iida K, Kajiwara M (2008) Carbon source dependence of the ratio of δ-aminolevulinic acid biosynthesis via the C5 and Shemin pathways in Euglena gracilis (Euglenophyceae). J Phycol 44:292–298
Acknowledgment
The author would like to thank Prof. Kajiwara for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iida, K. Investigation of the biosynthesis of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetic acid from pyruvic acid and the quantitative evaluation of incorporated 13C-labeled l-alanine in Arthrobacter hyalinus . J Radioanal Nucl Chem 301, 897–904 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3172-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3172-4