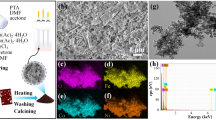
Abstract
This research is aimed towards a facile one-step preparation of magnetic poly(styrene-glycidyl methacrylate)-Fe3O4 nanocomposite particles named as P(S-GMA)-Fe3O4. The nanocomposite particles are prepared by a simultaneous free-radical copolymerization and co-precipitation of Fe2+ and Fe3+ salts. Two variable w/w ratios of styrene to GMA (98/2 and 96/4) are used. But, the overall copolymer to iron oxide ratio is kept identical. The structural analyses and morphology revealed the uniform distribution of Fe3O4 nanoparticles and the nanocomposites showed paramagnetic property. The potentiality of nanocomposite particles as glucose bisenosors via adsorption of glucose oxidase (GOD) is investigated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and cyclic voltammetry (CV). A comparative analysis of the glucose concentration dependent current response suggested that the modified electrode fabricated from P(S-GMA)-Fe3O4(2) (w/w ratio, 98/2) possessed superior response to other electrodes made from PS, P(S-GMA), PS-Fe3O4 and P(S-GMA)-Fe3O4(4) (w/w ratio, 96/4), respectively. The P(S-GMA)-Fe3O4(2)/GOD/Pt biosensor could measure glucose in the range of 2.2 × 10− 4 to 6.0 × 10− 3 M with a sensitivity of 14.47 µA mM− 1 and exhibited a detection limit of 5.07 µM at a signal to noise ratio of 3. The value of Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) is calculated as 0.019 mM. Overall results indicate that P(S-GMA)-Fe3O4(2) nanocomposite prepared in one-step is suitable for use in glucose biosensors.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behren S, Appel I (2016) Magnetic nanocomposites. Curr Opin Biotechnol 39:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2016.02.005
Bithi KA, Minami H, Hossain MK, Rahman MM, Rahman MA, Gafur MA, Ahmad H (2020) Cationic polyelectrolyte grafted mesoporous magnetic silica composite particles for targeted drug delivery and thrombolysis. Materialia 11:100676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2020.100676
Tanjim M, Rahman MA, Rahman MM, Minami H, Hoque SM, Sharafat MK, Gafur MA, Ahmad H (2018) Mesoporous magnetic silica particles modified with stimuli-responsive P(NIPAM–DMA) valve for controlled loading and release of biologically active molecules. Soft Matter 14:5469–5479. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SM00560E
Padmavathy N, Chakraborty I, Kumar A, Roy A, Bose S, Chatterjee K (2022) Fe3O4@Ag and Ag@Fe3O4 core-shell nanoparticles for radio frequency shielding and bactericidal activity. ACS Appl Nano Mater 5:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c02722
Martins PM, Lima AC, Ribeiro S, Lanceros-Mendez S, Martins P (2021) Magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical applications: from the soul of the earth to the deep history of ourselves. ACS Appl Bio Mater 4:5839–5870. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.1c00440
Xu Y-P, Zhou H-Y, Wang G-C, Zhang Y, Yang T, Zhao Y, Li R-T, Zhang R-R, Guo Y, Wang X, Li X-F, Qin C-F, Tang R (2020) Rational design of a replication-competent and inheritable magnetic viruses for targeting biomedical applications. Small 16:2002435. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202002435
Kharey P, Indoliya A, Gupta R, Poddar R, Sharma D, Gupta S (2022) Near-infrared active superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetomotive optical coherence tomography imaging and magnetic hyperthermia therapeutic application. J Magn Magn Mater 549:169038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2022.169038
Song X, Mo J, Fang Y, Luo S, Xu J, Wang X (2022) Synthesis of magnetic nanocomposite Fe3O4@ZIF-8@ZIF-67 and removal of tetracycline in water. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:35204–35216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18042-9
Liu F, Niu F, Peng N, Su Y, Yang Y (2015) Synthesis, characterization, and application of Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 nanoparticles. RSC Adv 5:18128–18136. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA15968C
Joshi S, Garg VK, Kataria N, Kadirvelu K (2019) Applications of Fe3O4@AC nanoparticles for dye removal from simulated wastewater. Chemosphere 236:124280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.07.011
Ma M, Hou P, Zhang P, Cao J, Loi H, Yue H, Tian G, Feng S (2020) Magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles as easily separable catalysts for efficient catalytic transfer hydrogenation of biomass-derived furfural to furfuryl alcohol. Appl Catal A: General 602:117709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2020.117709
Sarker MZ, Rahman MM, Minami H, Suzuki T, Rahman MA, Khan A, Hoque SM, Ahmad H (2022) Magnetite incorporated amine-functional SiO2 support for bimetallic Cu-Ni alloy nanoparticles produced highly effective nanocatalyst. Colloids Surf A Physicoochem Eng Aspects 647:129044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.129044
Zhang W, Li X, Zou R, Wu H, Shi H, Yu S, Liu Y (2015) Multifunctional glucose biosensors from Fe3O4 nanoparticles modified chitosan/graphene nanocomposites. Sci Rep 5:11129. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11129
He C, Xie M, Hong F, Chai X, Mi H, Zhou X, Fan L, Zhang Q, Ngai T, Liu J (2016) A highly sensitive glucose biosensor based on gold nanoparticles/bovine serum albumin/Fe3O4 biocomposite nanoparticles. Electrochim Acta 222:1709–1715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2016.11.162
Peng L, Luo Y, Xiong H, Yao S, Zhu M, Song H (2021) A novel amperometric glucose biosensor based on Fe3O4-chitosan-β-cyclodextrin/MWCNTs nanobiocomposite. Electroanalysis 33:723–732. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060399
Rocha-Santos TAP (2014) Sensors and biosensors based on magnetic nanoparticles. Trends Anal Chem 62:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2014.06.016
Bakker E (2004) Electrochemical sensors. Anal Chem 76:3285–3298. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac049580z
Sanaeifar N, Rabiee M, Abdolrahim M, Tahriri M, Vashaee D, Tayebi L (2017) A novel electrochemical biosensor based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles-polyvinyl alcohol composite for sensitive detection of glucose. Anal Biochem 519:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.12.006
Shabnam R, Rahman MA, Miah MAJ, Sharafat MK, Islam HMT, Gafur MA, Ahmad H (2017) Novel magnetically doped epoxide functional cross-linked hydrophobic poly(lauryl methacrylate) composite polymer particles for removal of as(III) from aqueous solution. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:7747–7756. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b01741
Bristy SS, Rahman MM, Rahman MM, Alam MA, Karim MR, Ahmad H (2019) Epoxide functionalized γ-Al2O3/Fe3O4/SiO2 nanocomposite particles and comparative adsorption behavior of a model reactive azo dye. Int J Appl Cer Technol 16:1239–1252. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijac.13141
Kaushik A, Khan R, Solanki PR, Pandey P, Alam J, Ahmad S, Malhotra BD (2008) Iron-oxide nanoparticles-chitosan composite based glucose biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:676–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2008.06.032
Dizajyekan BS, Jafari A, Hasani M, Vafaei-Sefti M, Fakhroueian DZ, Baghbansalehi M (2020) Surface modification of synthesized Fe3O4 super-paramagnetic nanoparticles and performance investigation in gelation parameters enhancement: application in enhanced oil recovery. Appl Nanosci 10:955–969. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-01187-y
Rodriguez-Abetxuko A, Sánchez-deAlcázar D, Muñmer P, Beloqui A (2020) Tunable polymeric scaffolds for enzyme immobilization. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:830. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.00830
Liu S, Yu B, Wang S, Shen Y, Cong H (2020) Preparation, surface functionalization and application of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 281:102165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2020.102165
Yang L, Ren X, Tang F, Zhang L (2009) A practical glucose biosensor based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles and chitosan/nafion composite film. Biosens Bioelectron 25:889–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.09.002
Yee YC, Hashim R, Yahya ARM, Bustami Y (2019) Colorimetric analysis of glucose oxidase-magnetic cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) for glucose detection. Sensors 19:2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19112511
Yang Z, Zhang C, Zhang J (2014) Potentiometric glucose biosensor based on core-shell Fe3O4-enzyme-polypyrrole nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 51:268–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.07.054
Mao Q, Jing W, Gao W, Wei Z, Tian B, Liu M, Ren W, Jiang Z (2021) High-sensitivity enzymatic glucose sensor based on ZnO urchin-like nanostructure modified with Fe3O4 magnetic particles. Micromachines 12:977. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12080977
Pakapongpan S, Pooarporn RP (2017) Self-assembly of glucose oxidase on reduced graphene oxide-magnetic nanoparticles nanocomposite-based direct electrochemistry for reagent less glucose biosensor. Mater Sci Eng C 76:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.031
Baghayeria M, Veisib H, Ghanei-Motlagh M (2017) Amperometric glucose biosensor based on immobilization of glucose ooxidase on a magnetic glassy carbon electrode modified with a novel magnetic nanocomposite. Sens Actuators B 249:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.100
Bristy SS, Rahman MA, Tauer K, Minami H, Rahman MM, Ahmad H (2018) Preparation and characterization of magnetic γ-Al2O3 ceramic nanocomposite particles with variable Fe3O4 content and modification with epoxide functional polymer. Ceram Int 44:3951–3959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.187
Horák D, Trchová M, Beneš MJ, Veverka M, Pollert E (2010) Monodispersed magnetic composite poly(glycidyl methacrylate)/La0.75Sr0.25MnO3 microspheres by the dispersion polymerization. Polymer 51:3116–3122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2010.04.055
Ahmad H, Alam MM, Rahman MA, Minami H, Gafur MA (2018) Epoxide functional temperature-sensitive semi-IPN hydrogel microspheres for isolating inorganic nanoparticles. Adv Polym Technol 37:21645. https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21645
Nahar Y, Rahman MA, Hossain MK, Sharafat MK, Karim MR, Elaissari A, Ochiai B, Ahmad H, Rahman MM (2020) A facile one-pot synthesis of poly(acrylic acid)-functionnalized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for suppressing reactive oxygen species generation and adsorption of biocatalyst. Mater Res Express 7:016102. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab5be1
Karakus G, Ece A, Yaglioglu AS, Zengin HB, Karahan M (2017) Synthesis, structural characterization, and antiproliferative/cytotoxic effects of a novel modified poly(maleic anhydride-co-vinyl acetate)/doxorubicin conjugate. Polym Bull 74:2159–2184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-016-1821-1
Shabnam R, Miah MAJ, Sharafat MK, Alam MA, Islam HMT, Ahmad H (2019) Cumulative effect of hydrophobic PLMA and surface epoxide groups in composite polymer particles on adsorption behavior of congo red and direct red-75. Arab J Chem 12:4989–4999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.10.016
Hossain MK, Minami H, Hoque SM, Rahman MM, Sharafat MK, Begum MF, Islam ME, Ahmad H (2019) Mesoporous electromagnetic composite particles: electric current responsive release of biologically active molecules and antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 181:85–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.05.040
Asab G, Zereffa EA, Seghne TA (2020) Synthesis of silica-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles by microemulsion method: characterization and evaluation of antimicrobial activity. Int J Biomater 2020:4783612. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4783612
Li X, Li H, Liu G, Deng Z, Wu S, Li P (2012) Magnetite-loaded fluorine–containing polymeric micelles for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Biomaterials 33:3013–3024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.12.042
Ahmad H, Nurunnabi M, Rahman MM, Kumar K, Tauer K, Minami H, Gafur MA (2014) Magnetically doped multi stimuli-responsive hydrogel microspheres with IPN structure and application in dye removal. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 459:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.06.038
Chen MZ, Chu CY, Mansel BW, Chang PC (2021) Hierarchical structure in poly(N-vinyl carbazole)/Fe3O4 nanocomposites and the relevant magnetic coercivity. Soft Matter 17:3055–3067. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0SM02275F
Squillace O, Esnault C, Pilard J–F, Brotons G (2019) Electrodes for membrane surface science. Bilayer lipid membranes tethered by commercial surfactants on electrochemical sensors. ACS Sens 4:1337–1345. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00267
Clerico A, Zaninotto M, Padoan A, Masotti S, Musetti V, Prontera C, Ndreu R, Zucchelli G, Passino C, Migliardi M, Plebani M (2019) Evaluation of analytical performance of immunoassay methods for cTnI and cTnT: from theory to practice. Adv Clin Chem 93:239–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acc.2019.07.005
Gao X, Du X, Liu D, Gao H, Wang P, Yang J (2020) Core-shell gold-nickel nanostructures as highly selective and stable nonenzymatic glucose sensor for fermentation process. Sci Rep 10:1365. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58403-x
Tasca F, Zafar MN, Harreither W, Noll G, Ludwig R, Gorton L (2011) A third generation glucose biosensor based on cellobiose dehydrogenase from Corynascus thermophilus and single-walled carbon nanotubes. Analyst 136:2033–2036. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0AN00311E
Jiang X, Wu Y, Mao X, Cui X, Zhu L (2011) Amperometric glucose biosensor based on integration of glucose oxidase with platinum nanoparticles/ordered mesoporous carbon nanocomposite. Sens Actuators B 153:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2010.10.023
Lu BW, Chen WC (2006) A disposable glucose biosensor based on drop-coating of screen-printed carbon electrodes with magnetic nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 304:400–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2006.01.222
Shukla S, Deshpande SR, Shukla SK, Tiwari A (2012) Fabrication of a tunable glucose biosensor based on zinc oxide/chitosan-graft-poly(vinyl alcohol) core-shell nanocomposite. Talanta 99:283–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.05.052
Paul G, Verma S, Jalil O, Thakur D, Pandey CM, Kumar D (2021) PEDOT: PSS-grafted graphene oxide-titanium dioxide nanohybrid-based conducting paper for glucose detection. Polym Adv Technol 32:1774–1782. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5213
Lin MS, Leu HJ (2005) A Fe3O4-based chemical sensor for cathodic determination of hydrogen peroxide. Electroanalysis 17:2068–2073. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200503335
Lee J, Lee D, Oh E, Kim J, Kim YP, Jin S, Kim HS, Hwang Y, Kwak JH, Park JG, Shin CH, Kim J, Hyeon T (2005) Preparation of a magnetically switchable bio-electrocatalytic system employing cross-linked enzyme aggregates in magnetic mesocellular carbon foam. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:7427–7432. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200502995
Luo XL, Xu JJ, Zhao W, Chen HY (2004) Glucose biosensor based on ENFET doped with SiO2 nanoparticles. Sens Actuators B 97:249–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2003.08.024
Li X, Du Y, Wang H, Ma H, Wu D, Ren X, Wei Q, Xu J–J (2022) Self-supply of H2O2 and O2 by hydrolyzing CaO2 to enhance the electrochemiluminescence of luminol based on closed bipolar electrode. Anal Chem 92:12693–12699. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03170
Acknowledgements
Financial supports were obtained from UGC, Dhaka. Instrument support from Central Science Laboratory of Rajshahi University is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The Authors confrm that there is no confict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hossain, M.K., Sharafat, M.K., Minami, H. et al. Facile one-step synthesis of poly(styrene-glycidyl methacrylate)-Fe3O4 nanocomposite particles and application potency in glucose biosensors. J Polym Res 30, 118 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03498-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03498-9