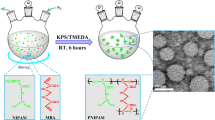
Abstract
Nanogels are polymeric nanoparticles that have similar characteristic to hydrogels, but have the size in nano range. The pH-sensitive nanogel have gained much interest in the field of pharmaceutical nanotechnology as they have potential to be used as nanocarriers in drug delivery system. The aim of the present study was to synthesize pH-sensitive polyelectrolyte MMA/IA nanogels using free radical polymerization containing methyl methacrylate (MMA), itaconic acid (IA), and a crosslinker ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA). In the synthesis of nanogels four parameters i.e. ethanol/water ratios (v/v), dilution volume using ethanol/water (v/v), crosslinker EGDMA concentration, and monomers MMA/IA ratios were optimized. Their effect on particle size, PdI, zeta potential and swelling ratio were evaluated. The swelling behaviour of the nanogels was studied by measuring swelling ratio using gravimetric method. The optimized nanogels were characterized by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), liquid chromatography/time-of-flight/mass spectrometry (LC-TOF-MS), X-ray powder diffraction (X-RD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Polyelectrolyte characteristic was confirmed by measuring isoelectric point using aqueous electrophoresis. The in-vitro and in-vivo toxicity studies were performed by MTT assays using Caco-2 cells and Limit test using female Sprague Dawly rats, respectively. The nanogels were amorphous in nature, exhibited pH-responsive property and polyelectrolyte characteristics, which showed an isoelectric point at pH 2.78. They had an average particle size <250 nm, narrow size distribution (PdI < 0.3), and negative zeta potential. The in-vitro MTT assays indicated that the nanogels had no sign of cytotoxicity. The in vivo Limit test showed that the LD50 was greater than 2000 mg/kg body weight. The necrospy, histopathology and hematological studies also revealed no sign of toxicity. These findings suggested that the MMA/IA nanogels are pH-sensitive, non-toxic and have potential to form a polyelectrolyte complex with oppositely charged of macromolecular drugs.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiang Y, Chen J, Deng C, Suuronen EJ, Zhong Z (2014) Click hydrogels, microgels and nanogels: emerging platforms for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 35(18):4969–4985
Cao H, Wang Q, Li M, Chen Z (2015) Synthesis of stimuli-responsive poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate/methacrylic acid-based nanogels and their application as drug delivery vehicle. Colloid Polym Sci 293(2):441–451
Manchun S, Dass CR, Cheewatanakornkool K, Sriamornsak P (2015) Enhanced anti-tumor effect of pH-responsive dextrin nanogels delivering doxorubicin on colorectal cancer. Carbohydr Polym 126:222–230
Sharma A, Garg T, Aman A, Panchal K, Sharma R, Kumar S, Markandeywar T (2016) Nanogel—an advanced drug delivery tool: current and future. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44(1):165–177
Zhang X, Malhotra S, Molina M, Haag R (2015) Micro-and nanogels with labile crosslinks–from synthesis to biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev 44(7):1948–1973
Deng L, Zhai Y, Guo S, Jin F, Xie Z, He X, Dong A (2009) Investigation on properties of P ((MAA-co-DMAEMA)-g-EG) polyampholyte nanogels. J Nanopart Res 11(2):365–374
Krieg A, Arici E, Windhab N, Schattka JH, Schubert S, Schubert US (2014) Toward pH-responsive coating materials· high-throughput study of (meth) acrylic copolymers. ACS Comb Sci 16(8):386–392
Fathi M, Entezami AA, Arami S, Rashidi M-R (2015) Preparation of N-isopropylacrylamide/itaconic acid magnetic nanohydrogels by modified starch as a crosslinker for anticancer drug carriers. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 64(10):541–549
Lee J-M, Kang S-J, Park S-J (2009) Synthesis of polyacrylonitrile based nanoparticles via aqueous dispersion polymerization. Macromol Res 17(10):817–820
Tian P, Wu Q, Lian K (2008) Preparation of temperature-and pH-sensitive, stimuli-responsive poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-methacrylic acid) nanoparticles. J Appl Polym Sci 108(4):2226–2232
Zhang X, Zhang X, Yang B, Yang Y, Wei Y (2014) Renewable itaconic acid based cross-linked fluorescent polymeric nanoparticles for cell imaging. Polym Chem 5(20):5885–5889. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4PY00794H
Habibi D, Kaamyabi S, Amini MM (2014) Doxorubicin poly N-vinylpyrrolidone and poly N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-vinylpyrrolidone coated magnetic nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 320:301–308
Subrahmanyam S, Guerreiro A, Poma A, Moczko E, Piletska E, Piletsky S (2013) Optimisation of experimental conditions for synthesis of high affinity MIP nanoparticles. Eur Polym J 49(1):100–105
Madhusudana Rao K, Mallikarjuna B, Krishna Rao KSV, Siraj S, Chowdoji Rao K, Subha MCS (2013) Novel thermo/pH sensitive nanogels composed from poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) for controlled release of an anticancer drug. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 102:891–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.09.009
Abd El-Rehim HA, Hegazy E-SA, Hamed AA, Swilem AE (2013) Controlling the size and swellability of stimuli-responsive polyvinylpyrrolidone–poly(acrylic acid) nanogels synthesized by gamma radiation-induced template polymerization. Eur Polym J 49(3):601–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2012.12.002
He Q, Liu J, Huang C, Wu Z (2014) A nanoscale system for remarkably enhanced drug delivery based on hollow magnetic particles encapsulated within temperature-responsive poly (methylmethacrylate). Sci Adv Mater 6(2):387–398
Hao S, Wang B, Wang Y (2015) Porous hydrophilic core/hydrophobic shell nanoparticles for particle size and drug release control. Mater Sci Eng C 49:51–57
Gandhi A, Jana S, Sen KK (2014) In-vitro release of acyclovir loaded Eudragit RLPO® nanoparticles for sustained drug delivery. Int J Biol Macromol 67:478–482
Steiger MG, Blumhoff ML, Mattanovich D, Sauer M (2013) Biochemistry of microbial itaconic acid production. Front Microbiol 4:23
Winkler M, Lacerda TM, Mack F, Meier MA (2015) Renewable polymers from itaconic acid by polycondensation and ring-opening-metathesis polymerization. Macromolecules 48(5):1398–1403
Elsaeed SM, Farag RK, Maysour NS (2012) Synthesis and characterization of pH-sensitive crosslinked (NIPA-co-AAC) nanohydrogels copolymer. J Appl Polym Sci 124(3):1947–1955
Chen L, Remondetto G, Rouabhia M, Subirade M (2008) Kinetics of the breakdown of cross-linked soy protein films for drug delivery. Biomaterials 29(27):3750–3756
Mudassir J, Ranjha NM (2008) Dynamic and equilibrium swelling studies: crosslinked pH sensitive methyl methacrylate-co-itaconic acid (MMA-co-IA) hydrogels. J Polym Res 15(3):195–203
Camerlynck S, Cormack P, Sherrington D, Saunders G (2005) Control of branching vs. cross-linking in conventional free radical copolymerization of MMA and EGDMA using CoBF as a catalytic chain transfer agent. J Macromol Sci, Part B: Phys 44(6):881–895
Yu D-G, An JH, Bae J-Y, Ahn SD, Kang S-Y, Suh K-S (2005) Negatively charged ultrafine black particles of P (MMA-co-EGDMA) by dispersion polymerization for electrophoretic displays. Macromolecules 38(17):7485–7491
Wang X, Wang L, Yang S, Zhang M, Xiong Q, Zhao H, Liu L (2014) Construction of multifunctionalizable, core-cross-linked polymeric nanoparticles via dynamic covalent bond. Macromolecules 47(6):1999–2009
El-Hamshary H (2007) Synthesis and water sorption studies of pH sensitive poly (acrylamide-co-itaconic acid) hydrogels. Eur Polym J 43(11):4830–4838
Russo E, Gaglianone N, Baldassari S, Parodi B, Cafaggi S, Zibana C, Donalisio M, Cagno V, Lembo D, Caviglioli G (2014) Preparation, characterization and in vitro antiviral activity evaluation of foscarnet-chitosan nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 118:117–125
Morse A, Armes S, Thompson K, Dupin D, Fielding L, Mills P, Swart R (2013) Novel Pickering emulsifiers based on pH-responsive poly (2-(diethylamino) ethyl methacrylate) latexes. Langmuir 29(18):5466–5475
Swarbrick J (2004) Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology, 2nd revised ed. Informa Healthcare,New York
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1–2):55–63
Wang J, Xu M, Cheng X, Kong M, Liu Y, Feng C, Chen X (2016) Positive/negative surface charge of chitosan based nanogels and its potential influence on oral insulin delivery. Carbohydr Polym 136:867–874
Shi B, Huang K, Ding J, Xu W, Yang Y, Liu H, Yan L, Chen X (2017) Intracellularly swollen polypeptide Nanogel assists hepatoma chemotherapy. Theranostics 7(3):703
Ding J, Shi F, Li D, Chen L, Zhuang X, Chen X (2013) Enhanced endocytosis of acid-sensitive doxorubicin derivatives with intelligent nanogel for improved security and efficacy. Biomater Sci 1(6):633–646. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3BM60024F
Ding J, Shi F, Xiao C, Lin L, Chen L, He C, Zhuang X, Chen X (2011) One-step preparation of reduction-responsive poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (amino acid) s nanogels as efficient intracellular drug delivery platforms. Polym Chem 2(12):2857–2864
Huang K, Shi B, Xu W, Ding J, Yang Y, Liu H, Zhuang X, Chen X (2015) Reduction-responsive polypeptide nanogel delivers antitumor drug for improved efficacy and safety. Acta Biomater 27:179–193
Organization for Economic Cooperation & Development (OECD) (2001) Test Guideline 425. Acute oral toxicity: up-and-down procedure. In: OECD (ed) OECD guideline for testing of chemicals. Organization for Economic Cooperation & Development, Paris, pp. 1–26
Huang JX, Yuan XY, Yu XL, Zhang HT (2003) Dispersion copolymerization of methyl methacrylate and acrylic acid in polar media: effects of reaction parameters on the particle size and size distribution of the copolymer microspheres. Polym Int 52(5):819–826
Şen M, Yakar A (2005) Enhancement of copolymerization of itaconic acid with N-vinyl 2-pyrrolidone by radiation in the presence of cross-linking agent. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect B 234(3):226–234
Şen M, Güven O (1999) Radiation synthesis of poly(N-vinyl 2-pyrrolidone/itaconic acid) hydrogels and their controlled release behaviours. Radiat Phys Chem 55(2):113–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0969-806X(98)00315-6
Çavuş S, Ei Ç (2012) Synthesis and characterization of novel poly (N-vinylcaprolactam-co-itaconic acid) gels and analysis of pH and temperature sensitivity. Ind Eng Chem Res 51(3):1218–1226
El Halah A, Contreras J, Rojas-Rojas L, Rivas M, Romero M, López-Carrasquero F (2015) New superabsorbent hydrogels synthesized by copolymerization of acrylamide and N-2-hydroxyethyl acrylamide with itaconic acid or itaconates containing ethylene oxide units in the side chain. J Polym Res 22(12):233
Kadlubowski S (2014) Radiation-induced synthesis of nanogels based on poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone)—a review. Radiat Phys Chem 102:29–39
Funke W, Okay O, Joos-Müller B (1998) Microgels: intramolecularly crosslinked macromolecules with a globular structure. Adv Polym Sci 136:139–234
Wang L, Li D, Sun J, Zhang Y (2015) Preparation and characterization of amphoteric poly (acrylamide-itaconic acid-diallyl dimethyl ammonium chloride) uniform spherical particles by aqueous dispersion polymerization. J Macromol Sci A 52(7):523–531
Gonzalez-Ayon MA, Cortez-Lemus NA, Zizumbo-Lopez A, Licea-Claverie A (2014) Nanogels of poly (N-Vinylcaprolactam) Core and Polyethyleneglycol Shell by surfactant free emulsion polymerization. Soft Materials 12(3):315–325
Serrano-Medina A, Cornejo-Bravo J, Licea-Claveríe A (2012) Synthesis of pH and temperature sensitive, core–shell nano/microgels, by one pot, soap-free emulsion polymerization. Journal of colloid and interface science 369 (1):82-90
Medeiros SF, Oliveira PF, Silva TM, Lara BR, Elaissari A, Santos AM (2015) Biocompatible and multi-responsive poly (Nvinylcaprolactam)-based microgels: The role of acidic comonomers in the colloidal properties and phase transition as a function of temperature and pH. European Polymer Journal 73:191-201
Bialik-Wąs K, Pielichowski K (2013) Poly (acrylic acid-co-methyl methacrylate)/metronidazole systems: synthesis and complexation. Acta Biochim Pol 60(4):835–838
Babić MM, Antić KM, Vuković JSJ, Božić BĐ, Davidović SZ, Filipović JM, Tomić SL (2015) Oxaprozin/poly (2-hydroxyethyl acrylate/itaconic acid) hydrogels: morphological, thermal, swelling, drug release and antibacterial properties. J Mater Sci 50(2):906–922
Tomić SL, Dimitrijević SI, Marinković AD, Najman S, Filipović JM (2009) Synthesis and characterization of poly (2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate/itaconic acid) copolymeric hydrogels. Polym Bull 63(6):837
Rangel-Rangel E, Torres CM, Koteich-Khatib S, Rincón L, López-Carrasquero F (2011) Copolymerizations of long side chain di N-alkyl itaconates and methyl N-alkyl itaconates with styrene: determination of monomers reactivity ratios by NMR. Revista Latinoamericana de Metalurgiay Materiales 32(1):79–88
Mokhtar S (1997) Reactivity and characterization of the radical copolymerization of itaconic acid with some conventional monomers. J Macromol Sci, Part A: Pure Appl Chem 34(5):865–879
Lindsjö M-C, Ekman KB, Näsman JH (1996) Glass-ionomer cements based on poly (acrylic acid-co-vinyl alcohol) in drug release model formulations. Biomaterials 17(9):913–919
Yan X, Gemeinhart RA (2005) Cisplatin delivery from poly (acrylic acid-co-methyl methacrylate) microparticles. J Control Release 106(1):198–208
Ogawa K, Nakayama A, Kokufuta E (2003) Preparation and characterization of thermosensitive polyampholyte nanogels. Langmuir 19(8):3178–3184
Zhang Q, Zha L, Ma J, Liang B (2009) A novel route to prepare pH-and temperature-sensitive nanogels via a semibatch process. J Colloid Interface Sci 330(2):330–336
Ding J, Xu W, Zhang Y, Sun D, Xiao C, Liu D, Zhu X, Chen X (2013) Self-reinforced endocytoses of smart polypeptide nanogels for “on-demand” drug delivery. J Control Release 172(2):444–455
Shi F, Ding J, Xiao C, Zhuang X, He C, Chen L, Chen X (2012) Intracellular microenvironment responsive PEGylated polypeptide nanogels with ionizable cores for efficient doxorubicin loading and triggered release. J Mater Chem 22(28):14168–14179. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM32033A
Weiss L, Poste G, MacKearnin A, Willett K (1975) Growth of mammalian cells on substrates coated with cellular microexudates. I. Effect on cell growth at low population densities. J Cell Biol 64(1):135–145
Sarika P, Kumar PA, Raj DK, James NR (2015) Nanogels based on alginic aldehyde and gelatin by inverse miniemulsion technique: synthesis and characterization. Carbohydr Polym 119:118–125
Nandi G, Patra P, Priyadarshini R, Kaity S, Ghosh LK (2015) Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of methacrylamide grafted gellan as sustained release tablet matrix. Int J Biol Macromol 72:965–974
Piao Y, Liu Y, Xie X (2013) Change trends of organ weight background data in sprague dawley rats at different ages. J Toxicol Pathol 26(1):29
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Ministry of Education Malaysia for providing Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (203/PFarmasi/6711450) to support this work. The author (Jahanzeb Mudassir) gratefully acknowledges Universiti Sains Malaysia, Penang, Malaysia for awarding of the Fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
“Acute oral toxicity study on pH-sensitive nanogels for oral drug delivery” was approved by Animal Ethics Committee, Universiti Sains Malaysia (AECUSM).
Ethical approval
“USM/Animal Ethics Approval/2012/(82) (422)”.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in publishing this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mudassir, J., Darwis, Y. & Yusof, S.R. Synthesis, characterization and toxicological evaluation of pH-sensitive polyelectrolyte Nanogels. J Polym Res 24, 164 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1321-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-017-1321-5