Abstract
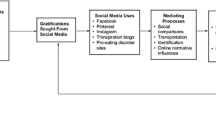
Adolescents are spending considerable time on social media, yet it is unclear whether motivations for social media use drive different forms of social media engagement, and their relationships with body satisfaction and well-being. This study tested a proposed model of the relationships between motivations for social media use, types of social media engagement and body satisfaction and well-being. Responses to an online survey from 1432 Australian adolescents (Mage = 13.45 years, SD = 1.14, range 11–17; 55.4% boys) were collected. Structural equational modelling indicates excellent model fit. Specifically, motivations for social media use (information sharing, passing time, escapism, social interaction, social capital and appearance feedback) were associated with engagement (intensity, photo-based use, active use, passive use and liking use) and revealed mixed associations with body satisfaction and well-being. The findings support the importance of considering motivations for social media use in future research.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Model invariance was established between schools. Following the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure, this multi-group analysis suggest only one parameter was significantly different by school; the covariance between passive use and liking use (β = −0.03, SE = 0.01, p < 0.001). Overall, this provides support for model invariance across schools, suggesting the appropriateness of a single analysis including both schools.
References
Anderson, M., & Jiang, J. (2018). Teens, social media, and technology 2018. https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2018/05/31/teens-social-media-technology-2018/.
Australian Bureau of Statistics (2018). Census of population and housing: socio-economic indexes for areas (seifa) 2016. Australian Government: Australia.
Benjamini, Y., & Hochberg, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate- a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal statistical society, series B (Methodological), 57(1), 289–300.
Blomfield-Neira, C. J., & Barber, B. L. (2014). Social networking site use: linked to adolescents’ social self-concept, self-esteem, and depressed mood. Australian Journal of Psychology, 66(1), 56–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajpy.12034.
Boateng, G. O., Neilands, T. B., Frongillo, E. A., Melgar-Quinonez, H. R., & Young, S. L. (2018). Best practices for developing and validating scales for health, social, and behavioral research: a primer. Front Public Health, 6, 149. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00149.
Bucchianeri, M. M., Arikian, A. J., Hannan, P. J., Eisenberg, M. E., & Neumark-Sztainer, D. (2013). Body dissatisfaction from adolescence to young adulthood: Findings from a 10-year longitudinal study. Body Image, 10(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2012.09.001.
Burnell, K., George, M. J., Vollet, J. W., Ehrenreich, S. E., & Underwood, M. K. (2019). Passive social networking site use and well-being: the mediating roles of social comparison and the fear of missing out. Cyberpsychology: Journal of Psychosocial Research on Cyberspace, 13(3). https://doi.org/10.5817/cp2019-3-5.
Carlisle, E., Fildes, J., Hall, S., Perrens, B., Perdriau, A., & Plummer, J. (2019). Youth survey report. Sydney, NSW: Mission Australia.
Carrotte, E. R., Prichard, I., & Lim, M. S. (2017). “Fitspiration” on social media: a content analysis of gendered images. J Med Internet Res, 19(3), e95. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.6368.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences. 2nd ed. Hillside, New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
de Vries, D. A., Peter, J., de Graaf, H., & Nikken, P. (2016). Adolescents’ social network site use, peer appearance-related feedback, and body dissatisfaction: testing a mediation model. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 45(1), 211–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-015-0266-4.
Dhir, A., & Tsai, C.-C. (2017). Understanding the relationship between intensity and gratifications of facebook use among adolescents and young adults. Telematics and Informatics, 34(4), 350–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2016.08.017.
Diedrichs, P. C., Atkinson, M. J., Steer, R. J., Garbett, K. M., Rumsey, N., & Halliwell, E. (2015). Effectiveness of a brief school-based body image intervention ‘dove confident me: single session’ when delivered by teachers and researchers: Results from a cluster randomised controlled trial. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 74, 94–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2015.09.004.
Diener, E., Emmons, R. A., Larsen, R. J., & Griffin, S. (1985). The satisfaction with life scale. Journal of Personality Assessment, 49(1), 71–75.
Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C., & Lampe, C. (2007). The benefits of facebook “friends:” social capital and college students’ use of online social network sites. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication, 12(4), 1143–1168. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1083-6101.2007.00367.x.
Erikson, E. H. (1968). Identity: Youth and crisis. New York, NY: Norton.
Fairburn, C. G., & Beglin, S. J. (1994). Assessment of eating disorders: interview or self-report questionnaire?. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 16(4), 363–370. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-108X(199412)16:4<363::AID-EAT2260160405>3.0.CO;2-#.
Fardouly, J., Diedrichs, P. C., Vartanian, L. R., & Halliwell, E. (2015). Social comparisons on social media: the impact of facebook on young women’s body image concerns and mood. Body Image, 13, 38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2014.12.002.
Frison, E., & Eggermont, S. (2015). Toward an integrated and differential approach to the relationships between loneliness, different types of facebook use, and adolescents’ depressed mood. Communication Research, 47(5), 701–728. https://doi.org/10.1177/0093650215617506.
Frison, E., & Eggermont, S. (2016). Gender and facebook motives as predictors of specific types of facebook use: a latent growth curve analysis in adolescence. Journal of Adolescence, 52, 182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.08.008.
Frison, E., & Eggermont, S. (2017). Browsing, posting, and liking on instagram: the reciprocal relationships between different types of instagram use and adolescents’ depressed mood. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 20(10), 603–609. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2017.0156.
González-Carrasco, M., Casas, F., Malo, S., Viñas, F., & Dinisman, T. (2017). Changes with age in subjective well-being through the adolescent years: differences by gender. Journal of Happiness Studies, 18(1), 63–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-016-9717-1.
Holland, G., & Tiggemann, M. (2016). A systematic review of the impact of the use of social networking sites on body image and disordered eating outcomes. Body Image, 17, 100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2016.02.008.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118.
Huang, C. (2017). Time spent on social network sites and psychological well-being: a meta-analysis. Cyberpsychology, Behavior and Social Networking, 20(6), 346–354. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2016.0758.
Katz, E., Haas, H., & Gurevitch, M. (1973). On the use of the mass media for important things. American Sociological Review, (pp. 164–181). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Keery, H., van den Berg, P., & Thompson, J. K. (2004). An evaluation of the tripartite influence model of body dissatisfaction and eating disturbance with adolescent girls. Body Image, 1(3), 237–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2004.03.001.
Kling, J., Kwakkenbos, L., Diedrichs, P. C., Rumsey, N., Frisen, A., & Brandao, M. P., et al. (2019). Systematic review of body image measures. Body Image, 30, 170–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2019.06.006.
Lai, H., Hsieh, P., & Zhang, R. (2018). Understanding adolescent students’ use of facebook and their subjective wellbeing: a gender-based comparison. Behaviour & Information Technology, 38(5), 533–548. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2018.1543452.
Lee, H. R., Lee, H. E., Choi, J., Kim, J. H., & Han, H. L. (2014). Social media use, body image, and psychological well-being: a cross-cultural comparison of korea and the united states. Journal of Health Communication, 19(12), 1343–1358. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2014.904022.
Li, J., Lau, J. T., Mo, P. K., Su, X., Wu, A. M., & Tang, J., et al. (2016). Validation of the social networking activity intensity scale among junior middle school students in china. PLoS ONE, 11(10), e0165695. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0165695.
Little, R. J. (1988). A test of missing completely at random for multivariate data with missing values. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 83, 1198–1202. https://doi.org/10.1080/01621459.1988.10478722.
Mackinnon, D. P., Lockwood, C. M., & Williams, J. (2004). Confidence limits for the indirect effect: distribution of the product and resampling methods. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39(1), 99–128. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327906mbr3901_4.
McLean, S. A., Paxton, S. J., Wertheim, E. H., & Masters, J. (2015). Photoshopping the selfie: self photo editing and photo investment are associated with body dissatisfaction in adolescent girls. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 48(8), 1132–1140. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.22449.
Mendelson, B. K., Mendelson, M. J., & White, D. R. (2001). Body-esteem scale for adolescents and adults. Journal of Personality Assessment, 76(1), 90–106. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327752JPA7601_6.
Mingoia, J., Hutchinson, A. D., Gleaves, D. H., Corsini, N., & Wilson, C. (2017a). Use of social networking sites and associations with skin tone dissatisfaction, sun exposure, and sun protection in a sample of australian adolescents. Psychology & Health, 32(12), 1502–1517. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2017.1347788.
Mingoia, J., Hutchinson, A. D., Gleaves, D. H., & Wilson, C. (2019). The relationship between posting and photo manipulation activities on social networking sites and internalization of a tanned ideal among australian adolescents and young adults. Social Media + Society, 5(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/2056305118820419.
Mingoia, J., Hutchinson, A. D., Wilson, C., & Gleaves, D. H. (2017b). The relationship between social networking site use and the internalization of a thin ideal in females: a meta-analytic review. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01351.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2017). Mplus user’s guide (8ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Neinstein, L., & Anderson, M. (2002). Adolescent development. In L. Neinstein (Ed.), Adolescent health care: A practical guide (pp. 767–792). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
Orben, A. (2020). Teenagers, screens and social media: a narrative review of reviews and key studies. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 55(4), 407–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-019-01825-4.
Orben, A., Dienlin, T., & Przybylski, A. K. (2019). Social media’s enduring effect on adolescent life satisfaction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 116(21), 10226–10228. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1902058116.
Papacharissi, Z., & Mendelson, A. (2010). Toward a new(er) sociability: Uses, gratifications, and social capital on facebook. In S. Papathanassopoulos (Ed.), Media perspectives for the 21st century (pp. 212–230). London, England: Routledge.
Perloff, R. M. (2014). Social media effects on young women’s body image concerns: theoretical perspectives and an agenda for research. Sex Roles, 71(11-12), 363–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11199-014-0384-6.
Pingitore, R., Spring, B., & Garfield, D. (1997). Gender differences in body satisfaction. Obesity Research, 5(5), 402–409. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1550-8528.1997.tb00662.x.
Proctor, C., Linley, A. P., & Maltby, J. (2009). Youth life satisfaction measures: a review. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 4(2), 128–144. https://doi.org/10.1080/17439760802650816.
Rae, J. R., & Lonborg, S. D. (2015). Do motivations for using facebook moderate the association between facebook use and psychological well-being? Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 771. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00771.
Rodgers, R. F. (2016). The relationship between body image concerns, eating disorders and internet use, part ii: an integrated theoretical model. Adolescent Research Review, 1(2), 121–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40894-015-0017-5.
Rodgers, R. F., McLean, S. A., Gordon, C. S., Slater, A., Marques, M. D., Jarman, H. K., et al. (2020). Development and validation of the motivations for social media use scale (msmu) among adolescents. Adolescent Research Review, pp. 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40894-020-00139-w.
Rodgers, R. F., & Melioli, T. (2016). The relationship between body image concerns, eating disorders and internet use, part i: a review of empirical support. Adolescent Research Review, 1(2), 95–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40894-015-0016-6.
Ryan, T., Chester, A., Reece, J., & Xenos, S. (2014). The uses and abuses of facebook: a review of facebook addiction. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 3(3), 133–148. https://doi.org/10.1556/JBA.3.2014.016.
Saiphoo, A. N., & Vahedi, Z. (2019). A meta-analytic review of the relationship between social media use and body image disturbance. Computers in Human Behavior, 101, 259–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.07.028.
Sheldon, P., & Newman, M. (2019). Instagram and american teens understanding motives for its use and relationship to excessive reassurance-seeking and interpersonal rejection. The Journal of Social Media in Society, 8(1), 1–16.
Tamplin, N. C., McLean, S. A., & Paxton, S. J. (2018). Social media literacy protects against the negative impact of exposure to appearance ideal social media images in young adult women but not men. Body Image, 26, 29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bodyim.2018.05.003.
Thompson, J. K., Heinberg, L. J., Altabe, M., & Tantleff-Dunn, S. (1999). Exacting beauty: Theory, assessment, and treatment of body image disturbance (Exacting beauty: Theory, assessment, and treatment of body image disturbance.). Washington, DC, US: American Psychological Association.
Vannucci, A., & Ohannessian, C. M. (2019). Social media use subgroups differentially predict psychosocial well-being during early adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 48(8), 1469–1493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-019-01060-9.
Verrastro, V., Fontanesi, L., Liga, F., Cuzzocrea, F., & Gugliandolo, M. C. (2020). Fear the instagram: beauty stereotypes, body image and instagram use in a sample of male and female adolescents. Qwerty-Open and Interdisciplinary Journal of Technology, Culture and Education, 15(1), 31–49. https://doi.org/10.30557/qw000021.
Yuan, K. H., & Bentler, P. M. (2000). Three likelihood-based methods for mean and covariance structure analysis with nonnormal missing data. Sociological Methodology, 30(1), 165–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/0081-1750.00078.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all schools, staff, students and research assistants for their support in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.K.J. conceived of the study, participated in its design, facilitated study coordination, conducted the analyses, and drafted the paper; M.D.M. conceived of the study, participated in its design and helped draft the paper; S.A.M. conceived of the study, participated in its design and helped draft the paper; A.S. conceived of the study, participated in its design and helped draft the paper; S.J.P. conceived of the study, participated in its design and helped draft the paper. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Funding
This research was supported by the Australian Research Council Discovery Grant [DP170100709] and La Trobe University, Melbourne.
Data Sharing and Declaration
This paper data will not be deposited.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
Research involving human participants and/or animals: The research involved human participants and was approved by the Human Research Ethics committee of La Trobe University (HEC18424).
Informed Consent
All participants’ parents provided consent, and participants provided assent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jarman, H.K., Marques, M.D., McLean, S.A. et al. Motivations for Social Media Use: Associations with Social Media Engagement and Body Satisfaction and Well-Being among Adolescents. J Youth Adolescence 50, 2279–2293 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01390-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-020-01390-z