Abstract
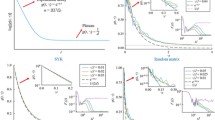
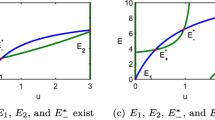
The evolution problem of individual wealth growth and control is investigated by applying the kinetic theory. The microscopic variation of individual wealth growth around a universal desired target is analyzed by discussing a suitable value function, which characterizes the internal trading mechanism. Inheritance, capital gifts from others, and capital gains from rising prices are treated as external mechanisms that result in the growth of individual wealth. Under the grazing collision limit, the steady-state solution of the Fokker–Planck type equation is the product of an inverse gamma distribution and a generalized inverse gamma distribution, and exhibits a fat-tailed property. To prevent the excessive growth of individual wealth, we design additive and multiplicative controls, which reduce the possibility of excessive growth of individual wealth.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Albi, G., Pareschi, L., Zanella, M.: Opinion dynamics over complex networks: kinetic modelling and numerical methods. Kinet. Relat. Model 10(1), 1–32 (2017)
Ajmone Marsan, G., Bellomo, N., Gibelli, L.: Stochastic evolutionary differential games toward a systems theory of behavioral social dynamics. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 26, 1051–1093 (2016)
Aristov, V.V.: Biological systems as nonequilibrium structures described by kinetic methods. Results Phys. 13, 102232 (2019)
Ballante, E., Bardelli, C., Zanella, M., Figini, S., Toscani, G.: Economic segregation under the action of trading uncertainties. Symmetry 12, 1390 (2020)
Bellomo, N., Burini, D., Dosi, G., Gibelli, L., Knopof, D., Outada, N., Terna, P., Virgillito, M.E.: What is life? A perspective of the mathematical kinetic theory of active particles. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 31(9), 1821–1866 (2021)
Bisi, M., Spiga, G., Toscani, G.: Kinetic models of conservative economies with wealth redistribution. Commun. Math. Sci. 7, 901–916 (2009)
Bisi, M.: Some kinetic models for a market economy. Boll. Unione Mat. Ital. 10, 143–158 (2017)
Boghosian, B.M., Devitt-Lee, A., Johnson, M., Marcq, J.A., Wang, H.: Oligarchy as a phase transition: the effect of wealth-attained advantage in a Fokker–Planck description of asset exchange. Physica A 476, 15–37 (2017)
Brugna, C., Toscani, G.: Kinetic models for goods exchange in a multi-agent market. Physica A 499, 362–375 (2018)
Chakraborti, A., Chakrabarti, B.K.: Statistical mechanics of money: effects of saving propensity. Eur. Phys. J. B 17, 167–170 (2000)
Chatterjee, A., Chakrabarti, B.K., Manna, S.S.: Pareto law in a kinetic model of market with random saving propensity. Physica A 335, 155–163 (2004)
Cordier, S., Pareschi, L., Toscani, G.: On a kinetic model for a simple market economy. J. Stat. Phys. 120, 253–277 (2005)
Cordier, S., Pareschi, L., Piatecki, C.: Mesoscopic modelling of financial markets. J. Stat. Phys. 134(1), 161–184 (2009)
Crooks, G.E.: The Amoroso distribution. Statistics (2010). https://arxiv.org/pdf/1005.3274v1.pdf.
Devitt-Lee, A., Wang, H., Li, J., Boghosian, B.: A nonstandard description of wealth concentration in large-scale economies. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 78(2), 996–1008 (2018)
Dimarco, G., Toscani, G.: Kinetic modeling of alcohol consumption. J. Stat. Phys. 177, 1022–1042 (2019)
Dimarco, G., Toscani, G.: Social climbing and Amoroso distribution. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 30(11), 2229–2262 (2020)
Dolfin, M., Lachowicz, M.: Modeling altruism and selfishness in welfare dynamics: the role of nonlinear interactions. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 24(12), 2361–2381 (2014)
Dolfin, M., Lachowicz, M.: Modeling opinion dynamics: how the network enhances consensus. Netw. Heterog. Media 4, 877–896 (2015)
Dolfin, M., Leonida, L., Outada, N.: Modeling human behavior in economics and social science. Phys. Life Rev. 22–23, 1–21 (2017)
Düring, B., Toscani, G.: International and domestic trading and wealth distribution. Commun. Math. Sci. 6, 1043–1058 (2008)
Düring, B., Pareschi, L., Toscani, G.: Kinetic models for optimal control of wealth inequalities. Eur. Phys. J. B 91(10), 265 (2018)
Furioli, G., Pulvirenti, A., Terraneo, E., Toscani, G.: Fokker–Planck equations in the modelling of socio-economic phenomena. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 27, 115–158 (2017)
Furioli, G., Pulvirenti, A., Terraneo, E., Toscani, G.: Non-Maxwellian kinetic equations modeling the dynamics of wealth distribution. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 30, 685–725 (2020)
Gualandi, S., Toscani, G.: Call center service times are lognormal. A Fokker–Planck description. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 28, 1513–1527 (2018)
Gualandi, S., Toscani, G.: Human behavior and lognormal distribution. A kinetic description. Math. Models Methods Appl. Sci. 29, 717–753 (2019)
Gualandi, S., Toscani, G.: The size distribution of cities: a kinetic explanation. Physica A 524, 221–234 (2019)
Islam, M.R., McGillivray, M.: Wealth inequality, governance and economic growth. Econ. Model. 88, 1–13 (2020)
Kahneman, D., Tversky, A.: Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 47(2), 263–292 (1979)
Kahneman, D., Tversky, A.: Choices, Values, and Frames. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Li, J., Boghosian, B.M., Li, C.: The affine wealth model: an agent-based model of asset exchange that allows for negative-wealth agents and its empirical validation. Physica A 516, 423–442 (2019)
Maldarella, D., Pareschi, L.: Kinetic models for socio-economic dynamics of speculative markets. Physica A 391, 715–730 (2012)
Pareschi, L., Toscani, G.: Interacting Multiagent Systems. Kinetic Equations & Monte Carlo Methods. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2013)
Pareschi, L., Toscani, G.: Wealth distribution and collective knowledge. A Boltzmann approach. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 372, 1–15 (2014)
Piketty, T.: On the long-run evolution of inheritance: France 1820–2050. Q. J. Econ. 126(3), 1071–1131 (2011)
Piketty, T.: About capital in the twenty-first century. Am. Econ. Rev. 105(5), 1–15 (2015)
Polk, S.L., Boghosian, B.M.: The nonuniversality of wealth distribution tails near wealth condensation criticality. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 81(4), 1717–1741 (2021)
Preziosi, L., Toscani, G., Zanella, M.: Control of tumor growth distributions through kinetic methods. J. Theor. Biol. 514(6), 110579 (2021)
Tobin, J., Golub, S.: Money, Credit and Capital. McGraw-Hill/Irwin, Boston (1998)
Toscani, G.: Kinetic models of opinion formation. Commun. Math. Sci. 4, 481–496 (2006)
Toscani, G., Brugna, C., Demichelis, S.: Kinetic models for the trading of goods. J. Stat. Phys. 151, 549–566 (2013)
Toscani, G.: Statistical description of human addiction phenomena. Trails Kinet. Theory 25, 209–226 (2019)
Trimborn, T., Pareschi, L., Frank, M.: Portfolio optimization and model predictive control: a kinetic approach. Discret. Cont. Dyn. B 24(11), 6209–6238 (2019)
Villani, C.: On a new class of weak solutions to the spatially homogeneous Boltzmann and Landau equations. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 143, 273–307 (1998)
Villani, C.: A review of mathematical topics in collisional kinetic theory. In: Friedlander, S., Serre, D. (eds.) Handbook of Mathematical Fluid Dynamics. Elsevier Press, New York (2002)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11471263). The authors are very grateful to the reviewers for their helpful and valuable comments, which have led to a meaningful improvement of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Pierpaolo Vivo.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Lai, S. A Kinetic Description of Individual Wealth Growth and Control. J Stat Phys 188, 30 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-022-02961-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-022-02961-z