Abstract
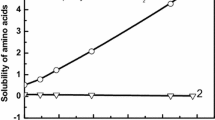
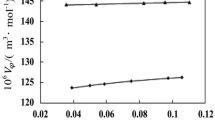
The aqueous solubility of L-tryptophan was measured with a wide range of pH (1.00–12.50) and different monovalent counterions (Na+, K+, Cl− and \({\text{NO}}_{\text{3}}^{-}\)) from 283.15 to 323.15 K by using a static equilibrium method. The results showed that the solubility of L-tryptophan increased with increasing temperature and the solubility–pH profile was a “U” shape with the lowest value at the isoelectric point. Additionally, the distribution of the ionic forms of L-tryptophan as a function of pH was obtained using the knowledge of the acid–base equilibria of amino acids, and it was found that the isoelectric points increased with temperature. Moreover, different counterions were introduced by using different acids or bases during pH adjustment and their effect on the solubility of L-tryptophan was investigated, which showed that more L-tryptophan could be dissolved in the presence of K+ (or \({\text{NO}}_{\text{3}}^{-}\)) than Na+ (or Cl−). Besides, the modified Apelblat model and the NRTL model were successfully used to correlate the aqueous solubility data with all the average relative deviation less than 2.1%.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matsui, D., Asano, Y.: Creation of thermostable L-tryptophan dehydrogenase by protein engineering and its application for L-tryptophan quantification. Anal. Biochem. 579, 57–63 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2019.05.010
Tröndle, J., Trachtmann, N., Sprenger, G.A., Weuster-Botz, D.: Fed-batch production of L-tryptophan from glycerol using recombinant escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 115, 2881–2892 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26834
Yang, X., Xu, M., Huang, G., Zhang, C., Pang, Y., Cheng, Y.: Effect of dietary L-tryptophan on the survival, immune response and gut microbiota of the Chinese mitten crab. Eriocheir sinensis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 84, 1007–1017 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2018.10.076
Russo, S., Kema, I.P., Bosker, F., Haavik, J., Korf, J.: Tryptophan as an evolutionarily conserved signal to brain serotonin: Molecular evidence and psychiatric implications. World J. Biol. Psychiatry. 10, 258–268 (2009). https://doi.org/10.3109/15622970701513764
Liu, W., Mi, S., Ruan, Z., Li, J., Shu, X., Yao, K., Jiang, M., Deng, Z.: Dietary tryptophan enhanced the expression of tight junction protein ZO-1 in intestine. J. Food Sci. 82, 562–567 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13603
Moehn, S., Pencharz, P.B., Ball, R.O.: Lessons learned regarding symptoms of tryptophan deficiency and excess from animal requirement studies. J. Nutr. (2012). https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.112.159061
Wen, H., Feng, L., Jiang, W., Liu, Y., Jiang, J., Li, S., Tang, L., Zhang, Y., Kuang, S., Zhou, X.: Dietary tryptophan modulates intestinal immune response, barrier function, antioxidant status and gene expression of TOR and Nrf2 in young grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 40, 275–287 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.07.004
Kawasaki, K., Yokota, A., Tomita, F.: L-Tryptophan production by a pyruvic acid-producing escherichia coli strain carrying the enterobacter aerogenes tryptophanase gene. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 82, 604–606 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0922-338X(97)81262-7
Donald Warner, B.T., Mob, O.A.: Amino acids I New synthesis of dl-tryptophan, dl-ornithine and dl-glutamic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 70, 2765–2767 (1948). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01188a038
Watanabe, T., Snell, E.E.: Reversiblility of the tryptophanase reaction: synthesis of tryptophan from indole, pyruvate and ammonia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 69, 1086–1090 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.69.5.1086
Yang, J., Wang, Y., Hao, H., Xie, C., Bao, Y., Yin, Q., Gong, J., Jiang, C., Hou, B., Wang, Z.: Spherulitic crystallization of L-tryptophan: Characterization, growth kinetics, and mechanism. Cryst. Growth Des. 15, 5124–5132 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b01089
Zhu, W., Fan, Y., Xu, Q., Liu, X., Heng, B., Yang, W., Hu, Y.: Saturated solubility and thermodynamic evaluation of l-tryptophan in eight pure solvents and three groups of binary mixed solvents by the gravimetric method at T = 278.15–333.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 64, 4154–4168 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.9b00562
Chen, Q., Wang, J., Bao, Y.: Determination of the crystallization thermodynamics and kinetics of L-tryptophan in alcohols-water system. Fluid Phase Equilib. 313, 182–189 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2011.09.028
Lee, C.Y., Chen, J.T., Chang, W.T., Shiah, I.M.: Effect of pH on the solubilities of divalent and trivalent amino acids in water at 298.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 343, 30–35 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2013.01.010
Liu, L.F., Yang, L.L., Jin, K.Y., Xu, D.Q., Gao, C.J.: Recovery of l-tryptophan from crystallization wastewater by combined membrane process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 66, 443–449 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2009.02.013
Liu, L., Bilal, M., Luo, H., Zhao, Y., Iqbal, H.M.N.: Metabolic engineering and fermentation process strategies for L-tryptophan production by escherichia coli. Processes. 7, 213 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7040213
Xu, L., Han, F., Dong, Z., Wei, Z.: Engineering improves enzymatic synthesis of l-tryptophan by tryptophan synthase from escherichia coli. Microorganisms 8, 519 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040519
Wu, C., Guo, C., Yang, J., Wei, J., Xu, Q.: Separaton and purification of L-tryptophan from fermentation liquor. Amino Acids Biotic Res. 29, 42–46 (2007)
Hu, Y., Wang, Y., Yu, H., Liu, J.: Advance of L-tryptophan application and production technology. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 30, 586–589 (2008)
Zhang, J., Huang, C., Xu, R.: Solubility of bifonazole in four binary solvent mixtures: experimental measurement and thermodynamic modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 64, 2641–2648 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.9b00097
Shen, Y., Farajtabar, A., Xu, J., Wang, J., Xia, Y., Zhao, H., Xu, R.: Thermodynamic solubility modeling, solvent effect and preferential solvation of curcumin in aqueous co-solvent mixtures of ethanol, n-propanol, isopropanol and propylene glycol. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 131, 410–419 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2018.11.022
Bing yao, G., Xiang xia, Z., Hui Li, Z., Shao, C.: Determination and modeling for solid-liquid phase equilibrium of ternary caprolactam + cyclohexanone oxime + methyl tert-butyl ether system. Fluid Phase Equilib. 417, 242–247 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2016.03.002
Xu, R., Huang, C.: Solubility Modeling and Solution Thermodynamics of 4-Amino-2,6-Dimethoxypyrimidine in Cosolvent Mixtures of Methanol, Ethanol, Isopropanol, and N,N-Dimethylformamide + Water. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 63, 4234–4240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.8b00719
Yao, G., Li, Z., Xia, Z., Yao, Q.: Solubility of N-phenylanthranilic acid in nine organic solvents from T = (283.15 to 318.15) K: Determination and modelling. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 103, 218–227 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2016.08.017
Tsuji, A., Nakashima, E., Hamano, S., Yamana, T.: Physicochemical properties of amphoteric β-lactam antibiotics I: Solubility and dissolution behavior of amino cephalosporins as a function of pH. J. Pharm. Sci. 67, 1059–1066 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600670810
Tsuji, A., Nakashima, E., Hamano, S., Yamana, T.: Physicochemical properties of amphoteric beta-lactam antibiotics. II: Solubility and dissolution behavior of aminocephalosporins as a function of pH. J. Pharm. Sci. 68, 308–311 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600680313
Apelblat, A., Manzurola, E.: SSolubilities of L-aspartic, DL-aspartic, DL-glutamic, p-hydroxybenzoic, o-anisic, p-anisic, and itaconic acids in water from 278 to 345 K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 29, 1527–1533 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcht.1997.0267
Apelblat, A., Manzurola, E.: Solubilities of o-acetylsalicylic, 4-aminosalicylic, 3,5-dinitrosalicylic, and p-toluic acid, and magnesium-DL-aspartate in water from T = (278 to 348) K. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 31, 85–91 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1006/jcht.1998.0424
Zhu, L., Wang, L.Y., Li, X.C., Sha, Z.L., Wang, Y.F., Yang, L.: bin: Experimental determination and correlation of the solubility of 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (DMHF) in six different solvents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 91, 369–377 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2015.08.028
Zhao, H., Xu, H., Yang, Z., Li, R.: Solubility of 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene in methanol, ethanol, and liquid mixtures (methanol + water, ethanol + water): Experimental measurement and thermodynamic modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 58, 3061–3068 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/je400507u
Renon, H., Prausnitz, J.M.: Local compositions in thermodynamic excess functions for liquid mixtures. AIChE J. 14, 135–144 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.690140124
Liu, Y., Chen, M., Lin, J., Li, M., Li, K., Gao, Z.: Solubility measurement and data correlation of clopidogrel hydrogen sulfate (form I) in four binary solvents systems at temperature from 278.15 to 318.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 65, 2903–2911 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.0c00190
Li, C., Ji, X., Li, J., Wu, D., Qi, L., Wang, A., Zhou, L., Xie, C., Gong, J., Chen, W.: Measurement and correlation of the solubility of kojic acid in pure and binary solvents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jct.2021.106712
Shakeel, F., Haq, N., Siddiqui, N.A., Alanazi, F.K., Alsarra, I.A.: Correlation of solubility of bioactive compound reserpine in eight green solvents at (298.15 to 338.15) K. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 60, 775–780 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/je500893g
Görbitz, C.H., Törnroos, K.W., Day, G.M.: Single-crystal investigation of L-tryptophan with Z′ = 16. Acta. Crystallogr. B. Struct. Sci. Cryst. Eng. Mater. 68, 549–557 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108768112033484
Felix, I.M.B., Moreira, L.C., Chiavone-Filho, O., Mattedi, S.: Solubility measurements of amoxicillin in mixtures of water and ethanol from 283.15 to 298.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 422, 78–86 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2016.02.040
Sun, H., Jiang, C., Liu, B., Zhang, J.: Determination and correlation of solubility of cephradine and cefprozil monohydrate in water as a function of pH. J. Chem. Eng. Data 62, 3423–3430 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.7b00446
Ji, X., Wang, J., Yang, J., Wang, N., Li, X., Tian, B., Huang, X., Hao, H.: Solubility and isoelectric point of cefradine in different solvent systems. J. Mol. Liq. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2019.112312
Collins, K.D.: Why continuum electrostatics theories cannot explain biological structure, polyelectrolytes or ionic strength effects in ion-protein interactions. Biophys. Chem. 167, 43–59 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2012.04.002
Beck, T.L.: Hydration free energies by energetic partitioning of the potential distribution theorem. J. Stat. Phys. 145, 335–354 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-011-0298-4
Kiriukhin, M.Y., Collins, K.D.: Dynamic hydration numbers for biologically important ions. Biophys. Chem. 99, 155–168 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4622(02)00153-9
Qiu, J., Patel, A., Stevens, J.M.: High-throughput salt screening of synthetic intermediates: Effects of solvents, counterions, and counterion solubility. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 24, 1262–1270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.0c00132
Gomes, M.T.M.S., Pelegrine, D.H.G.: Solubility of egg white proteins: Effect of pH and temperature. J. Food Eng. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1515/1556-3758.2847
Galcera, J., Molins, E.: Effect of the counterion on the solubility of isostructural pharmaceutical lamotrigine salts. Cryst. Growth Des. 9, 327–334 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/cg8005025
El-Dossoki, F.I.: Effect of the charge and the nature of both cations and anions on the solubility of zwitterionic amino acids, measurements and modeling. J. Solution. Chem. 39, 1311–1326 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-010-9580-3
Pradhan, A.A., Vera, J.H.: Effect of anions on the solubility of zwitterionic amino acids. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 45, 140–143 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1021/je9902342
Pradhan, A.A., Vera, J.H.: Effect of acids and bases on the solubility of amino acids. Fluid Phase Equilib 152, 121–132 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3812(98)00387-2
Guin, P.S., Roy, S.: Electrolytic effects on solubility and Gibbs free energies of 1,4-dihydroxy-9,10-anthraquinone in aqueous methanol media via UV–Vis spectroscopic and theoretical studies. Chem. Phys. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cplett.2020.137292
Bretti, C., Crea, F., De Stefano, C., Sammartano, S., Vianelli, G.: Some thermodynamic properties of DL-Tyrosine and DL-Tryptophan. Effect of the ionic medium, ionic strength and temperature on the solubility and acid-base properties. Fluid Phase Equilib. 314, 185–197 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2011.10.007
Bergen, R.L., Jr., Long, F.A.: The salting in of substituted benzenes by large ion salts. J. Phys. Chem. 60, 1131–1135 (1956). https://doi.org/10.1021/j150542a024
Battaglia, G., Cigala, R.M., Crea, F., Sammartano, S.: Solubility and acid-base properties of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid in aqueous NaCl solution at0 <= I <= 6 molkg.(-1) and T=298.15 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 53, 363–367 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/je700391c
Bretti, C., Crea, F., De Stefano, C., Sammartano, S.: Solubility and activity coefficients of 2,2 ’-bipyridyl, 1,10-phenanthroline and 2,2 ’,6 ’,2 ’ ’-terpyridine in NaCl(aq) at different ionic strengths and T=298.15 K. Fluid Phase Equilib. 272, 47–52 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fluid.2008.07.010
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by the Special project for the transformation of major scientific and technological achievements of Hebei Province (19042822Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
There is no conflict of interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Jia, L., Yang, W. et al. Measurement and Correlation of Solubility of L–Tryptophan in Aqueous Solutions with a Wide Range of pH and Different Monovalent Counterions from 283.15 to 323.15 K. J Solution Chem 52, 228–250 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-022-01229-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-022-01229-0